|
Kappa Aurigae
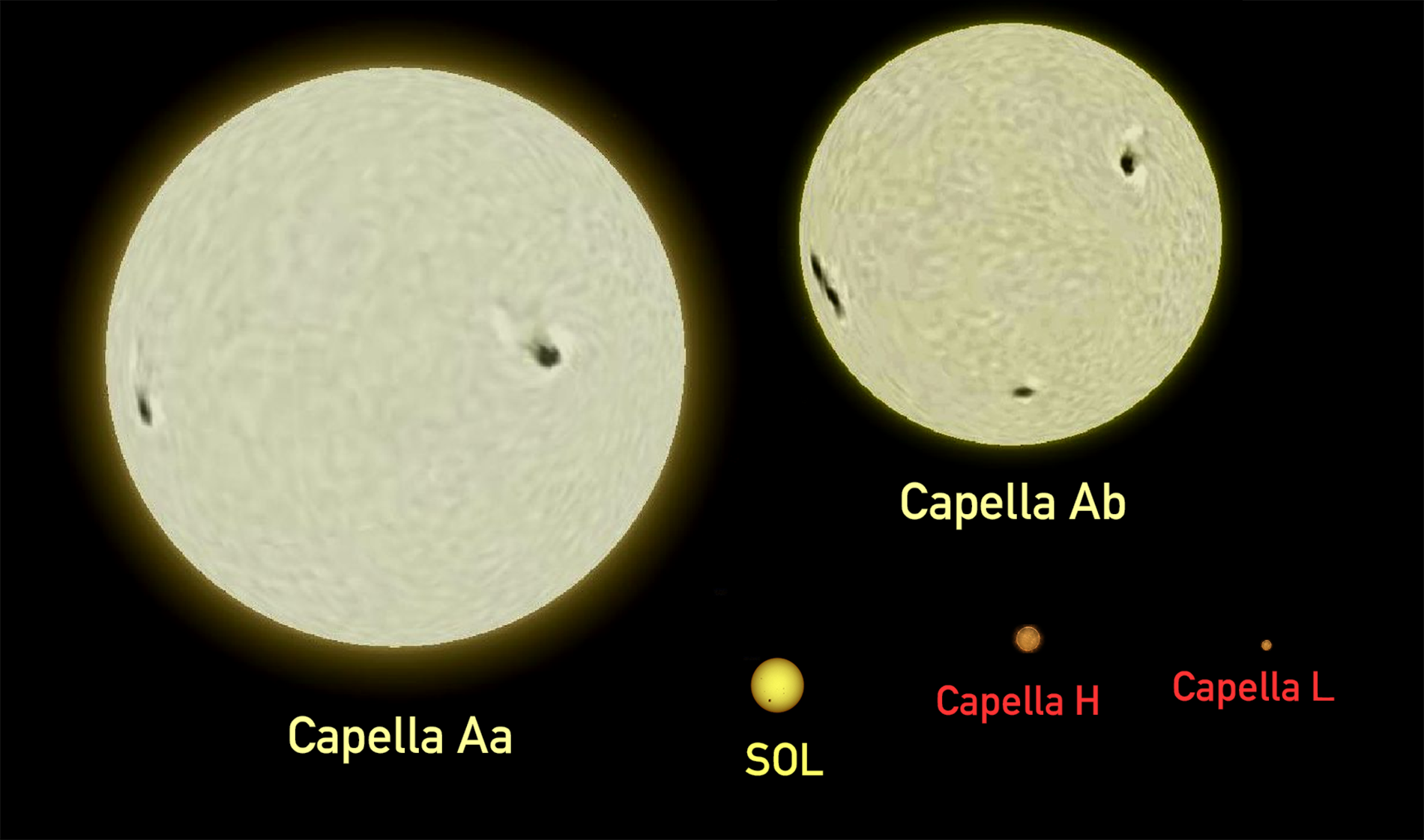
Kappa Aurigae is a star in the northern constellation of Auriga. Its name is a Bayer designation that is Latinised from κ Aurigae, and is abbreviated Kappa Aur or κ Aur. This star is visible to the naked eye with an apparent visual magnitude of 4.3. Based upon an annual parallax shift of , it is approximately distant from Earth. This is a high proper motion star, traversing the celestial sphere at an angular rate of yr−1. It is drifting further away with a radial velocity of +21 km/s. This is an evolved giant star with a stellar classification of G8.5 IIIb. It is a red clump star, which means it is towards the cool end of the horizontal branch and is generating energy through the fusion of helium at its core. The star is 5.6 billion years old and is spinning with a projected rotational velocity of 2.5 km/s. With 1.25 times the mass of the Sun, Kappa Aurigae has expanded to 11 times the radius of the Sun and shines with 54 times the Sun's lum ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Auriga (constellation)
Auriga is a constellation in the northern celestial hemisphere. It is one of the List of constellations, 88 modern constellations; it was among the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy. Its name is Latin for '(the) charioteer', associating it with various mythological beings, including Erichthonius of Athens, Erichthonius and Myrtilus. Auriga is most prominent during winter evenings in the northern Hemisphere, as are five other constellations that have stars in the Winter Hexagon asterism (astronomy), asterism. Because of its northern declination, Auriga is only visible in its entirety as far south as −34°; for observers farther south it lies partially or fully below the horizon. A large constellation, with an area of 657 square degrees, it is half the size of the largest, Hydra (constellation), Hydra. Its brightest star, Capella (star), Capella, is an unusual Star system, multiple star system among the brightest stars in the night sky. Beta Aurigae ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Red Clump
The red clump is a clustering of red giants in the Hertzsprung–Russell diagram at around 5,000 K and absolute magnitude (MV) +0.5, slightly hotter than most red-giant-branch stars of the same luminosity. It is visible as a denser region of the red-giant branch or a bulge towards hotter temperatures. It is prominent in many galactic open clusters, and it is also noticeable in many intermediate-age globular clusters and in nearby field stars (e.g. the Hipparcos stars). The red clump giants are cool horizontal branch stars, stars originally similar to the Sun which have undergone a helium flash and are now fusing helium in their cores. Properties Red clump stellar properties vary depending on their origin, most notably on the metallicity of the stars, but typically they have early K spectral types and effective temperatures around 5,000 K. The absolute visual magnitude of red clump giants near the sun has been measured at an average of +0.81 with metallicities between &min ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2MASS Objects
Mass is an intrinsic property of a body. It was traditionally believed to be related to the quantity of matter in a body, until the discovery of the atom and particle physics. It was found that different atoms and different elementary particles, theoretically with the same amount of matter, have nonetheless different masses. Mass in modern physics has multiple definitions which are conceptually distinct, but physically equivalent. Mass can be experimentally defined as a measure of the body's inertia, meaning the resistance to acceleration (change of velocity) when a net force is applied. The object's mass also determines the strength of its gravitational attraction to other bodies. The SI base unit of mass is the kilogram (kg). In physics, mass is not the same as weight, even though mass is often determined by measuring the object's weight using a spring scale, rather than balance scale comparing it directly with known masses. An object on the Moon would weigh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Auriga
Auriga is a constellation in the northern celestial hemisphere. It is one of the 88 modern constellations; it was among the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy. Its name is Latin for '(the) charioteer', associating it with various mythological beings, including Erichthonius and Myrtilus. Auriga is most prominent during winter evenings in the northern Hemisphere, as are five other constellations that have stars in the Winter Hexagon asterism. Because of its northern declination, Auriga is only visible in its entirety as far south as −34°; for observers farther south it lies partially or fully below the horizon. A large constellation, with an area of 657 square degrees, it is half the size of the largest, Hydra. Its brightest star, Capella, is an unusual multiple star system among the brightest stars in the night sky. Beta Aurigae is an interesting variable star in the constellation; Epsilon Aurigae, a nearby eclipsing binary with an unusually lon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Horizontal-branch Stars
The horizontal branch (HB) is a stage of stellar evolution that immediately follows the red-giant branch in stars whose masses are similar to the Sun's. Horizontal-branch stars are powered by helium fusion in the core (via the triple-alpha process) and by hydrogen fusion (via the CNO cycle) in a shell surrounding the core. The onset of core helium fusion at the tip of the red-giant branch causes substantial changes in stellar structure, resulting in an overall reduction in luminosity, some contraction of the stellar envelope, and the surface reaching higher temperatures. Discovery Horizontal branch stars were discovered with the first deep photographic photometric studies of globular clusters and were notable for being absent from all open clusters that had been studied up to that time. The horizontal branch is so named because in low-metallicity star collections like globular clusters, HB stars lie along a roughly horizontal line in a Hertzsprung–Russell diagram. Because the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
G-type Giants
G-Type G-Type is a fictional character from Marvel Comics. G-Type is one of the Shi'ar's Imperial Guard, and is also an alien. He was engineered in the stellar nurseries of Hodinn and was composed of a living solar plasma, with a constant surface temperature of 6000 kelvins (about 10,000 degrees Fahrenheit or 5,700 degrees Celsius). Because of this G-Type wears specially-constructed armor which assists him in retaining a humanoid form and contains the heat that he generates. G-Type is also a telepath, although the nature and extent of his telepathy are unknown. Similar to the other Imperial Guard members, he is based on DC Comics' Legion of Super-Heroes, sharing traits with Wildfire and Saturn Girl. His mind, like the minds of many other Shi'ar soldiers, was overtaken by the telepath Cassandra Nova. He was defeated by Cyclops and Xorn, whom he was planning to fire into the Earth's atmosphere. Gaea Gaea is a fictional character appearing in American comic books published ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Commonwealth Scientific And Industrial Research Organisation
The Commonwealth Scientific and Industrial Research Organisation (CSIRO) is an Australian Government agency that is responsible for scientific research and its commercial and industrial applications. CSIRO works with leading organisations around the world. From its headquarters in Canberra, CSIRO maintains more than 50 sites across Australia as well as in France and the United States, employing over 6,500 people. Federally funded scientific research in Australia began in 1916 with the creation of the Advisory Council of Science and Industry. However, the council struggled due to insufficient funding. In 1926, research efforts were revitalised with the establishment of the Council for Scientific and Industrial Research (CSIR), which strengthened national science leadership and increased research funding. CSIR grew rapidly, achieving significant early successes. In 1949, legislative changes led to the renaming of the organisation as Commonwealth Scientific and Industrial Research ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monthly Notices Of The Royal Astronomical Society
''Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society'' (MNRAS) is a peer-reviewed scientific journal in astronomy, astrophysics and related fields. It publishes original research in two formats: papers (of any length) and letters (limited to five pages). MNRAS publishes more articles per year than any other astronomy journal. The learned society journal has been in continuous existence since 1827 and became online only in 2020. It operates as a partnership between the Royal Astronomical Society (RAS), who select and peer-review the contents, and Oxford University Press (OUP), who publish and market the journal. Despite its name, MNRAS is no longer monthly, nor does it carry the notices of the RAS. In 2024 MNRAS became a purely gold open access journal. History The first issue of MNRAS was published on 9 February 1827 as ''Monthly Notices of the Astronomical Society of London'' and it has been in continuous publication ever since. It took its current name from the second vo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
G-type Star
In astronomy, stellar classification is the classification of stars based on their spectral characteristics. Electromagnetic radiation from the star is analyzed by splitting it with a prism or diffraction grating into a spectrum exhibiting the rainbow of colors interspersed with spectral lines. Each line indicates a particular chemical element or molecule, with the line strength indicating the abundance of that element. The strengths of the different spectral lines vary mainly due to the temperature of the photosphere, although in some cases there are true abundance differences. The ''spectral class'' of a star is a short code primarily summarizing the ionization state, giving an objective measure of the photosphere's temperature. Most stars are currently classified under the Morgan–Keenan (MK) system using the letters ''O'', ''B'', ''A'', ''F'', ''G'', ''K'', and ''M'', a sequence from the hottest (''O'' type) to the coolest (''M'' type). Each letter class is then subdivi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Effective Temperature
The effective temperature of a body such as a star or planet is the temperature of a black body that would emit the same total amount of electromagnetic radiation. Effective temperature is often used as an estimate of a body's surface temperature when the body's emissivity curve (as a function of wavelength) is not known. When the star's or planet's net emissivity in the relevant wavelength band is less than unity (less than that of a black body), the actual temperature of the body will be higher than the effective temperature. The net emissivity may be low due to surface or atmospheric properties, such as the greenhouse effect. Star The effective temperature of a star is the temperature of a black body with the same luminosity per ''surface area'' () as the star and is defined according to the Stefan–Boltzmann law . Notice that the total ( bolometric) luminosity of a star is then , where is the stellar radius. The definition of the stellar radius is obviously not ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Photosphere
The photosphere is a star's outer shell from which light is radiated. It extends into a star's surface until the plasma becomes opaque, equivalent to an optical depth of approximately , or equivalently, a depth from which 50% of light will escape without being scattered. A photosphere is the region of a luminous object, usually a star, that is transparent to photons of certain wavelengths. Stars, except neutron stars, have no solid or liquid surface. Therefore, the photosphere is typically used to describe the Sun's or another star's visual surface. Etymology The term ''photosphere'' is derived from Ancient Greek roots, φῶς, φωτός/''phos'', ''photos'' meaning "light" and σφαῖρα/''sphaira'' meaning "sphere", in reference to it being a spherical surface that is perceived to emit light. Temperature The surface of a star is defined to have a temperature given by the effective temperature in the Stefan–Boltzmann law. Various stars have photospheres of vari ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sun's Luminosity
The solar luminosity () is a unit of radiant flux ( power emitted in the form of photons) conventionally used by astronomers to measure the luminosity of stars, galaxies and other celestial objects in terms of the output of the Sun. One nominal solar luminosity is defined by the International Astronomical Union to be . This corresponds almost exactly to a bolometric absolute magnitude of +4.74. The Sun is a weakly variable star, and its actual luminosity therefore fluctuates. The major fluctuation is the eleven-year solar cycle (sunspot cycle) that causes a quasi-periodic variation of about ±0.1%. Other variations over the last 200–300 years are thought to be much smaller than this. Determination Solar luminosity is related to solar irradiance (the solar constant). Slow changes in the axial tilt of the planet and the shape of its orbit cause cyclical changes to the solar irradiance. The result is orbital forcing that causes the Milankovitch cycles, which determine Eart ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |