|
Karl Widerquist
Karl Widerquist () is an American political philosopher and economist at Georgetown University in their campus in Qatar. He is best known as an advocate of basic income, but is also an interdisciplinary academic writer who has published in journals in fields as diverse as economics, politics, philosophy, and anthropology. He is a consistent critic of propertarianism, right-libertarianism, social contract theory, and the belief that modern societies fulfill the Lockean proviso. Widerquist is the co-founder of the U.S. Basic Income Guarantee (USBIG) Network, which was the first Basic Income network in the United States. He was co-chair of the Basic Income Earth Network (BIEN) 2008-2017, and he co-founded ''Basic Income News'' in 2011. He has been a commentator on several television, radio, and print networks. According to the Atlantic Monthly, Karl Widerquist is "a leader of the worldwide basic income movement." Biography Widerquist was born in Chicago, Illinois, in 1965, and gre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chicago
(''City in a Garden''); I Will , image_map = , map_caption = Interactive Map of Chicago , coordinates = , coordinates_footnotes = , subdivision_type = List of sovereign states, Country , subdivision_name = United States , subdivision_type1 = U.S. state, State , subdivision_type2 = List of counties in Illinois, Counties , subdivision_name1 = Illinois , subdivision_name2 = Cook County, Illinois, Cook and DuPage County, Illinois, DuPage , established_title = Settled , established_date = , established_title2 = Municipal corporation, Incorporated (city) , established_date2 = , founder = Jean Baptiste Point du Sable , government_type = Mayor–council government, Mayor–council , governing_body = Chicago City Council , leader_title = Mayor of Chicago, Mayor , leader_name = Lori Lightfo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Political Philosophy
Political philosophy or political theory is the philosophical study of government, addressing questions about the nature, scope, and legitimacy of public agents and institutions and the relationships between them. Its topics include politics, liberty, justice, property, rights, law, and the enforcement of laws by authority: what they are, if they are needed, what makes a The purpose of government, government legitimate, what fundamental rights, rights and freedoms it should protect, what form it should take, what the law is, and what duties citizens owe to a legitimate government, if any, and when it may be legitimately overthrown, if ever. Political theory also engages questions of a broader scope, tackling the political nature of phenomena and categories such as Identity (social science), identity, Cultural studies, culture, Queer theory, sexuality, Critical race theory, race, Political economy, wealth, Critical animal studies, human-nonhuman relations, Political ethics, ethi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
YouTube
YouTube is a global online video sharing and social media platform headquartered in San Bruno, California. It was launched on February 14, 2005, by Steve Chen, Chad Hurley, and Jawed Karim. It is owned by Google, and is the second most visited website, after Google Search. YouTube has more than 2.5 billion monthly users who collectively watch more than one billion hours of videos each day. , videos were being uploaded at a rate of more than 500 hours of content per minute. In October 2006, YouTube was bought by Google for $1.65 billion. Google's ownership of YouTube expanded the site's business model, expanding from generating revenue from advertisements alone, to offering paid content such as movies and exclusive content produced by YouTube. It also offers YouTube Premium, a paid subscription option for watching content without ads. YouTube also approved creators to participate in Google's AdSense program, which seeks to generate more revenue for both parties. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Social Contract
In moral and political philosophy, the social contract is a theory or model that originated during the Age of Enlightenment and usually, although not always, concerns the legitimacy of the authority of the state over the individual. Social contract arguments typically are that individuals have consented, either explicitly or tacitly, to surrender some of their freedoms and submit to the authority (of the ruler, or to the decision of a majority) in exchange for protection of their remaining rights or maintenance of the social order. The relation between natural and legal rights is often a topic of social contract theory. The term takes its name from ''The Social Contract'' (French: ''Du contrat social ou Principes du droit politique''), a 1762 book by Jean-Jacques Rousseau that discussed this concept. Although the antecedents of social contract theory are found in antiquity, in Greek and Stoic philosophy and Roman and Canon Law, the heyday of the social contract was the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Guy Standing (economist)
Guy Standing (born 9 February 1948) is a British labour economist. He is a professor of development studies at the School of Oriental and African Studies, University of London, and a co-founder of the Basic Income Earth Network (BIEN). Standing has written widely in the areas of labour economics, labour market policy, unemployment, labour market flexibility, structural adjustment policies and social protection. He created the term ''precariat'' to describe an emerging class of workers who are harmed by low wages and poor job security as a consequence of globalisation. Since the 2011 publication of his book ''The Precariat: The New Dangerous Class'', his work has focused on the precariat, unconditional basic income, deliberative democracy, and the commons. Life and career Guy Standing gained his bachelor's degree in economics from the University of Sussex in 1971. After taking a masters in labour economics and industrial relations at the University of Illinois, he received ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Philippe Van Parijs
Philippe Van Parijs (; born 1951) is a Belgian political philosopher and political economist, best known as a proponent and main defender of the concept of an unconditional basic income and for the first systematic treatment of linguistic justice. In 2020, he was listed by ''Prospect'' as the eighth-greatest thinker for the COVID-19 era, with the magazine writing, "Today’s young UBI enthusiasts draw on the books and tap the networks of this Belgian polymath, who championed it before it was fashionable. For decades, he has warned that our proclaimed freedoms to start businesses or raise children count for nothing without the real freedom that comes with a basic income". Early life and education Born 23 May 1951, Philippe Van Parijs studied philosophy, law, political economy, sociology and linguistics at the Université Saint-Louis - Bruxelles in Brussels, at the Université catholique de Louvain (UCLouvain) in Louvain-la-Neuve, at the Katholieke Universiteit Leuven (KU Le ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Capitalism
Capitalism is an economic system based on the private ownership of the means of production and their operation for profit. Central characteristics of capitalism include capital accumulation, competitive markets, price system, private property, property rights recognition, voluntary exchange, and wage labor. In a market economy, decision-making and investments are determined by owners of wealth, property, or ability to maneuver capital or production ability in capital and financial markets—whereas prices and the distribution of goods and services are mainly determined by competition in goods and services markets. Economists, historians, political economists and sociologists have adopted different perspectives in their analyses of capitalism and have recognized various forms of it in practice. These include '' laissez-faire'' or free-market capitalism, anarcho-capitalism, state capitalism and welfare capitalism. Different forms of capitalism feature varying ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peter Kropotkin
Pyotr Alexeyevich Kropotkin (; russian: link=no, Пётр Алексе́евич Кропо́ткин ; 9 December 1842 – 8 February 1921) was a Russian anarchist, socialist, revolutionary, historian, scientist, philosopher, and activist who advocated anarcho-communism. Born into an aristocratic land-owning family, Kropotkin attended a military school and later served as an officer in Siberia, where he participated in several geological expeditions. He was imprisoned for his activism in 1874 and managed to escape two years later. He spent the next 41 years in exile in Switzerland, France (where he was imprisoned for almost four years) and England. While in exile, he gave lectures and published widely on anarchism and geography. Kropotkin returned to Russia after the Russian Revolution in 1917, but he was disappointed by the Bolshevik state. Kropotkin was a proponent of a decentralised communist society free from central government and based on voluntary association ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Michael Otsuka
Michael H. Otsuka (born 1964) is an American left-libertarian political philosopher and Professor in the Department of Philosophy at Rutgers University. Career Otsuka earned his Doctor of Philosophy degree in politics from Balliol College, Oxford, under the direction of G. A. Cohen, on a Marshall Scholarship, after graduating from Yale University with a bachelor's degree in political science ''summa cum laude'' in 1986. Prior to moving to the London School of Economics in 2013, Otsuka was Professor of Philosophy at University College London, where he had taught since 1998, and, before that taught at UCLA and the University of Colorado. He joined Rutgers University in September 2022. Philosophical work Otsuka has written extensively in political philosophy on topics such as equality and left-libertarianism. Otsuka is a proponent of actual-consent forms of government, in opposition to the mainstream of political theory which has thought such systems to be unworkable. H ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Georgist
Georgism, also called in modern times Geoism, and known historically as the single tax movement, is an economic ideology holding that, although people should own the value they produce themselves, the economic rent derived from land—including from all natural resources, the commons, and urban locations—should belong equally to all members of society. Developed from the writings of American economist and social reformer Henry George, the Georgist paradigm seeks solutions to social and ecological problems, based on principles of land rights and public finance which attempt to integrate economic efficiency with social justice. Georgism is concerned with the distribution of economic rent caused by land ownership, natural monopolies, pollution rights, and control of the commons, including title of ownership for natural resources and other contrived privileges (e.g. intellectual property). Any natural resource which is inherently limited in supply can generate economic rent, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
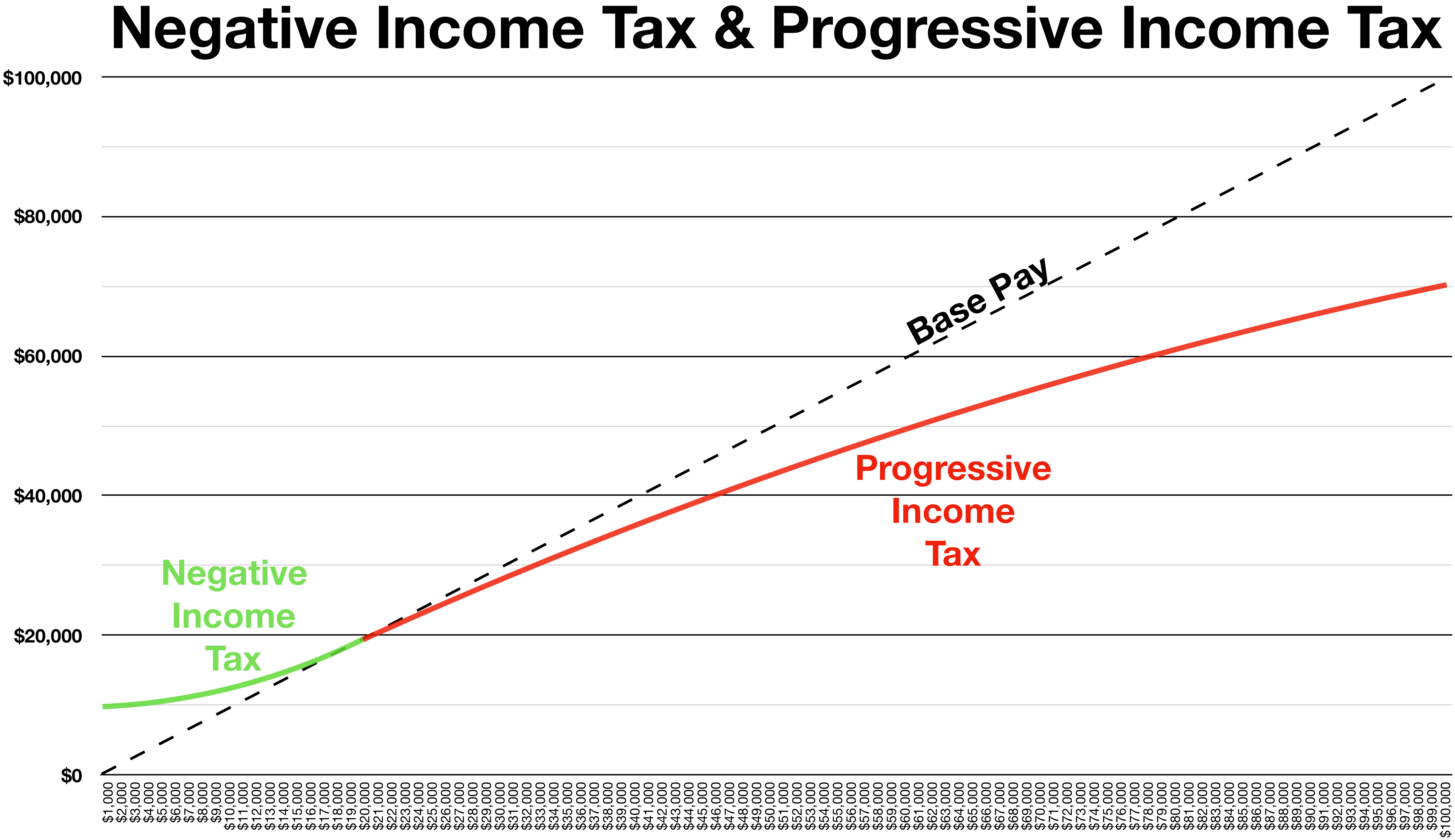
Negative Income Tax
In economics, a negative income tax (NIT) is a system which reverses the direction in which tax is paid for incomes below a certain level; in other words, earners above that level pay money to the state while earners below it receive money, as shown by the blue arrows in the diagram. NIT was proposed by Juliet Rhys-Williams while working on the Beveridge Report in the early 1940s and popularized by Milton Friedman in the 1960s as a system in which the state makes payments to the poor when their income falls below a threshold, while taxing them on income above that threshold. Together with Friedman, supporters of NIT also included James Tobin, Joseph A. Pechman, and Peter M. Mieszkowski, and even then-President Richard Nixon, who suggested implementation of modified NIT in his Family Assistance Plan. After the increase in popularity of NIT, an experiment sponsored by the US government was conducted between 1968 and 1982 on effects of NIT on labour supply, income, and substit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |