|
Kornilov Shock Regiment
The Kornilov Shock Regiment (), previously the 1st Shock Detachment () and also called Kornilovites (корниловцы), was a shock unit of the Russian Army founded during World War I that later was part of the Volunteer Army during the Russian Civil War. It became the last regiment of the Russian Army to be formed and the first regiment of the Volunteer Army. History Founding After the February Revolution in 1917 the Russian Army faced a rapid decline in discipline and morale. To address to the unwillingness to go on the offensive by ordinary infantry, the Russian Provisional Government, on the initiative of Southwestern Front commander General Aleksei Brusilov, began forming "revolutionary shock battalions" from existing military units, and "battalions of death" from civilian volunteers and troops in rear area or support units. Members of these units were identified by red and black chevrons and a death's head symbol on their uniform. They were given specialized training ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reforms Of Russian Orthography
Russian orthography has been reformed officially and unofficially by changing the Russian alphabet over the course of the history of the Russian language. Several important reforms happened in the 18th–20th centuries. Early changes Old East Slavic adopted the Cyrillic script, approximately during the 10th century and at about the same time as the introduction of Eastern Christianity into the territories inhabited by the Eastern Slavs. No distinction was drawn between the vernacular language and the liturgical, though the latter was based on South Slavic languages, South Slavic rather than East Slavic languages, Eastern Slavic norms. As the language evolved, several letters, notably the ''yuses'' (Ѫ, Ѭ, Ѧ, Ѩ) were gradually and unsystematically discarded from both secular and church usage over the next centuries. The emergence of the centralized Russian state in the 15th and 16th centuries, the consequent rise of the state bureaucracy along with the development of the com ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Volunteer Army
The Volunteer Army (; ), abbreviated to (), also known as the Southern White Army was a White Army active in South Russia during the Russian Civil War from 1917 to 1920. The Volunteer Army fought against Bolsheviks and the Makhnovists on the Southern Front and the Ukrainian War of Independence. On 8 January 1919, it was made part of the Armed Forces of South Russia, becoming the largest force of the White movement until it was merged with the Army of Wrangel in March 1920. History Formation The Volunteer Army began forming in November/December 1917 under the leadership of General Mikhail Alekseyev and General Lavr Kornilov in Novocherkassk, shortly after the Russian Civil War began following the October Revolution. It organized to fight against the Bolsheviks in South Russia. Alekseyev and Kornilov enlisted supporters, which initially included volunteering officers, cadets, students, and Cossacks. Of the first 3,000 recruits, only twelve were ordinary soldiers; the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Don Cossacks
Don Cossacks (, ) or Donians (, ), are Cossacks who settled along the middle and lower Don River (Russia), Don. Historically, they lived within the former Don Cossack Host (, ), which was either an independent or an autonomous democratic republic in present-day Southern Russia and parts of the Donbas region of Ukraine, from the end of the 16th century until 1918. As of 1992, by presidential decree of the Russian Federation, Cossacks can be enrolled on a special register. A number of Cossack communities have been reconstituted to further Cossack cultural traditions, including those of the Don Cossack Host. Don Cossacks have had a rich military tradition - they played an important part in the historical development of the Russian Empire and participated in most of its major wars. Etymology The name Cossack (; ) was widely used to characterise "free people" (compare Turkic languages, Turkic ''kazakhs, qazaq'', which means "free men") as opposed to others with different standi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Czechoslovak Legion
The Czechoslovak Legion ( Czech: ''Československé legie''; Slovak: ''Československé légie'') were volunteer armed forces consisting predominantly of Czechs and Slovaks fighting on the side of the Entente powers during World War I and the White Army during the Russian Civil War until November 1919. Their goal was to win the support of the Allied Powers for the independence of Lands of the Bohemian Crown from the Austrian Empire and of Slovak territories from the Kingdom of Hungary, which were then part of the Austro-Hungarian Empire. With the help of émigré intellectuals and politicians such as the Czech Tomáš Garrigue Masaryk and the Slovak Milan Rastislav Štefánik, they grew into a force over 100,000 strong. In Russia, they took part in several victorious battles of the war, including the Zborov and Bakhmach against the Central Powers, and were heavily involved in the Russian Civil War fighting Bolsheviks, at times controlling the entire Trans-Siberian rail ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Praporshchik
(, , ) is a rank used by the Russian Armed Forces and a number of former communist states. The rank is a non-commissioned officer's and is equivalent to in the corresponding navies. It is usually equivalent to warrant officer class 1 or sergeant major in English-speaking armies. Within NATO forces, the rank is rated as OR-7 or OR-8. Russia is a rank in the Russian military, also used in other uniformed services of the Russian government such as the police. It was a junior officer rank in Imperial Russia, but was abolished following the Russian Revolution. In 1940, the rank was restored as a separate career group between non-commissioned officers and officers. Imperial Russia was originally an Oberoffizer rank, as first introduced in Streltsy New Regiments. The name originates from Slavonic ''prapor'' (прапор), meaning flag; the ''praporshchik'' was a flag-bearer in Kievan Rus troops. In the New Regiments of the Streltsy and the "new army" of Peter the Great, '' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mitrofan Nezhentsev
Mitrofan is a Slavic name derived from Greek Μητροφάνης : μήτηρ "mother + φαίνω, "appear, shine". Its English equivalent is Metrophanes. Derived names: * Mitrokha/Mitroha/Mitroshka, Russian diminutive; Mitrofanushka, Russian hypocoristic Derived patronymics: * Mitrofanovich (masculine), Mitrofanovna (feminine) Derived surnames: Mitrofanov/ Mitrofanova, Russian; Mitrokhin/ Mitrokhina, Russian; Mitrofanenko, Ukrainian The name may refer to: * Mitrophan of Voronezh, an Orthodox Saint and bishop * Mitrofan Ban, Montenegrin bishop * Mitrofan Cioban, a Moldovan mathematician * Mitrofan Belyayev, a Russian music publisher, founder of the Glinka prize * Mitrofan Dovnar-Zapol'skiy, a Belarusian historian and ethnographer * Mitrofan Pyatnitsky, a Russian musician * Mitrofan Nedelin, Soviet military commander * Mihai Mitrofan * Sandu Mitrofan * Mitrofan Kodić Mitrofan Kodić (Serbian Cyrillic alphabet, Serbian Cyrillic: Митрофан Кодић; born 4 August ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
8th Army (Russian Empire)
The Russian Eight Army (8-я армия, ''8А'') was a World War I Russian field army that fought on the Eastern theatre of war. Field management was established in July 1914 at the headquarters of the Kiev Military District. The unit was disbanded in the beginning of 1918. At the beginning of the war the 8th Army was composed of the VII, VIII, XII, XXIV Army Corps. Military Fronts in which the 8th Army participated * Southwestern Front (July 1914 - August 1917) * Romanian Front The Romanian Front (, FR) was a moderate fascist party created in Romania in 1935. Led by former Prime Minister of Romania, Prime Minister Alexandru Vaida-Voevod, it originated as a right-wing splinter group from the mainstream National Peasants' ... (August 1917 - the beginning of 1918) Commanders * 28.07.1914 – 17.03.1916 — General of Cavalry Aleksei Brusilov * 23.03.1916 – 29.04.1917 — General of Cavalry Alexey Kaledin * 29.04.1917 – 10.07.1917 — General of Infantry Lavr Kornilov ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
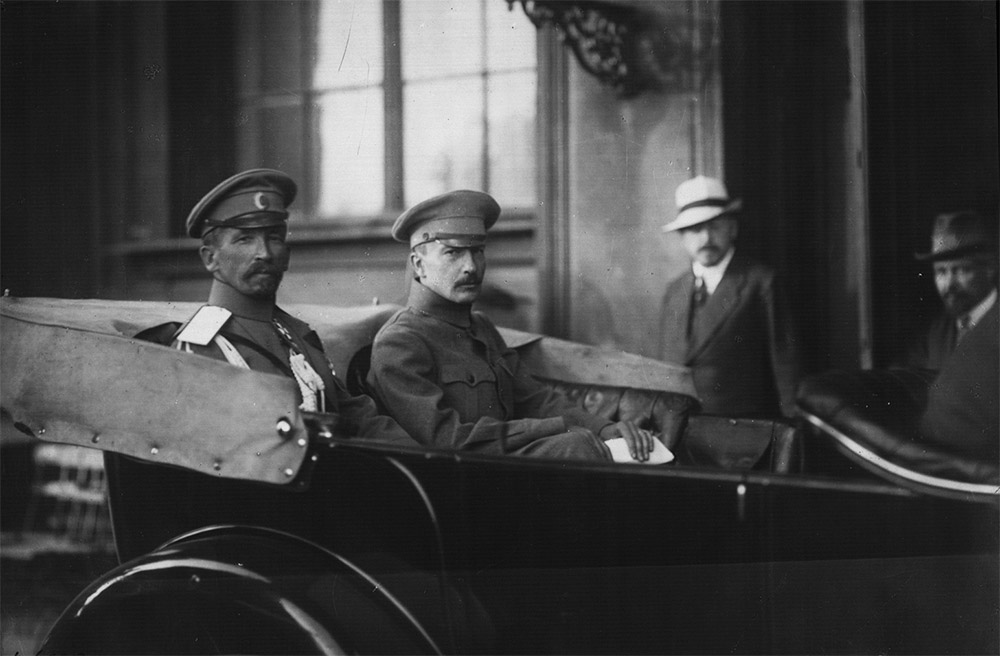
Lavr Kornilov
Lavr Georgiyevich Kornilov (, ; – 13 April 1918) was a Russian military intelligence officer, explorer, and general in the Imperial Russian Army during World War I. He served as Supreme Commander of the Russian Army and as the military leader of the Whites in the Russian Civil War. He is particularly remembered for the Kornilov affair, an unsuccessful coup d’etat against the Provisional Government led by Alexander Kerensky. The event became a significant turning point in the Russian Revolution, strengthening the Bolsheviks' position and influence. Born in Ust-Kamenogorsk, Kornilov began his military career after graduating from the Mikhailovsky Artillery School and the General Staff Academy. He distinguished himself during the Russo-Japanese War and later served as a military attaché in Qing China. During World War I, Kornilov commanded the 48th Infantry Division and gained recognition for his daring escape from Austrian captivity in 1915. His successes on the Easte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zen News
Dzen News ( tr. Zen Novosti; formerly ''Yandex.News'') is a Russian news aggregator. It was developed by Yandex in 2000 and acquired by VK in 2022. Zen.News aggregates articles submitted by publishers via RSS 2.0 and ranks them according to various parameters. The articles are sorted and added to collections related to key events (so-called Stories). The process is automated. Since 2016, the service only aggregates publications from publishers with a license issued by Roskomnadzor. In July 2019, the monthly audience of Zen.News (Yandex.News) totaled 34 million users. It had a market share of 36% in Russia. Controversies In 2014, a report stated that the government of Moscow manipulated Zen.News (Yandex.News) search results by running a network of local online newspapers that provided positive coverage of city events. In many contexts, such as the Russo-Georgian War, anti-Putin protests in Russia, and the Russo-Ukrainian War, search results and stories were apparently manipulate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Totenkopf
''Totenkopf'' (, i.e. ''skull'', literally "dead person's head") is the German word for skull. The word is often used to denote a figurative, graphic or sculptural symbol, common in Western culture, consisting of the representation of a human skull – usually frontal, more rarely in profile with or without the mandible. In some cases, other human skeletal parts may be added, often including two crossed long bones (femurs) depicted below or behind the skull (when it may be referred to in English as a " skull and crossbones"). The human skull is an internationally used symbol for death, the defiance of death, danger, or the dead, as well as piracy or toxicity. In English, the term ''Totenkopf'' is commonly associated with 19th- and 20th-century German military use, particularly in Nazi Germany. The german word for skull without emotional connotation is ''Schädel''. Naval use In early modern sea warfare to early modern sea piracy, buccaneers and pirates used the ''Totenkopf ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shock Troops
Shock troops, assault troops, or storm troops are special formations created to lead military attacks. They are often better trained and equipped than other military units and are expected to take heavier casualties even in successful operations. "Shock troop" is a calque, a loose translation of the German word ''Stoßtrupp'' (literally "thrust squad" or "push squad"). Assault troopers are typically organized for mobility with the intention that they will penetrate enemy defenses and attack into the enemy's vulnerable rear areas. Any specialized, elite unit formed to fight an engagement via overwhelming assault (usually) would be considered shock troops, as opposed to "special forces" or commando-style units (intended mostly for covert operations). However, both types of units could fight behind enemy lines, by surprise if required. Before 1914 The Companion cavalry of Alexander the Great (356-326 BC) are described as being the first example of shock cavalry being used in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aleksei Brusilov
Aleksei Alekseyevich Brusilov (, ; rus, Алексей Алексеевич Брусилов, p=ɐlʲɪkˈsʲej ɐlʲɪkˈsʲejɪvʲɪdʑ brʊˈsʲiɫəf; – 17 March 1926) was a Russian and later Soviet general most noted for the development of new offensive tactics used in the 1916 Brusilov offensive, which was his greatest achievement. Born into an aristocratic military family, Brusilov trained as a cavalry officer, but by 1914 had realized that cavalry was obsolete in an offensive capacity against modern weapons of warfare such as mass adoption of rifled guns, machine guns, and artillery. He is considered a very outstanding general who won many battles against the Austro-Hungarian army. His offensive in 1916 was the final major success of the Tsarist army. In the government, this offensive meant the transfer of the strategic initiative to the Russians and the beginning of preparations for the general offensive of 1917, which, however, was disrupted by the revolution. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |