|
Kingston Russell House
Kingston Russell House is a large mansion house and manor near Long Bredy in Dorset, England, west of Dorchester. The present house dates from the late 17th century but in 1730 was clad in a white Georgian stone facade. The house was restored in 1913, and at the same time the gardens were laid out. Location The house is on land which was granted to the Russell family (previously thought not ancestors of the Russell Dukes of Bedford), by an early king, probably John, King of England (reigned 1199–1216) at the end of his reign, or his son Henry III of England. Kingston Russell manor is now part of Long Bredy parish, but earlier appears to have had its own church. The main part of the manor adjoins Winterbourne Abbas to the east and Compton Valence to the north, whilst the house itself adjoins Long Bredy. It is situated in an area known for ancient tumuli and the Kingston Russell Stone Circle. The Poor Lot barrow group forms a boundary with Littlebredy and Winterbourne A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kingston Russell (other)
Kingston Russell is a settlement in Dorset, England. Kingston Russell may also refer to: * Kingston Russell House, mansion near Long Bredy, Dorset, England * Kingston Russell Stone Circle, monument in Dorset, England {{Disambiguation, geo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Serjeanty
Under feudalism in France and England during the Middle Ages, tenure by serjeanty () was a form of tenure in return for a specified duty other than standard knight-service. Etymology The word comes from the French noun , itself from the Latin , "serving", the present participle of the verb , "to keep, preserve, save, rescue, deliver". "Sergeant" is derived from the same source, though developing an entirely different meaning. Origins and development Serjeanty originated in the assignation of an estate in land on condition of the performance of a certain duty other than knight-service, usually the discharge of duties in the household of the king or a noble. It ranged from non-standard service in the king's army (distinguished only by equipment from that of the knight), to petty renders (for example the rendering of a quantity of basic food such as a goose) scarcely distinguishable from those of the rent-paying tenant or socager. The legal historians Frederick Pollock and Fr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Berry Pomeroy
Berry Pomeroy is a village and civil parish in the South Hams district of Devon, England, east of the town of Totnes. The parish is surrounded clockwise from the north by the parishes of Ipplepen, Marldon, Torbay (unitary authority), Stoke Gabriel, Ashprington, Totnes, and Littlehempston. In 2001 its population was 973, down from 1193 in 1901. The main road access is via the A385 road between Paignton and Totnes that runs through the parish, south of the village. History Berry Pomeroy was the centre of the large feudal barony of Berry Pomeroy, which was held at the time of the Domesday Book (1086) by Ralph de Pomeroy. The Pomeroy family retained the barony until 1547. William of Orange is said to have held his first parliament at Parliament Cottage in Longcombe within the parish, after landing at Brixham at the start of the Glorious Revolution in November 1688. He was afterwards entertained at Berry Pomeroy Castle by Sir Edward Seymour, 3rd Baronet. Between 1681 and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
English Feudal Baron
In the kingdom of England, a feudal barony or barony by tenure was the highest degree of feudal land tenure, namely ''per baroniam'' (Latin for "by barony"), under which the land-holder owed the service of being one of the king's barons. The duties owed by and the privileges granted to feudal barons are not exactly defined, but they involved the duty of providing soldiers to the royal feudal army on demand by the king, and the privilege of attendance at the king's feudal court, the ''Magnum Concilium'', the precursor of parliament. If the estate-in-land held by barony contained a significant castle as its ''caput baroniae'' and if it was especially large – consisting of more than about 20 knight's fees (each loosely equivalent to a manor) – then it was termed an honour. The typical honour had properties scattered over several shires, intermingled with the properties of others. This was a specific policy of the Norman kings, to avoid establishing any one area under the cont ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hugh X Of Lusignan
Hugh X de Lusignan or Hugh V of La Marche (c. 1183 – c. 5 June 1249, Angoulême) was Seigneur de Lusignan and Count of La Marche in November 1219 and was Count of Angoulême by marriage. He was the son of Hugh IX. Background Hugh's father, Hugh IX of Lusignan, was betrothed to marry 12-year-old Isabel of Angoulême in 1200, but King John of England married her instead. As a result, the entire de Lusignan family rebelled against the English king. Hugh IX married Agathe de Preuilly instead. Hugh was born in 1183. He married Isabella, widow of King John of England, on 10 May 1220. By Hugh's marriage to Isabella, he became Count of Angoulême until her death in 1246. Together they founded the abbey of Valence. In 1224, Hugh joined with King Louis VIII of France against the Angevins, being promised the city of Bordeaux. By 1226, he had become embittered against Louis' lack of support in conquering Gascony. Marriage and issue Hugh and Isabella had: * Hugh XI de Lusign ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Joan Of England, Queen Of Scotland
Joan of England (22 July 1210 – 4 March 1238), was Queen of Alba (Scotland) from 1221 until her death as the wife of Alexander II. She was the third child of John, King of England and Isabella of Angoulême. Life Joan was sought as a bride by Philip II of France for his son. In 1214, however, her father King John promised her in marriage to Hugh X of Lusignan, as compensation for his father Hugh IX of Lusignan being jilted by her mother Isabella. She was promised Saintes, Saintonge and the Isle of Oléron as dowry, and was sent to her future spouse in that year to be brought up at his court until marriage. Hugh X laid claim on her dowry already prior to their marriage, but when this did not succeed, he reportedly became less eager to marry her. On the death of John of England in 1216, queen dowager Isabella decided she should marry Hugh X herself. Hugh X kept Joan with him in an attempt to keep her dowry as well as having the dowry of her mother Isabella released fro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
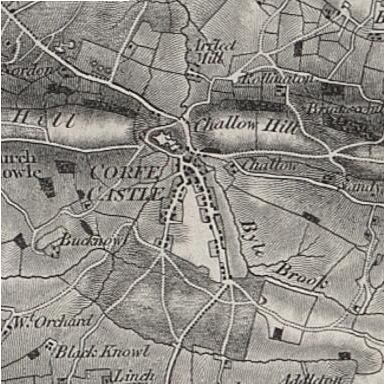
Corfe Castle
Corfe Castle is a fortification standing above the Corfe Castle (village), village of the same name on the Isle of Purbeck peninsula in the English county of Dorset. Built by William the Conqueror, the castle dates to the 11th century and commands a gap in the Purbeck Hills on the route between Wareham, Dorset, Wareham and Swanage. The first phase was one of the earliest castles in England to be built at least partly using stone when the majority were built with earth and timber. Corfe Castle underwent major structural changes in the 12th and 13th centuries. In 1572, Corfe Castle left the Crown's control when Elizabeth I sold it to Sir Christopher Hatton. Sir John Bankes bought the castle in 1635, and was the owner during the English Civil War. While Bankes was fighting in London and Oxford, his wife, Lady Mary Bankes, led the defence of the castle when it was twice besieged by Roundhead, Parliamentarian forces. The first siege, in 1643, was unsuccessful, but by 1645 C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
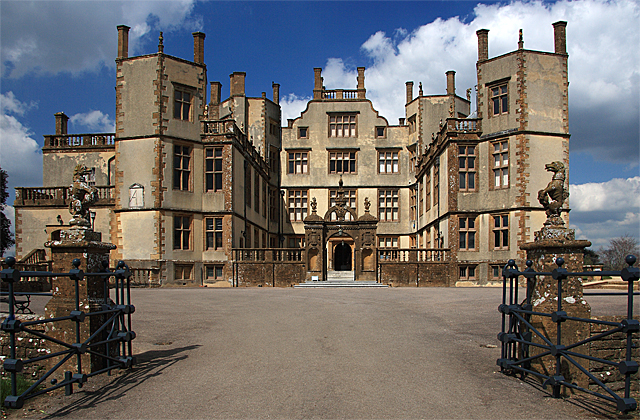
Sherborne Castle
Sherborne Castle (sometimes called Sherborne New Castle) is a 16th-century Tudor mansion southeast of Sherborne Sherborne is a market town and civil parishes in England, civil parish in north west Dorset, in South West England. It is sited on the River Yeo (South Somerset), River Yeo, on the edge of the Blackmore Vale, east of Yeovil. The parish include ... in Dorset, England, within the parish of Castleton, Dorset, Castleton. Originally built by Sir Walter Raleigh as Sherborne Lodge, and extended in the 1620s, it stands in a park which formed a small part of the Baron Digby, Digby estate. Within the grounds lie the ruins of the 12th-century Sherborne Old Castle, now in the care of English Heritage. Origins The building now known as Sherborne Old Castle () was constructed in the 12th century as the fortified palace of Roger de Caen, Bishop of Salisbury and Chancellor of England. In the early 1140s, the castle was captured by Robert, 1st Earl of Gloucester, Robert Earl o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Richard I Of England
Richard I (8 September 1157 – 6 April 1199), known as Richard the Lionheart or Richard Cœur de Lion () because of his reputation as a great military leader and warrior, was King of England from 1189 until his death in 1199. He also ruled as Duke of Normandy, Duke of Aquitaine, Aquitaine, and Duchy of Gascony, Gascony; Lord of Cyprus in the Middle Ages, Cyprus; Count of Poitiers, Counts and dukes of Anjou, Anjou, Count of Maine, Maine, and Count of Nantes, Nantes; and was overlord of Brittany at various times during the same period. He was the third of five sons of Henry II of England and Eleanor of Aquitaine and was therefore not expected to become king, but his two elder brothers predeceased their father. By the age of 16, Richard had taken command of his own army, putting down rebellions in Poitou against his father. Richard was an important Christian commander during the Third Crusade, leading the campaign after the departure of Philip II of France and achieving sev ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Russell, Knight
Sir John Russell (died c. 1224) of Kingston Russell in Dorset, England, was a household knight of King John (1199–1216), and of the young King Henry III (1216–1272), to whom he also acted as steward. He served in this capacity as custodian of the royal castles of Corfe (1221 and 1224) and Sherborne (1224) in Dorset and of the castles of Peveril and Bolsover in Derbyshire. He served as Sheriff of Somerset in 1223-1224. He was granted the royal manor of Kingston Russell in Dorset under a feudal land tenure of grand serjeanty. Between 1212 and about 1215 he acquired a moiety of the feudal barony of Newmarch, (shared with John de Bottrel/Bottreaux) the caput of which was at North Cadbury, Somerset, in respect of which he received a summons for the military service of one knight in 1218. Debt to Jews Russell had obtained a loan from Aaron the Jew of Lincoln (died 1186), the greatest of the Jewish financiers licensed to trade in England, and on the seizure of Jewish assets b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pentecost
Pentecost (also called Whit Sunday, Whitsunday or Whitsun) is a Christianity, Christian holiday which takes place on the 49th day (50th day when inclusive counting is used) after Easter Day, Easter. It commemorates the descent of the Holy Spirit in Christianity, Holy Spirit upon the Apostles in the New Testament, Apostles of Jesus, Mary, mother of Jesus, Mary, and other followers of the Christ, while they were in Jerusalem during the Second Temple Period, Jerusalem celebrating the Feast of Weeks, as described in the Acts of the Apostles (Acts 2:1–31). Pentecost marks the "Birthday of the Church". Pentecost is one of the Great feasts in the Eastern Orthodox Church, a Solemnity in the Roman Rite of the Catholic Church, a Liturgical calendar (Lutheran)#Festivals, Festival in the Lutheranism, Lutheran Churches, and a Principal Feast in the Anglican Communion. Many Christian denominations provide a special liturgy for this holy celebration. Since its date depends on the date of Eas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William The Conqueror
William the Conqueror (Bates ''William the Conqueror'' p. 33– 9 September 1087), sometimes called William the Bastard, was the first Norman king of England (as William I), reigning from 1066 until his death. A descendant of Rollo, he was Duke of Normandy (as William II) from 1035 onward. By 1060, following a long struggle, his hold on Normandy was secure. In 1066, following the death of Edward the Confessor, William invaded England, leading a Franco-Norman army to victory over the Anglo-Saxon forces of Harold Godwinson at the Battle of Hastings, and suppressed subsequent English revolts in what has become known as the Norman Conquest. The rest of his life was marked by struggles to consolidate his hold over England and his continental lands, and by difficulties with his eldest son, Robert Curthose. William was the son of the unmarried Duke Robert I of Normandy and his mistress Herleva. His Legitimacy (family law), illegitimate status and youth caused some difficulties for h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |