|
Killing Vector Field
In mathematics, a Killing vector field (often called a Killing field), named after Wilhelm Killing, is a vector field on a pseudo-Riemannian manifold that preserves the metric tensor. Killing vector fields are the infinitesimal generators of isometries; that is, flows generated by Killing vector fields are continuous isometries of the manifold. This means that the flow generates a symmetry, in the sense that moving each point of an object the same distance in the direction of the ''Killing vector'' will not distort distances on the object. Definition Specifically, a vector field X is a Killing vector field if the Lie derivative with respect to X of the metric tensor g vanishes: : \mathcal_ g = 0 \,. In terms of the Levi-Civita connection, this is : g\left(\nabla_Y X, Z\right) + g\left(Y, \nabla_Z X\right) = 0 for all vectors Y and . In local coordinates, this amounts to the Killing equation : \nabla_\mu X_\nu + \nabla_ X_\mu = 0 \,. This condition is expressed in covarian ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mathematics
Mathematics is a field of study that discovers and organizes methods, Mathematical theory, theories and theorems that are developed and Mathematical proof, proved for the needs of empirical sciences and mathematics itself. There are many areas of mathematics, which include number theory (the study of numbers), algebra (the study of formulas and related structures), geometry (the study of shapes and spaces that contain them), Mathematical analysis, analysis (the study of continuous changes), and set theory (presently used as a foundation for all mathematics). Mathematics involves the description and manipulation of mathematical object, abstract objects that consist of either abstraction (mathematics), abstractions from nature orin modern mathematicspurely abstract entities that are stipulated to have certain properties, called axioms. Mathematics uses pure reason to proof (mathematics), prove properties of objects, a ''proof'' consisting of a succession of applications of in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
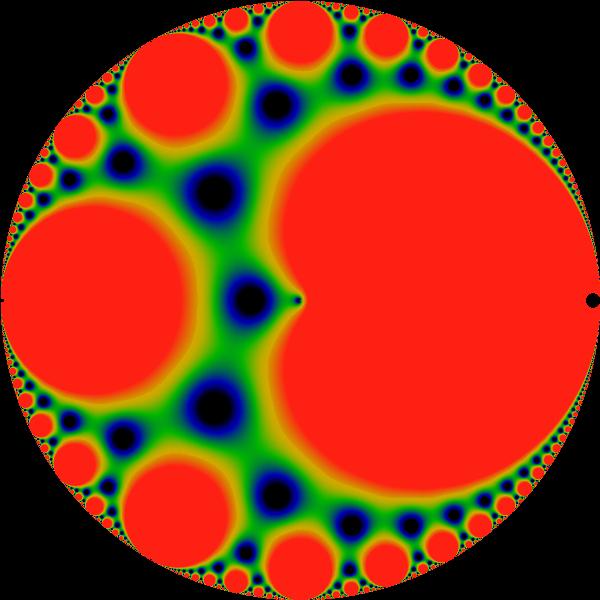
Poincaré Metric
In mathematics, the Poincaré metric, named after Henri Poincaré, is the metric tensor describing a two-dimensional surface of constant negative curvature. It is the natural metric commonly used in a variety of calculations in hyperbolic geometry or Riemann surfaces. There are three equivalent representations commonly used in two-dimensional hyperbolic geometry. One is the Poincaré half-plane model, defining a model of hyperbolic space on the upper half-plane. The Poincaré disk model defines a model for hyperbolic space on the unit disk. The disk and the upper half plane are related by a conformal map, and isometries are given by Möbius transformations. A third representation is on the punctured disk, where relations for ''q''-analogues are sometimes expressed. These various forms are reviewed below. Overview of metrics on Riemann surfaces A metric on the complex plane may be generally expressed in the form :ds^2=\lambda^2(z,\overline)\, dz\,d\overline where λ is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lorentz Group
In physics and mathematics, the Lorentz group is the group of all Lorentz transformations of Minkowski spacetime, the classical and quantum setting for all (non-gravitational) physical phenomena. The Lorentz group is named for the Dutch physicist Hendrik Lorentz. For example, the following laws, equations, and theories respect Lorentz symmetry: * The kinematical laws of special relativity * Maxwell's field equations in the theory of electromagnetism * The Dirac equation in the theory of the electron * The Standard Model of particle physics The Lorentz group expresses the fundamental symmetry of space and time of all known fundamental laws of nature. In small enough regions of spacetime where gravitational variances are negligible, physical laws are Lorentz invariant in the same manner as special relativity. Basic properties The Lorentz group is a subgroup of the Poincaré group—the group of all isometries of Minkowski spacetime. Lorentz transformations are, precise ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lorentz Boost
In physics, the Lorentz transformations are a six-parameter family of linear transformations from a coordinate frame in spacetime to another frame that moves at a constant velocity relative to the former. The respective inverse transformation is then parameterized by the negative of this velocity. The transformations are named after the Dutch physicist Hendrik Lorentz. The most common form of the transformation, parametrized by the real constant v, representing a velocity confined to the -direction, is expressed as \begin t' &= \gamma \left( t - \frac \right) \\ x' &= \gamma \left( x - v t \right)\\ y' &= y \\ z' &= z \end where and are the coordinates of an event in two frames with the spatial origins coinciding at , where the primed frame is seen from the unprimed frame as moving with speed along the -axis, where is the speed of light, and \gamma = \frac is the Lorentz factor. When speed is much smaller than , the Lorentz factor is negligibly different from 1, but a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Little Group
In mathematics, a group action of a group G on a set (mathematics), set S is a group homomorphism from G to some group (under function composition) of functions from S to itself. It is said that G acts on S. Many sets of transformation (function), transformations form a group (mathematics), group under function composition; for example, the rotation (mathematics), rotations around a point in the plane. It is often useful to consider the group as an abstract group, and to say that one has a group action of the abstract group that consists of performing the transformations of the group of transformations. The reason for distinguishing the group from the transformations is that, generally, a group of transformations of a mathematical structure, structure acts also on various related structures; for example, the above rotation group also acts on triangles by transforming triangles into triangles. If a group acts on a structure, it will usually also act on objects built from that st ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Minkowski Space
In physics, Minkowski space (or Minkowski spacetime) () is the main mathematical description of spacetime in the absence of gravitation. It combines inertial space and time manifolds into a four-dimensional model. The model helps show how a spacetime interval between any two events is independent of the inertial frame of reference in which they are recorded. Mathematician Hermann Minkowski developed it from the work of Hendrik Lorentz, Henri Poincaré, and others said it "was grown on experimental physical grounds". Minkowski space is closely associated with Einstein's theories of special relativity and general relativity and is the most common mathematical structure by which special relativity is formalized. While the individual components in Euclidean space and time might differ due to length contraction and time dilation, in Minkowski spacetime, all frames of reference will agree on the total interval in spacetime between events.This makes spacetime distance an inva ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cartan Decomposition
In mathematics, the Cartan decomposition is a decomposition of a semisimple Lie group or Lie algebra, which plays an important role in their structure theory and representation theory. It generalizes the polar decomposition or singular value decomposition of matrices. Its history can be traced to the 1880s work of Élie Cartan and Wilhelm Killing. Cartan involutions on Lie algebras Let \mathfrak be a real semisimple Lie algebra and let B(\cdot,\cdot) be its Killing form. An involution on \mathfrak is a Lie algebra automorphism \theta of \mathfrak whose square is equal to the identity. Such an involution is called a ''Cartan involution'' on \mathfrak if B_\theta(X,Y) := -B(X,\theta Y) is a positive definite bilinear form. Two involutions \theta_1 and \theta_2 are considered equivalent if they differ only by an inner automorphism. Any real semisimple Lie algebra has a Cartan involution, and any two Cartan involutions are equivalent. Examples * A Cartan involution on \m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Symmetric Spaces
In mathematics, a symmetric space is a Riemannian manifold (or more generally, a pseudo-Riemannian manifold) whose group of isometries contains an inversion symmetry about every point. This can be studied with the tools of Riemannian geometry, leading to consequences in the theory of holonomy; or algebraically through Lie theory, which allowed Cartan to give a complete classification. Symmetric spaces commonly occur in differential geometry, representation theory and harmonic analysis. In geometric terms, a complete, simply connected Riemannian manifold is a symmetric space if and only if its curvature tensor is invariant under parallel transport. More generally, a Riemannian manifold (''M'', ''g'') is said to be symmetric if and only if, for each point ''p'' of ''M'', there exists an isometry of ''M'' fixing ''p'' and acting on the tangent space T_pM as minus the identity (every symmetric space is complete, since any geodesic can be extended indefinitely via symmetries about ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
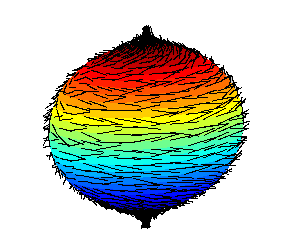
Hairy Ball Theorem
The hairy ball theorem of algebraic topology (sometimes called the hedgehog theorem in Europe) states that there is no nonvanishing continuous function, continuous tangent vector field on even-dimensional n‑sphere, ''n''-spheres. For the ordinary sphere, or 2‑sphere, if ''f'' is a continuous function that assigns a Vector (geometric), vector in to every point ''p'' on a sphere such that ''f''(''p'') is always tangent to the sphere at ''p'', then there is at least one pole, a point where the field vanishes (a ''p'' such that ''f''(''p'') = Null vector, 0). The theorem was first proved by Henri Poincaré for the 2-sphere in 1885, and extended to higher even dimensions in 1912 by Luitzen Egbertus Jan Brouwer. The theorem has been expressed colloquially as "you can't comb a hairy ball flat without creating a cowlick" or "you can't comb the hair on a coconut". Counting zeros Every zero of a vector field has a (non-zero) "Vector field#Index of a vector field, index", and it ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pullback
In mathematics, a pullback is either of two different, but related processes: precomposition and fiber-product. Its dual is a pushforward. Precomposition Precomposition with a function probably provides the most elementary notion of pullback: in simple terms, a function f of a variable y, where y itself is a function of another variable x, may be written as a function of x. This is the pullback of f by the function y. f(y(x)) \equiv g(x) It is such a fundamental process that it is often passed over without mention. However, it is not just functions that can be "pulled back" in this sense. Pullbacks can be applied to many other objects such as differential forms and their cohomology classes; see * Pullback (differential geometry) * Pullback (cohomology) Fiber-product The pullback bundle is an example that bridges the notion of a pullback as precomposition, and the notion of a pullback as a Cartesian square. In that example, the base space of a fiber bundle is pulled b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SO(3)
In mechanics and geometry, the 3D rotation group, often denoted SO(3), is the group of all rotations about the origin of three-dimensional Euclidean space \R^3 under the operation of composition. By definition, a rotation about the origin is a transformation that preserves the origin, Euclidean distance (so it is an isometry), and orientation (i.e., ''handedness'' of space). Composing two rotations results in another rotation, every rotation has a unique inverse rotation, and the identity map satisfies the definition of a rotation. Owing to the above properties (along composite rotations' associative property), the set of all rotations is a group under composition. Every non-trivial rotation is determined by its axis of rotation (a line through the origin) and its angle of rotation. Rotations are not commutative (for example, rotating ''R'' 90° in the x-y plane followed by ''S'' 90° in the y-z plane is not the same as ''S'' followed by ''R''), making the 3D rotation group ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sphere Killing Field Z-rotation
A sphere (from Greek , ) is a surface analogous to the circle, a curve. In solid geometry, a sphere is the set of points that are all at the same distance from a given point in three-dimensional space.. That given point is the ''center'' of the sphere, and the distance is the sphere's ''radius''. The earliest known mentions of spheres appear in the work of the ancient Greek mathematicians. The sphere is a fundamental surface in many fields of mathematics. Spheres and nearly-spherical shapes also appear in nature and industry. Bubbles such as soap bubbles take a spherical shape in equilibrium. The Earth is often approximated as a sphere in geography, and the celestial sphere is an important concept in astronomy. Manufactured items including pressure vessels and most curved mirrors and lenses are based on spheres. Spheres roll smoothly in any direction, so most balls used in sports and toys are spherical, as are ball bearings. Basic terminology As mentioned earlier is th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |