|
Knifegrinder
A scissor grinder (German: ''Scherenschleifer''), sometimes also scissor and knife grinder or knife and scissor grinder, for short also knife grinder, is a craftsman who sharpens and repairs blunt knives, scissors and other cutting tools. It is an Apprenticeship, apprenticeship profession that nevertheless requires much experience. Wandering knife and scissors sharpeners, also known as itinerant sharpeners or, more antiquatedly, cart sharpeners, have existed in Europe since the Middle Ages. Traditionally, they came from a few regions of origin in northern Italy and northwestern Spain. In addition, the Migrant worker, itinerant craft was practiced by the so-called traveling people, including Sinti and Romani people, Roma, and is one of the traditional occupations of the Yenish people, Yenish, especially in Central and Western Europe. They moved through the towns and offered sharpening and sharpening knives and scissors. In the second half of the 20th century, the demand declined ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Knife Grinder, Topsham (Maine), 2018-01
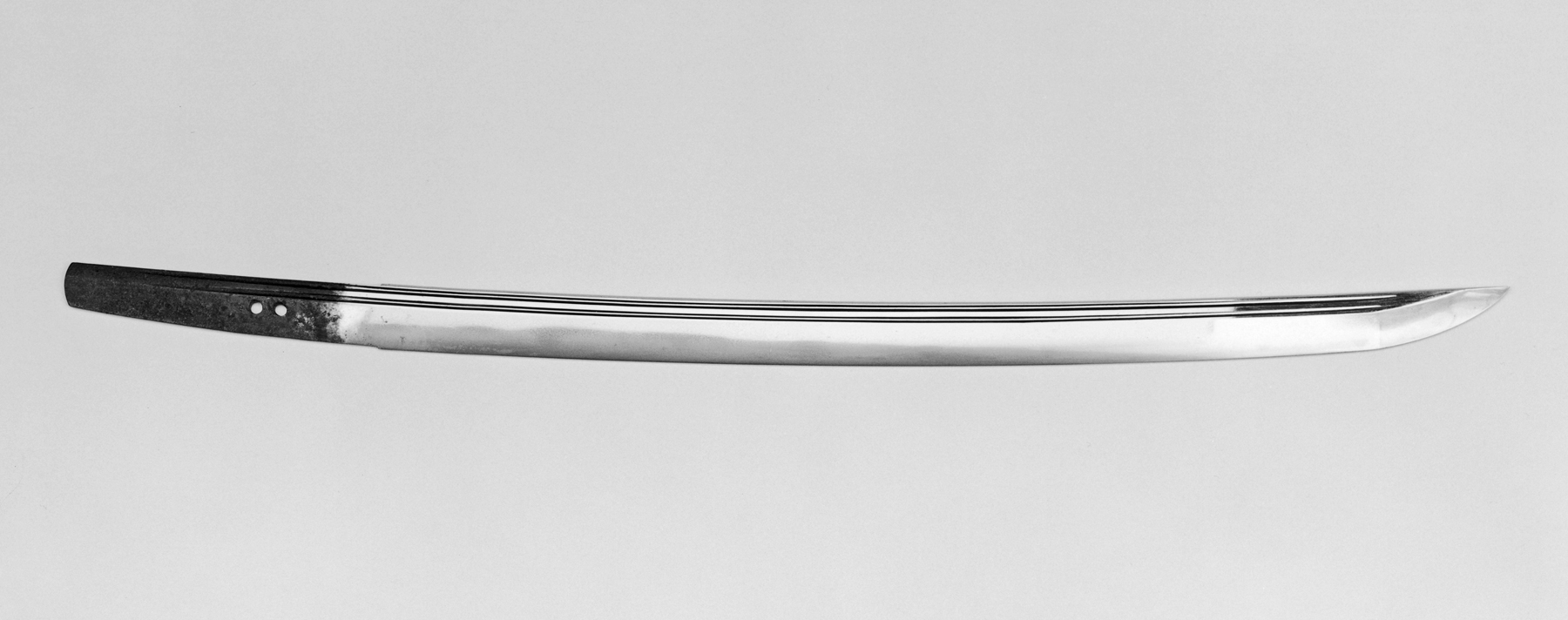
A knife (: knives; from Old Norse 'knife, dirk') is a tool or weapon with a cutting edge or blade, usually attached to a handle or hilt. One of the earliest tools used by humanity, knives appeared at least Stone Age, 2.5 million years ago, as evidenced by the Oldowan tools. Originally made of wood, bone, and stone (such as flint and obsidian), over the centuries, in step with improvements in both metallurgy and manufacturing, knife blades have been made from copper, bronze, iron, steel, ceramic, and titanium. Most modern knives have either fixed or folding blades; blade patterns and styles vary by maker and country of origin. Knives can serve various purposes. Hunters use a hunting knife, soldiers use the combat knife, scouts, campers, and hiking, hikers carry a pocketknife; there are kitchen knives for preparing foods (the chef's knife, the paring knife, bread knife, cleaver), table knife (butter knives and steak knives), weapons (daggers or switchblades), knives for throwing o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grinder (occupation)
Grinder may refer to: Machinery *Various types of grinding machine, used in a machining operation to refine the surface of materials *Food grinders **Blade grinder, includes food processors, blenders, electric coffee and spice grinders, etc. **Coffee grinder, a machine used for grinding coffee **Herb grinder, a grinder used for herbs including marijuana **Meat grinder, a machine used for grinding food **Wet grinder, a grinder that uses water either to soften the product ground or to keep the grinding elements cool *Grinder winch, a device for tensioning a rope to control a sail on a boat People * Grinder (surname) * Bob Baker (boxer) (1926–2002), American heavyweight boxer nicknamed "The Grinder" *Michael Mizrachi (born 1981), American professional poker player nicknamed "The Grinder" *Cliff Thorburn (born 1948), Canadian retired professional snooker player, nicknamed "The Grinder" *Grinder (biohacking community), also known as a biohacker, designer and installer of DIY body enh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pedal Drive
A pedal (from the Latin '' pes'' ''pedis'', "foot") is a lever designed to be operated by foot and may refer to: Computers and other equipment * Footmouse, a foot-operated computer mouse * In medical transcription, a pedal is used to control playback of voice dictations Geometry * Pedal curve, a curve derived by construction from a given curve * Pedal triangle, a triangle obtained by projecting a point onto the sides of a triangle Music Albums * ''Pedals'' (Rival Schools album) * ''Pedals'' (Speak album) Other music * Bass drum pedal, a pedal used to play a bass drum while leaving the drummer's hands free to play other drums with drum sticks, hands, etc. * Effects pedal, a pedal used commonly for electric guitars * Pedal keyboard, a musical keyboard operated by the player's feet * Pedal harp, a modern orchestral harp with pedals used to change the tuning of its strings * Pedal point, a type of nonchord tone, usually in the bass * Pedal tone, a fundamental tone played ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hand Crank
A crank is an arm attached at a right angle to a rotating shaft by which circular motion is imparted to or received from the shaft. When combined with a connecting rod, it can be used to convert circular motion into reciprocating motion, or vice versa. The arm may be a bent portion of the shaft, or a separate arm or disk attached to it. Attached to the end of the crank by a pivot is a rod, usually called a connecting rod (conrod). The term often refers to a human-powered crank which is used to manually turn an axle, as in a bicycle crankset or a brace and bit drill. In this case a person's arm or leg serves as the connecting rod, applying reciprocating force to the crank. There is usually a bar perpendicular to the other end of the arm, often with a freely rotatable handle or pedal attached. Examples Familiar examples include: Hand-powered cranks * Spinning wheel * Mechanical pencil sharpener * Fishing reel and other reels for cables, wires, ropes, etc. *Starting h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Folklore
Folklore is the body of expressive culture shared by a particular group of people, culture or subculture. This includes oral traditions such as Narrative, tales, myths, legends, proverbs, Poetry, poems, jokes, and other oral traditions. This also includes material culture, such as traditional building styles common to the group. Folklore also encompasses customary lore, taking actions for folk beliefs, including folk religion, and the forms and rituals of celebrations such as Christmas, weddings, folk dances, and Rite of passage, initiation rites. Each one of these, either singly or in combination, is considered a Cultural artifact, folklore artifact or Cultural expressions, traditional cultural expression. Just as essential as the form, folklore also encompasses the transmission of these artifacts from one region to another or from one generation to the next. Folklore is not something one can typically gain from a formal school curriculum or study in the fine arts. Instead, thes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Patron Saint
A patron saint, patroness saint, patron hallow or heavenly protector is a saint who in Catholicism, Anglicanism, Eastern Orthodoxy or Oriental Orthodoxy is regarded as the heavenly advocate of a nation, place, craft, activity, class, clan, family, or person. The term may be applied to individuals to whom similar roles are ascribed in other religions. In Christianity Saints often become the patrons of places where they were born or had been active. However, there were cases in medieval Europe where a city which grew to prominence obtained for its cathedral the remains or some relics of a famous saint who had lived and was buried elsewhere, thus making them the city's patron saint – such a practice conferred considerable prestige on the city concerned. In Latin America and the Philippines, Spanish and Portuguese explorers often named a location for the saint on whose feast or commemoration day they first visited the place, with that saint naturally becoming the area's patron ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Catherine Of Alexandria
Catherine of Alexandria, also spelled Katherine, was, according to tradition, a Christian saint and Virginity, virgin, who was martyred in the early 4th century at the hands of the emperor Maxentius. According to her hagiography, she was both a princess and a noted scholar who became a Christians, Christian around age 14, converted hundreds of people to Christianity, and was martyred around age 18. The Eastern Orthodox Church venerates her as a great martyr and celebrates her Calendar of saints, feast day on 24 or 25 November, depending on the regional tradition. In Catholic Church, Catholicism, Catherine is traditionally revered as one of the Fourteen Holy Helpers, and she is commemorated in the Roman Martyrology on 25 November. Her feast was removed from the General Roman Calendar in 1969 but restored in 2002 as an optional memorial. In the Episcopal Church (United States), Episcopal Church, St. Catherine is commemorated on 24 November, together with the martyrs Saint Barbara, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sharpening
Sharpening is the process of creating or refining a blade, the edge joining two non-coplanar faces into a converging apex, thereby creating an edge of appropriate shape on a tool or implement designed for cutting. Improving sharpness is done by removing material on an implement with an abrasive substance harder than the material of the implement, followed sometimes by processes to polish/hone the sharp surface to increase smoothness. Tools and materials There are many ways of sharpening tools. Malleable metal surfaces such as bronze, iron and mild steel may be formed by beating or peening a flat surface into a sharp edge. This process also causes work hardening. An abrasive material may be rubbed against the cutting edge to be sharpened. The most traditional abrasive material is a natural stone such as sandstone or granite. Modern synthetic grinding wheels and flat sharpening stones can be manufactured in precise grades of abrasiveness according to the intended pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blade
A blade is the Sharpness (cutting), sharp, cutting portion of a tool, weapon, or machine, specifically designed to puncture, chop, slice, or scrape surfaces or materials. Blades are typically made from materials that are harder than those they are intended to cut. This includes early examples made from flaked stones like flint or obsidian, evolving through the ages into metal forms like copper, bronze, and iron, and culminating in modern versions made from steel or ceramics. Serving as one of humanity's oldest tools, blades continue to have wide-ranging applications, including in combat, cooking, and various other everyday and specialized tasks. Blades function by concentrating force at the cutting edge. Design variations, such as serrated edges found on bread knives and saws, serve to enhance this force concentration, adapting blades for specific functions and materials. Blades thus hold a significant place both historically and in contemporary society, reflecting an evolution i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Billhook
A billhook or bill hook is a versatile cutting tool used widely in agriculture and forestry for cutting woody material such as shrubs, small trees and branches. It is distinct from the sickle. It was commonly used in Europe with an important variety of traditional local patterns. Elsewhere, it was also developed locally such as in the Indian subcontinent, or introduced regionally as in the Americas, South Africa, and Oceania by European settlers. Design The blade is usually made from a medium-carbon steel in varying weights and lengths, but typically long. Blades are straight near the handle but have an increasingly strong curve towards the end. The blade is generally sharpened only on the inside of the curve, but double-edged billhooks, or "broom hooks", also have a straight secondary edge on the back. The blade is fixed to a wooden handle, in Europe usually made from Fraxinus excelsior, ash due to its strength and ability to deal with repeated impact. Handles are mostly ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
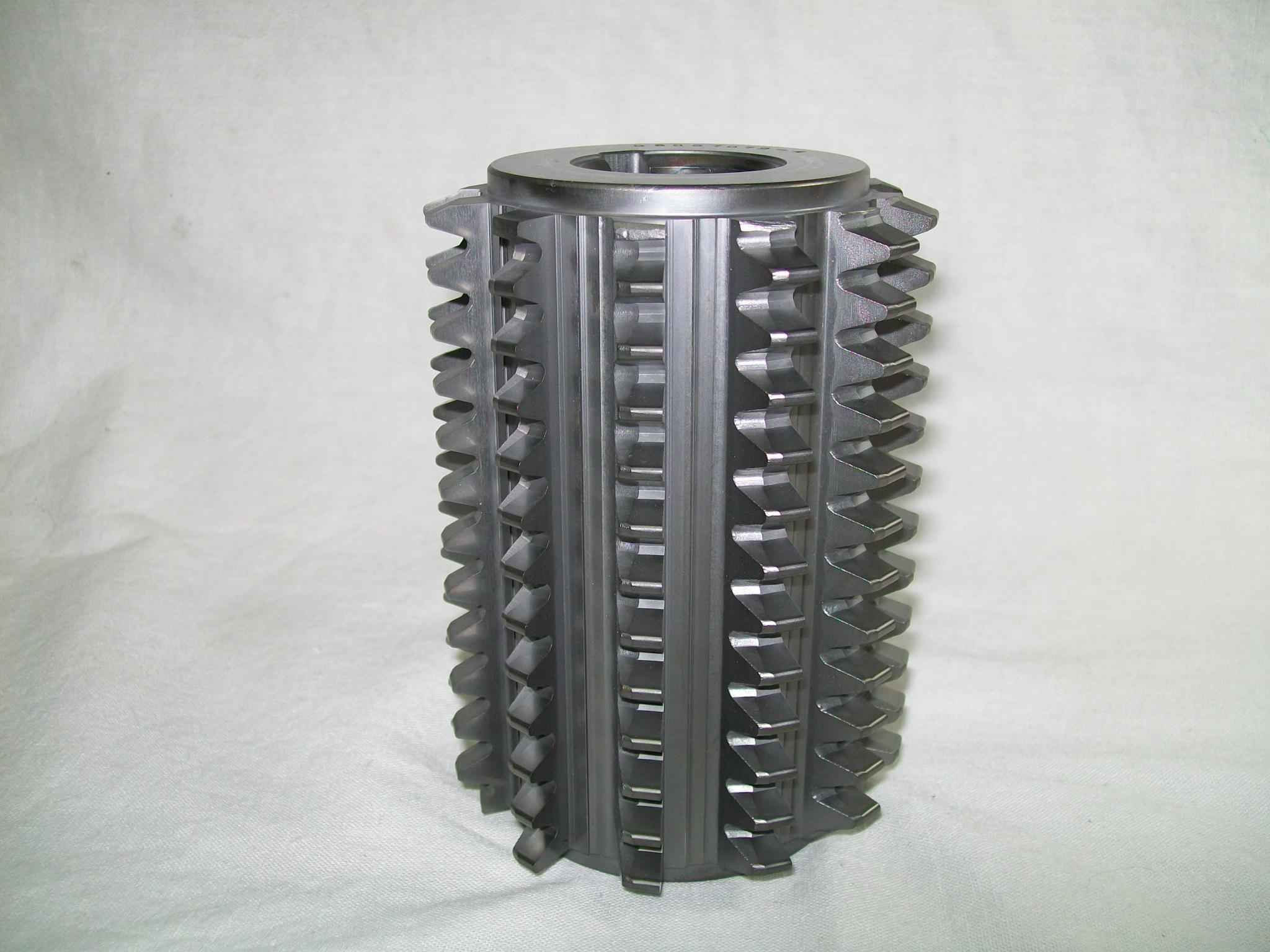
Milling Cutter
Milling cutters are cutting tools typically used in milling machines or machining centres to perform milling operations (and occasionally in other machine tools). They remove material by their movement within the machine (e.g., a ball nose mill) or directly from the cutter's shape (e.g., a form tool such as a hobbing cutter). Features Milling cutters come in several shapes and many sizes. There is also a choice of coatings, as well as rake angle and number of cutting surfaces. * Shape: Several standard shapes of milling cutters are used in industry today, which are explained in more detail below. * Flutes / teeth: The flutes of the milling bit are the deep helical grooves running up the cutter, while the sharp blade along the edge of the flute is known as the tooth. The tooth cuts the material, and chips of this material are pulled up the flute by the rotation of the cutter. There is almost always one tooth per flute, but some cutters have two teeth per flute. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |