|
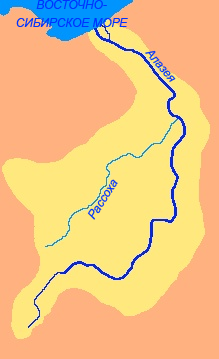
Kolyma Lowland
The Kolyma Lowland () is a lowland plain in the northeastern parts of Sakha Republic in the basin of the Alazeya, Bolshaya Chukoch'ya and lower reaches of the Kolyma rivers. The lowland is formed by fluvio-lacustrine loam soil about 120 m thick. The climate is subarctic. Geography The Kolyma Lowland stretches for along the Kolyma River from the East Siberian Sea to the Chersky Range, between the Alazeya and Yukagir plateaus. Besides the Kolyma, other rivers in the lowland include the Alazeya, its tributary Rossokha, and the Chukochya. The average elevation of the Kolyma lowland is with occasional heights, such as the high Suor Uyata.Google Earth The Kolyma Lowland is part of the wider Yana-Kolyma system of lowlands, which include the Aby to the south of the Polousny Range and the Yana-Indigirka on the northern and western sides.Oleg Leonidovič Kryžanovskij, ''A Checklist of the Ground-beetles of Russia and Adjacent Lands.'' p. 16 See also *Northeast Siberian coastal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plain
In geography, a plain, commonly known as flatland, is a flat expanse of land that generally does not change much in elevation, and is primarily treeless. Plains occur as lowlands along valleys or at the base of mountains, as coastal plains, and as plateaus or Highland, uplands. Plains are one of the major landforms on earth, being present on all continents and covering more than one-third of the world's land area. Plains in many areas are important for agriculture. There are various types of plains and biomes on them. Description A plain or flatland is a flat expanse of land with a layer of grass that generally does not change much in elevation, and is primarily treeless. Plains occur as lowlands along valleys or at the base of mountains, as coastal plains, and as plateaus or Highland, uplands. Plains are one of the major landforms on earth, where they are present on all continents, and cover more than one-third of the world's land area. In a valley, a plain is enclosed on tw ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alazeya Plateau
The Alazeya Plateau () is a mountain plateau in the Sakha Republic, Far Eastern Federal District, Russia. The area is named after river Alazeya, which has its source in the plateau. There are kigilyakhs in the Alazeya Plateau. The particularity of the kigilyakhs found in this location is that their lower part (corresponding to the legs) is thinner than the upper part. Geography The Alazeya Plateau is located in eastern Sakha Republic, between the Indigirka, Kolyma, Alazeya and Ozhogina rivers. The average height of the plateau surface is around . There are slightly higher tableland type elevations cutting across the plateau area; the highest point is a high unnamed summit. The plateau is limited by the Yana-Indigirka Lowland, including the Aby Lowland, to the west, with rivers Yana and Indigirka, the Ozhogina to the south, and the Kolyma Lowland with the Kolyma to the east and northeast.Google Earth Besides the Alazeya, the Sededema and the Shangina also have their sou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Northeast Siberian Coastal Tundra
The Northeast Siberian coastal tundra ecoregion (WWF ID: PA1107) is an ecoregion that covers the coastal plain of the central north region of Siberia in Russia. This coastal region borders the Laptev Sea and the East Siberian Sea, both marginal seas of the Arctic Ocean, from the Lena River delta in the west to the Kolyma River delta in the east. There are several large river deltas in the area that support breeding grounds for 60 to 80 species of migratory birds. The region is in the Palearctic realm, and the tundra biome. It has an area of . Location and description The ecoregion stretches 1,100 km along the north coast of Siberia, from the Lena River delta in the west to the Kolyma River delta in the east. The terrain is flat and rolling tundra. The entire region is on continuous permafrost. Thermokarst lakes are common, caused by the freezing and thawing of permafrost. Climate The region has a subarctic (Dfc) and tundra climate (ET). Mean precipitation is about 200 mm/y ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kolyma Lowland ONC C-7 (2)
Kolyma (, ) or Kolyma Krai () is a historical region in the Russian Far East that includes the basin of Kolyma River and the northern shores of the Sea of Okhotsk, as well as the Kolyma Mountains (the watershed of the two). It is bounded to the north by the East Siberian Sea and the Arctic Ocean, and by the Sea of Okhotsk to the south. Kolyma Krai was never formally defined and over time it was split among various administrative units. , it consists roughly of the Magadan Oblast, north-eastern areas of Yakutia, and the Bilibinsky District of Chukotka Autonomous Okrug. The area, part of which is within the Arctic Circle, has a subarctic climate with very cold winters lasting up to six months of the year. Permafrost and tundra cover a large part of the region. Average winter temperatures range from (even lower in the interior), and average summer temperatures, from . There are rich reserves of gold, silver, tin, tungsten, mercury, copper, antimony, coal, oil, and peat. Twen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yana-Indigirka Lowland
The Yana-Indigirka Lowland (; ) is a large, low alluvial plain located in northern Siberia, Far Eastern Federal District, Russia. Administratively most of the territory of the lowland is part of the Sakha Republic (Yakutia). There are inhabited centers of population in the lowlands such as Chokurdakh, Olenegorsk and Nizhneyansk, but these are very few and scattered. Geography The lowland is named after the Yana River in the west and the Indigirka River in the east and is crossed by both rivers in their middle and lower courses. The area is mostly flat and very marshy, its northern limits extending for over from the Buor Khaya Gulf of the Laptev Sea in the west to the delta of river Indigirka in the East Siberian Sea in the east. It is limited by the Kyundyulyun, the northern end of the Selennyakh Range and the Polousny Range in the south. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polousny Range
The Polousny Range (; ) is a mountain range in the Sakha Republic, Far Eastern Federal District, Russia.Полоусный кряж (Polousny Range) / Great Soviet Encyclopedia; in 35 vols. / Ch. ed. Yu. S. Osipov. 2004—2017. This range is one of the areas of Yakutia where kigilyakhs are found. History The area of the Polousny Range was first mapped by geographer and ethnologist Baron Gerhard von Maydell (1835–1894) during his pioneering research of East Siberia. The Chondon mammoth was discovered in 2013, at the feet of the Polousny Range in the Chondon basin, 66 km south-west of the village of Tumat. Geography The Polousny Range is part of the Momsko-Chersk Mountain Region (). It rises in the southern area of the Yana-Indigirka Lowland, north of the Aby Lowland in the Sakha region. It is made up of mountains of middle height and smooth slopes. It includes separate low mountain ranges with stretches of plain in between roughly aligned from east to west. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aby Lowland
The Aby Lowland (; ) is a low alluvial plain located in the Sakha Republic, Far Eastern Federal District, Russia. Administratively most of the territory of the lowland is part of Aby District ''(Aby Ulus)''. Geography The lowland is crossed by the Indigirka River in its middle course. Besides many smaller rivers and streams, three large left hand tributaries of the great river flow into it, the Selennyakh, Uyandina (with the Khatyngnakh) and Druzhina rivers. The Badyarikha limits the area in the east. The area is flat and mostly marshy, the average height of the plain being between and above sea level. The rivers are generally slow-flowing and meandering, connected by channels and with very boggy shores. The Aby Lakes, mostly small and numbering over 15,000, are dotting the lowlands. The largest are Lake OzhoginoIndigirka / |
Google Earth
Google Earth is a web mapping, web and computer program created by Google that renders a 3D computer graphics, 3D representation of Earth based primarily on satellite imagery. The program maps the Earth by superimposition, superimposing satellite images, aerial photography, and geographic information system, GIS data onto a 3D globe, allowing users to see cities and landscapes from various angles. Users can explore the globe by entering addresses and coordinates, or by using a Computer keyboard, keyboard or computer mouse, mouse. The program can also be downloaded on a smartphone or Tablet computer, tablet, using a touch screen or stylus to navigate. Users may use the program to add their own data using Keyhole Markup Language and upload them through various sources, such as forums or blogs. Google Earth is able to show various kinds of images overlaid on the surface of the Earth and is also a Web Map Service client. In 2019, Google revealed that Google Earth covers more than 97 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Suor Uyata
The Suor Uyata (; ) is a mountain range in the Sakha Republic, Far Eastern Federal District, Russia. The village of Andryushkino, a small inhabited locality of the Lower Kolyma District, is located to the SSE.Google Earth Kigilyakhs, rock formations that are an important element of the culture of the Yakuts, are found in the Suor Uyata range. to the ESE of the eastern end of the range, on the right bank of the Alazeya River, rises the high Kisilyakh-Tas, another important Kigilyakh site. History The Suor Uyata was first mapped in the summer of 1870 by geographer and ethnologist Baron Gerhard von Maydell (1835–1894) during his pioneering research of East Siberia. Geography The Suor Uyata rises in the northwestern area of the Kolyma Lowland, only to the east of the eastern end of the Ulakhan-Sis Range. It is a smaller range than the latter, of which it can be considered an eastern prolongation. The main ridge stretches in a roughly WNW/ESE direction for about . Its h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chukochya River
The Bolshaya Chukochya or Chukochya (; , ''Revum-Revu'') is a river in the Sakha Republic (Yakutia) of the Russian Federation. It is long, and has a drainage basin of . Course It has its sources in Lake Usun-Kyuel and crosses the tundra roughly northeastwards. In its lower course it flows south of Lake Bolshoye Morskoye. Finally it flows into the Kolyma Gulf of the East Siberian Sea west of the mouths of the Kolyma. Owing to its extreme northerly location the Bolshaya Chukochya freezes up in early October and remains icebound until June. The Bolshaya Chukochya basin is located between the basins of the Alazeya and the Kolyma. There are study sites near the Bolshaya Chukochya in order to investigate the mineral transformations in the soils affected by permafrost. Tributaries The main tributaries of the Bolshaya Chukochya are the long Olyor (Олёр) and the long Semen-Yuryakh (Семен-Юрях) on the left, as well as the long Savva-Yuryakh (Савва-Юрях) on t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rossokha River
The Rassokha (, also Россоха; ) is a river in the northeastern part of Yakutia, Russia. It is the major tributary of the Alazeya.Google Earth Geography The river is long. The area of its basin is . The Rassokha is formed by the confluence of the rivers Ilin-Yuryakh and Arga-Yuryakh in the Kolyma Lowland. The original sources of the uppermost river in the network are in the Ulakhan-Sis Range. The Rassokha flows across the Middle Kolyma District and the Lower Kolyma District in an area marked by permafrost, with numerous swamps and lakes. Finally it joins the left bank of the Alazeya from its mouth.Rossokha - Water (in Russian) The Rassokha has 145 tributaries that are longer than and in its basin there are 7,442 lakes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yukaghir Highlands
The Yukaghir Highlands () are a mountainous area in the Sakha Republic and Magadan Oblast, Far Eastern Federal District, Russia. The area is named after the Yukaghir people. Geography The Yukaghir Highlands are a mountain region located at the eastern limits of the Sakha Republic and the northwestern end of Magadan Oblast, as well as a little part in the westernmost limit of Chukotka Autonomous Okrug. They include two medium height mountain ranges, the Chubukulakh Range and the Siversky Range, as well as a plateau, the Yukaghir Tableland.Oleg Leonidovič Kryžanovskij, ''A Checklist of the Ground-beetles of Russia and Adjacent Lands.'' p. 16 The average height of the intermontane basins of the plateau is between and . In the ranges a few scattered mountains rise above and the highest point is high Mount Chubukulakh (Чубукулах). The highlands are limited by the Kolyma Lowland to the west and the courses of the Bulun and Namyndykan rivers to the south. The Kolym ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |