|
Kodjabashi
The kodjabashis (; singular κοτζάμπασης, ''kotzabasis''; ; from from and ) were local Christian notables in parts of the Ottoman Balkans, most often referring to Ottoman Greece and especially the Peloponnese. They were also known in Greek as ''proestoi'' or ''prokritoi'' (προεστοί/πρόκριτοι, "primates") or ''demogerontes'' (δημογέροντες, "elders of the people"). In some places they were elected (such in the islands for example), but, especially in the Peloponnese, they soon became a hereditary oligarchy, who exercised considerable influence and held posts in the Ottoman administration. The title was also present in Ottoman Serbia and Bosnia, where it was known as ''starešina'' ("elder, chief") instead of the official Turkish name. The terms '' chorbaji'' (from Turkish ''çorbacı'') and '' knez'' (a Slavic title) were also used for this type of primates, in Bulgaria and Serbia respectively. The equivalent of the kodjabashis in Orthodox v ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phanariotes
Phanariots, Phanariotes, or Fanariots (, , ) were members of prominent Greek families in Phanar (Φανάρι, modern ''Fener''), the chief Greek quarter of Constantinople where the Ecumenical Patriarchate is located, who traditionally occupied four important positions in the Ottoman Empire: Hospodar of Moldavia, Hospodar of Wallachia, Grand Dragoman of the Porte and Grand Dragoman of the Fleet. Despite their cosmopolitanism and often-Western education, the Phanariots were aware of their Greek ancestry and culture; according to Nicholas Mavrocordatos' ''Philotheou Parerga'', "We are a race completely Hellenic". They emerged as a class of wealthy Greek merchants (of mostly noble Byzantine descent) during the second half of the 16th century, and were influential in the administration of the Ottoman Empire's Balkan domains in the 18th century. The Phanariots usually built their houses in the Phanar quarter to be near the court of the Patriarch, who (under the Ottoman millet sys ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Knez (title)
A , also , ''knjaz'' or (), is a historical Slavic title, used both as a royal and noble title in different times. It is usually translated into English as 'prince', 'king' or 'duke', depending on specific historical context and the potentially known Latin equivalents at the time; the word was originally derived from the common Germanic ('king'). Feminine forms of the word may be divided into two groups: * "Princess", be it princess consort (wife of a reigning prince), princess regnant (reigning princess ''suo jure''), or princess regent (reigning on behalf of an underage prince, usually her son after her husband's death) ** Belarusian: ''kniahinia'' (княгіня) ** Bulgarian and Russian: () ** Slovene, Serbo-Croatian, and Macedonian: (in Serbian and Macedonian Cyrillic: ) ** Ukrainian: (княгиня) * "Daughter of the prince" ** Belarusian: ''kniazioŭna'' (князёўна) ** Russian: (; the son of a ''knyaz'' is ' ( in its old form). ** Ukrain ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ioannis Logothetis
Ioannis or Ioannes (), shortened to Giannis or Yannis (Γιάννης) is a Greek given name cognate with Johannes and John (given name), John and the Arabic name Yahya (name), Yahya . Notable people with the name include: *John I Tzimiskes, Ioannis I, Tzimiskis, Byzantine Emperor *John Plagis, Ioannis Agorastos-Plagis (John Plagis), Southern Rhodesian flying ace during World War II *Ioannis Alevras, Greek politician who served as Speaker of the Hellenic Parliament *Ioannis Altamouras, Greek painter of the 19th century *John Aniston, Ioannis Anastassakis, professionally known as John Aniston, a Greek-born American actor *Giannis Andrianopoulos, Ioannis Andrianopoulos, Greek footballer and one of the founding members of football club Olympiacos CFP *Giannis Antetokounmpo, Ioannis Antetokounmpo, commonly known as Giannis Antetokounmpo, Greek basketball player *Ioannis Apakas, Greek painter and priest in the latter part of the 16th century to the early 17th century *John Argyropoulos, I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Greek War Of Independence
The Greek War of Independence, also known as the Greek Revolution or the Greek Revolution of 1821, was a successful war of independence by Greek revolutionaries against the Ottoman Empire between 1821 and 1829. In 1826, the Greeks were assisted by the British Empire, Bourbon Restoration in France, Kingdom of France, and the Russian Empire, while the Ottomans were aided by their vassals, especially by the Eyalet of Egypt. The war led to the formation of modern Greece, which would be expanded to its modern size in later years. The revolution is celebrated by Greek diaspora, Greeks around the world as Greek Independence Day, independence day on 25 March. All Greek territory, except the Ionian Islands, the Mani Peninsula, and mountainous regions in Epirus, came under Ottoman rule in the 15th century. During the following centuries, there were Ottoman Greece#Uprisings before 1821, Greek uprisings against Ottoman rule. Most uprisings began in the independent Greek realm of the Mani Pe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Christians From The Ottoman Empire
A Christian () is a person who follows or adheres to Christianity, a monotheistic Abrahamic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus Christ. Christians form the largest religious community in the world. The words ''Christ'' and ''Christian'' derive from the Koine Greek title (), a translation of the Biblical Hebrew term '' mashiach'' () (usually rendered as ''messiah'' in English). While there are diverse interpretations of Christianity which sometimes conflict, they are united in believing that Jesus has a unique significance. The term ''Christian'' used as an adjective is descriptive of anything associated with Christianity or Christian churches, or in a proverbial sense "all that is noble, and good, and Christ-like." According to a 2011 Pew Research Center survey, there were 2.3 billion Christians around the world, up from about 600 million in 1910. Today, about 37% of all Christians live in the Americas, about 26% live in Europe, 24% live in sub-Saharan Africa, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Turkish Words And Phrases
Turkish may refer to: * Something related to Turkey ** Turkish language *** Turkish alphabet ** Turkish people, a Turkic ethnic group and nation *** Turkish citizen, a citizen of Turkey *** Turkish communities in the former Ottoman Empire * The word that Iranian Azerbaijanis use for the Azerbaijani language * Ottoman Empire (Ottoman Turkey), 1299–1922, previously sometimes known as the Turkish Empire ** Ottoman Turkish, the Turkish language used in the Ottoman Empire * Turkish Airlines, an airline * Turkish music (style), a musical style of European composers of the Classical music era * Turkish, a character in the 2000 film '' Snatch'' See also * * * Turk (other) * Turki (other) * Turkic (other) * Turkey (other) * Turkiye (other) * Turkish Bath (other) * Turkish population, the number of ethnic Turkish people in the world * Culture of Turkey * History of Turkey ** History of the Republic of Turkey * Turkic languages ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Government Of The Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire developed over the years as a despotism with the List of sultans of the Ottoman Empire, Sultan as the supreme ruler of a centralized government that had an effective control of its Administrative divisions of the Ottoman Empire, provinces, officials and inhabitants. Wealth and rank could be inherited but were just as often earned. Positions were perceived as List of Ottoman titles and appellations, titles, such as viziers and ''Agha (Ottoman Empire), aghas''. Military of the Ottoman Empire, Military service was a key to many problems. The expansion of the Empire called for a systematic administrative organization that developed into a dual system of military ("Central Government") and civil administration ("Provincial System") and developed a kind of separation of powers: higher executive functions were carried out by the military authorities and judiciary, judicial and basic administration were carried out by civil authorities. Outside this system were vario ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oligarchy
Oligarchy (; ) is a form of government in which power rests with a small number of people. Members of this group, called oligarchs, generally hold usually hard, but sometimes soft power through nobility, fame, wealth, or education; or through corporate, religious, political, or military control. Throughout history, power structures considered to be oligarchies have often been viewed as coercive, relying on public obedience or oppression to exist. Aristotle pioneered the use of the term as meaning rule by the rich, contrasting it with aristocracy, arguing that oligarchy was a corruption of aristocracy. Types Minority rule The consolidation of power by a dominant minority, whether religious or ethnic, can be considered a form of oligarchy. Examples include South Africa during apartheid, Liberia under Americo-Liberians, the Sultanate of Zanzibar, and Rhodesia. In these cases, oligarchic rule was often tied to the legacy of colonialism. In the early 20th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Balkans Since 1453
''The Balkans Since 1453'' is a book by the Greek-Canadian historian L.S. Stavrianos published in 1958. It is a large, synthetic work which encompasses the major political, economic and cultural events of the Balkans from the fall of the Byzantine Empire to the late 1940s. Stavrianos paid particular attention to the national awakening and the nation-building Nation-building is constructing or structuring a national identity using the power of the state. Nation-building aims at the unification of the people within the state so that it remains politically stable and viable. According to Harris Mylonas, ... process in the Balkans. The book was highly acclaimed by many historians of the Balkans, including Traian Stoianovich and Mark Mazower. External links Jason C. Mavrovitis on the book 1958 non-fiction books History books about the Balkans 20th-century history books English-language non-fiction books {{Europe-hist-book-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
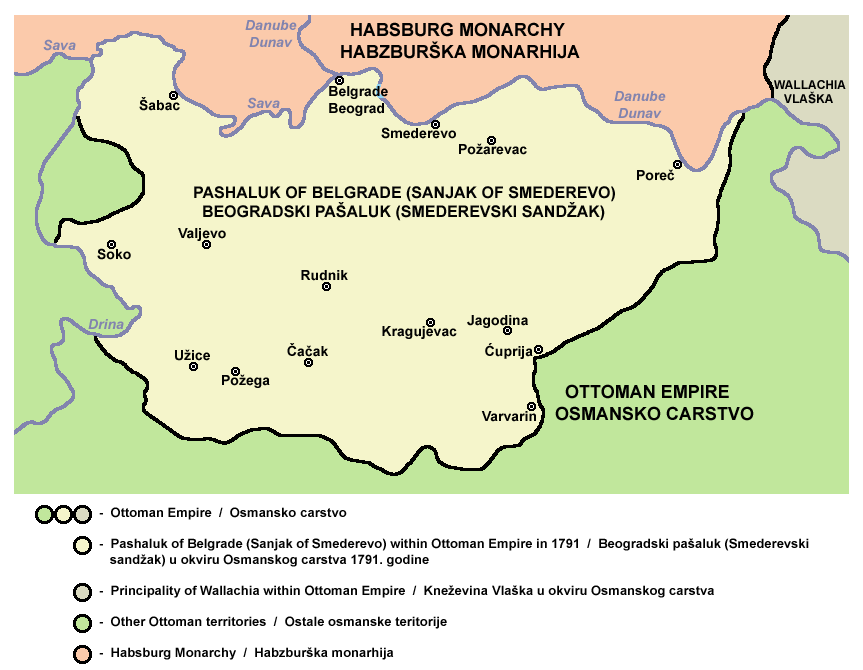
Obor-knez
''Ober-knez'' ( sr-Cyrl, обер-кнез) was a title borne by elected local native Serbs, Serbian chiefs (''Knyaz'') of the ''Nahiye (Ottoman), nahiyah'' (district of a group of villages) in the Sanjak of Smederevo (also known as the Pashalik of Belgrade) within the Ottoman Empire. The ''ober-knez'' was the senior chief and responsible for his district's people and was their spokesman (intermediary) in direct relations with the Pasha, though usually through the ''sipahi'' (elite cavalry), and was in charge of the transfer of taxes levied on the villages. The ''vojvoda'' and ''ober-knez'' titles were given to people approved by the Pasha. The title was hereditary, being Patrilineality, succeeded by one's son. The ''ober-knez'', as a senior, had several ''knezes'' under him, who held sub-districts or one village each. History In 1788, Koča's frontier rebellion saw eastern Šumadija occupied by Austrian Serbian freikorps and hajduks. The Siege of Belgrade (1789), Siege of Belgra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydra Island
Hydra, or Ydra or Idra (; , ), and in antiquity Hydrea, is one of the Saronic Islands of Greece, located in the Aegean Sea between the Myrtoan Sea and the Argolic Gulf. It is separated from the Peloponnese by a narrow strip of water. In ancient times, the island was known as Hydrea (Ὑδρέα, derived from the Greek word for "water"), a reference to the natural springs on the island. The municipality of Hydra consists of the islands Hydra (area ), Dokos (area ), and a few uninhabited islets, with a total area of . The province of Hydra () was one of the provinces of the Argolis and Corinthia Prefecture from 1833 to 1942, Attica prefecture from 1942 to 1964, Piraeus prefecture from 1964 to 1972 and then back to Attica as part of the newly established Piraeus prefecture of Attica. Its territory corresponded with that of the current municipality. It was abolished in 2006. Today the municipality of Hydra is part of the Islands regional unit of Attica region. There is one ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |