|
Kallar (caste)
Kallar (or Kallan, formerly spelled as Colleries) is one of the three related castes of South India, southern India which constitute the Mukkulathor confederacy. The Kallar, along with the Maravar and Agamudayar, constitute a united social caste on the basis of parallel professions, though their locations and heritages are wholly separate from one another. Etymology ''Kallar'' is a Tamil word meaning ''thief''. Their history has included periods of banditry. Kallars themselves use titles such as "landlord", Other proposed etymological origins include "black skinned", "hero", and "Palm wine, toddy-tappers". The anthropologist Susan Bayly notes that the name Kallar, as with that of Maravar, was a title bestowed by Tamil Polygar, ''palaiyakkarars'' (warrior-chiefs) on pastoral peasants who acted as their armed retainers. The majority of those poligars, who during the late 17th and 18th centuries controlled much of the Telugu people, Telugu region as well as the Tamil area, had t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tamil Nadu
Tamil Nadu (; , TN) is the southernmost States and union territories of India, state of India. The List of states and union territories of India by area, tenth largest Indian state by area and the List of states and union territories of India by population, sixth largest by population, Tamil Nadu is the home of the Tamil people, who speak the Tamil language—the state's official language and one of the longest surviving Classical languages of India, classical languages of the world. The capital and largest city is Chennai. Located on the south-eastern coast of the Indian peninsula, Tamil Nadu is straddled by the Western Ghats and Deccan Plateau in the west, the Eastern Ghats in the north, the Eastern Coastal Plains lining the Bay of Bengal in the east, the Gulf of Mannar and the Palk Strait to the south-east, the Laccadive Sea at the southern Cape (geography), cape of the peninsula, with the river Kaveri bisecting the state. Politically, Tamil Nadu is bound by the Indian sta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Presidency Armies
The presidency armies were the armies of the three Presidencies of British India, presidencies of the East India Company's Company rule in India, rule in India, later the forces of the the Crown, British Crown in British Raj, India, composed primarily of Indian sepoys. The presidency armies were named after the presidencies: the Bengal Army, the Madras Army and the Bombay Army. Initially, only Europeans served as commissioned or non-commissioned officers. In time, Indian Army units were garrisoned from Peshawar in the north, to Sind in the west, and to Rangoon in the east. The army was engaged in the wars to extend British control in India (the Anglo-Mysore Wars, Mysore, Anglo-Maratha Wars (other), Maratha and Second Anglo-Sikh War, Sikh wars) and beyond (the Anglo-Burmese wars, Burma, Anglo-Afghan War, Afghan, First Opium War, First and Second Opium Wars, and the Expedition to Abyssinia). The presidency armies, like the presidencies themselves, belonged to the Company ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kalaripayattu
Kalaripayattu (), also known simply as Kalari, is an Indian martial art that originated on the southwestern coast of India, in what is now Kerala, during the 3rd century BCE. Etymology Kalaripayattu is a martial art which developed out of combat techniques of the 11th–12th century battlefield, with weapons and combative techniques that are unique to Kerala. The word is a combination of two Malayalam words – (training ground or battleground) and (training of martial arts), which is roughly translated as "practice in the arts of the battlefield". may also be derived from the Malayalam or Sanskrit term , which is the name of a goddess associated with Shaktism who is worshipped in Kalaripayattu. The , a 5th century CE South Indian ancient text on Shaiva Siddhanta, discusses the construction of the , as place for military exercise. History Associations with Indian folklore and legends According to legend, Parashurama, the sixth avatar of Vishnu, learned the art from S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adimurai
Adimurai is an Indian martial art originating in modern-day Kanyakumari, the southernmost region in India. It was traditionally practiced in the Kanyakumari district of modern-day Tamil Nadu as well as nearby areas in southeastern Kerala. Its preliminary empty-hand techniques are called Adithada and application of vital points are called Varma Adi, although these terms are sometimes interchangeably used to refer to the martial art itself. Adimurai is a portmanteau in the Tamil language where ''adi'' means "to hit or strike" and ''murai'' means method or procedure. In modern period it is used alongside other Tamil martial arts. History Adithada is a non-lethal version of Adimurai which was developed in the Tamilnadu region of ancient India. It saw most of its practice in the Chola and Pandya kingdoms, where preliminary empty hand techniques were used. Practice Adimurai is traditionally practiced outdoors or in unroofed areas. It is mainly practiced by, Kallars, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Piramalai Kallar
Piramalai Kallars is a sub caste of the Kallars and thus are part of the Mukkulathor community that also includes the Maravar and Agamudayar castes. They belong to Other Backward class/Denotified class in Tamil nadu. History Copper plate inscriptions dated 1645, 1652, 1655 and 1656 are the most important artefacts about the Piramalai Kallars. According to these, during the period of Thirumalai Nayak, members of the community were appointed as guards ("kavalkarars") of villages. The Piramalai Kallar group responsible for a village had to compensate for any theft in that village. Piramalai Kallar local chieftains, such as Tirumal Pinna Thevar, also performed judicial duties by organising panchayats. This is described in the 1655 inscription. With a separate system of judiciary and policing, they refused to accede to British rule. In 1767, around 5000 Kallars were killed by British forces near Melur in a single day when they refused to pay tax. With the introduction of Br ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Louis Dumont
Louis Charles Jean Dumont (11 August 1911 – 19 November 1998) was a French anthropologist. Dumont was born in Thessaloniki, in the Salonica Vilayet of the Ottoman Empire. He taught at Oxford University during the 1950s, and was then director of the '' École des Hautes Études en Sciences Sociales'' (EHESS) in Paris. A specialist on the cultures and societies of India, Dumont also studied western social philosophy and ideologies. Works His works include '' Homo Hierarchicus: Essai sur le système des castes'' (1966), ''From Mandeville to Marx: The Genesis and Triumph of Economic Ideology'' (1977) and ''Essais sur l'individualisme: Une perspective anthropologique sur l'idéologie moderne'' (1983), in which he contrasts holism with individualism. Dumont died in 1998, aged 87, in Paris. See also *Alliance theory Alliance theory, also known as the general theory of exchanges, is a Structuralism, structuralist method of studying kinship relations. It finds its origins in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Throwing Stick
The throwing stick or throwing club is a wooden rod with either a pointed tip or a spearhead attached to one end, intended for use as a weapon. A throwing stick can be either straight or roughly boomerang-shaped, and is much shorter than the javelin. It became obsolete as Sling (weapon), slings and Bow (weapon), bows became more prevalent, except on the Australia, Australian continent, where the Indigenous Australians, native people continued refining the basic design. Throwing sticks shaped like returning boomerangs are designed to fly straight to a target at long ranges, their surfaces acting as airfoils. When tuned correctly they do not exhibit curved flight, but rather they fly on an extended straight flight path. Straight flight ranges greater than have been reported by historical sources as well as in recent research. Distribution The ancient Egyptians used throwing sticks to hunt small game and waterfowl, as seen in several wall paintings. The Eighteenth Dynasty of Egy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Valai Tādi
A valari () is a traditional weapon, primarily used by the Tamil people of the Indian subcontinent. The valari resembles, and is used similarly to a boomerang or throwing stick. It was used by the Tamil people in ancient battles, for protecting cattle from predators, and for hunting. The British called valari "collery-sticks" after the Kallar caste that used them. The valari has a long history, dating back to pre-historic times. Valaris are described in the Tamil Sangam ''Purananuru'': a historical version of the Sangam literature, the Purananuru 233rd Poem, mentions the ''thigri'' or valari. Weapons similar to this were also called Valaithadi, Tigiri, Paravallai, Cuḻalpaṭai, Kallartadi and Pataivattam. The techniques and philosophies of valari are long periods of interaction with Tamil (India) peoples, cultures, and Traditional Arts. Valari is a synthesis of the game which is played in various methods with same name. Valari received international exposure from 2018 onwar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
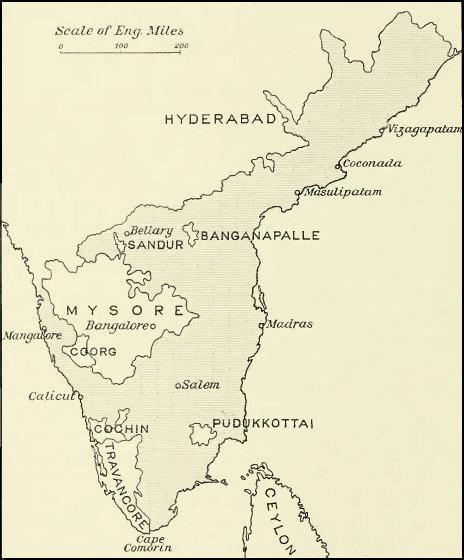
Pudukkottai State
Pudukkottai was a kingdom and later a princely state in British India, which existed from 1680 until 1948. The Thondaman dynasty, Kingdom of Pudukkottai was founded in about 1680 as a feudatory of Ramnad estate, Ramnad and grew with subsequent additions from Thanjavur Maratha kingdom, Tanjore, Sivaganga estate, Sivaganga and Ramnad. One of the staunch allies of the British East India Company in the Carnatic Wars, Carnatic, Anglo-Mysore Wars, Anglo-Mysore and Polygar War, Polygar wars, the kingdom was brought under the Company's protection in 1800 as per the system of Subsidiary Alliance. The state was placed under the control of the Madras Presidency from 1800 until 1 October 1923, when the Madras States Agency was created, and until 1948 it was under the political control of the Government of India. Pudukkottai State covered a total area of and had a population of 438,648 in 1941. It extended over the whole of the present-day Pudukkottai district of Tamil Nadu (with the excep ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thondaman Dynasty
The Thondaman or Thondaiman was a dynasty ruled the region in and around Pudukkottai from the 17th to 20th century. The Pudukkottai Thondaiman dynasty was founded by Raghunatha Thondaiman, the brother-in-law of the then Raja of Ramnad, RaghunathaKilavan Setupati. The Pudukottai Samasthanam was under Thondaiman dynasty for one year even after Indian Independence. The Thondaiman dynasty had a special Valari regiment. History In 1686, the Ramnad kingdom was ruled by Raghunatha Kilavan Setupati, the Raja of Ramnad and the Pudukottai region was ruled by a chief called Pallavarayan. The Raja of Ramnad suspected the chief's loyalty to the Ramnad kingdom and believed that the chief would shift his allegiance to the ruler of Thanjavur. So the Raja of Ramnad ousted the chief and appointed his brother-in-law Ragunatha Raya Tondaman, the brother of his queen Kathayi Nachiar, as the new ruler of Pudukottai. Thondaiman, the son of Avadai Raghunatha Tondaiman, was earlier ruling T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Agrarian Distress
Agrarian distress refers to the Economy, economic, Politics, political, and social challenges faced by farmers and Types of rural communities, rural communities due to factors such as Harvest, low crop yields, Volatility (finance), fluctuating prices of Agriculture, agricultural produce, high input costs, Debt, indebtedness, and lack of access to credit, markets, and infrastructure. The term "agrarian distress" gained prominence in India in the 1990s when a wave of Farmers' suicides in India, farmer suicides occurred in the country. The reason for the suicides were due to various causes such as inadequate credit, poor market conditions, and insufficient technology that led to indebtedness. In the 2020–2021 Indian farmers' protest, the issue of agrarian distress gained renewed attention due to the protests by farmers in India against agricultural bills that they claimed would hurt their livelihoods. The protests highlighted the long-standing issues faced by farmers in India, such ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mercenaries
A mercenary is a private individual who joins an War, armed conflict for personal profit, is otherwise an outsider to the conflict, and is not a member of any other official military. Mercenaries fight for money or other forms of payment rather than for political interests. Beginning in the 20th century, mercenaries have increasingly come to be seen as less entitled to protection by rules of war than non-mercenaries. The Geneva Conventions declare that mercenaries are not recognized as legitimate combatants and do not have to be granted the same legal protections as captured service personnel of the armed forces. In practice, whether or not a person is a mercenary may be a matter of degree, as financial and political interests may overlap. International and national laws of war Protocol I, Protocol Additional GC 1977 (APGC77) is a 1977 amendment Protocol (diplomacy), protocol to the Geneva Conventions. Article 47 of the protocol provides the most widely accepted internati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |