|
KCNE4
Potassium voltage-gated channel subfamily E member 4, originally named MinK-related peptide 3 or MiRP3 when it was discovered, is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''KCNE4'' gene. Function Voltage-gated potassium channels (Kv) represent the most complex class of voltage-gated ion channels from both functional and structural standpoints. Their diverse functions include regulating neurotransmitter release, heart rate, insulin secretion, neuronal excitability, epithelial electrolyte transport, smooth muscle contraction, and cell volume. The ''KCNE4'' gene encodes KCNE4 (originally named MinK-related peptide 3 or MiRP3), a member of the KCNE family of voltage-gated potassium (Kv) channel ancillary or β subunits. KCNE4 is best known for modulating the KCNQ1 Kv α subunit, but it also regulates KCNQ4, Kv1.x, Kv2.1, Kv4.x and BK α subunits in heterologous co-expression experiments and/or ''in vivo''. KCNE4 often, but not always, acts as an inhibitory subunit to suppress ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
KCNQ1
Kv7.1 (KvLQT1) is a potassium channel protein whose primary subunit in humans is encoded by the ''KCNQ1'' gene. Its mutation causes Long QT syndrome, Kv7.1 is a voltage and lipid-gated potassium channel present in the cell membranes of cardiac tissue and in inner ear neurons among other tissues. In the cardiac cells, Kv7.1 mediates the IKs (or slow delayed rectifying K+) current that contributes to the repolarization of the cell, terminating the cardiac action potential and thereby the heart's contraction. It is a member of the KCNQ family of potassium channels. Structure KvLQT1 is made of six membrane-spanning domains S1-S6, two intracellular domains, and a pore loop. The KvLQT1 channel is made of four KCNQ1 subunits, which form the actual ion channel. Function This gene encodes a protein for a voltage-gated potassium channel required for the repolarization phase of the cardiac action potential. The gene product can form heteromultimers with two other potassium ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Voltage-gated Potassium Channel
Voltage-gated potassium channels (VGKCs) are potassium channel, transmembrane channels specific for potassium and Voltage-gated ion channel, sensitive to voltage changes in the cell's membrane potential. During action potentials, they play a crucial role in returning the depolarized cell to a resting state. Classification Alpha subunits Alpha subunits form the actual conductance pore. Based on sequence homology of the hydrophobic transmembrane cores, the alpha subunits of voltage-gated potassium channels are grouped into 12 classes. These are labeled Kvα1-12. The following is a list of the 40 known human voltage-gated potassium channel alpha subunits grouped first according to function and then subgrouped according to the Kv sequence homology classification scheme: Delayed rectifier slowly inactivating or non-inactivating *Kvα1.x - shaker superfamily of potassium channels, Shaker-related: Kv1.1 (KCNA1), Kv1.2 (KCNA2), Kv1.3 (KCNA3), Kv1.5 (KCNA5), Kv1.6 (KCNA6), Kv1.7 (KCN ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residue (biochemistry), residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including Enzyme catalysis, catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, Cell signaling, responding to stimuli, providing Cytoskeleton, structure to cells and Fibrous protein, organisms, and Intracellular transport, transporting molecules from one location to another. Proteins differ from one another primarily in their sequence of amino acids, which is dictated by the Nucleic acid sequence, nucleotide sequence of their genes, and which usually results in protein folding into a specific Protein structure, 3D structure that determines its activity. A linear chain of amino acid residues is called a polypeptide. A protein contains at least one long polypeptide. Short polypeptides, containing less than 20–30 residues, are rarely considered to be proteins and are commonly called pep ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HEK Cell
Human embryonic kidney 293 cells, also often referred to as HEK 293, HEK-293, 293 cells, are an immortalised cell line derived from HEK cells isolated from a female fetus in the 1970s. The HEK 293 cell line has been widely used in research for decades due to its reliable and fast growth and propensity for transfection. The cell line is used by the biotechnology industry to produce therapeutic proteins and viruses for gene therapy as well as safety testing for a vast array of chemicals. History HEK 293 cells were generated in 1973 by transfection of cultures of normal human embryonic kidney cells with sheared adenovirus 5 DNA in Alex van der Eb's laboratory in Leiden, the Netherlands. The cells were obtained from a single, aborted or miscarried fetus, the precise origin of which is unclear. The cells were cultured by van der Eb; the transfection with adenoviral DNA was performed by Frank Graham, a post-doc in van der Eb's lab. They were published in 1977 after Graham left Leid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cardiac Arrhythmia
Arrhythmias, also known as cardiac arrhythmias, are irregularities in the heartbeat, including when it is too fast or too slow. Essentially, this is anything but normal sinus rhythm. A resting heart rate that is too fast – above 100 beats per minute in adults – is called tachycardia, and a resting heart rate that is too slow – below 60 beats per minute – is called bradycardia. Some types of arrhythmias have no symptoms. Symptoms, when present, may include palpitations or feeling a pause between heartbeats. In more serious cases, there may be lightheadedness, passing out, shortness of breath, chest pain, or decreased level of consciousness. While most cases of arrhythmia are not serious, some predispose a person to complications such as stroke or heart failure. Others may result in sudden death. Arrhythmias are often categorized into four groups: extra beats, supraventricular tachycardias, ventricular arrhythmias and bradyarrhythmias. Extra beats incl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
House Mouse
The house mouse (''Mus musculus'') is a small mammal of the rodent family Muridae, characteristically having a pointed snout, large rounded ears, and a long and almost hairless tail. It is one of the most abundant species of the genus '' Mus''. Although a wild animal, the house mouse has benefited significantly from associating with human habitation to the point that truly wild populations are significantly less common than the synanthropic populations near human activity. The house mouse has been domesticated as the pet or fancy mouse, and as the laboratory mouse, which is one of the most important model organisms in biology and medicine. The complete mouse reference genome was sequenced in 2002. Characteristics House mice have an adult body length (nose to base of tail) of and a tail length of . The weight is typically . In the wild they vary in color from grey and light brown to black (individual hairs are actually agouti coloured), but domesticated fancy mice and l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alpha-helical
An alpha helix (or α-helix) is a sequence of amino acids in a protein that are twisted into a coil (a helix). The alpha helix is the most common structural arrangement in the secondary structure of proteins. It is also the most extreme type of local structure, and it is the local structure that is most easily predicted from a sequence of amino acids. The alpha helix has a right-handed helix conformation in which every backbone N−H group hydrogen bonds to the backbone C=O group of the amino acid that is four residues earlier in the protein sequence. Other names The alpha helix is also commonly called a: * Pauling–Corey–Branson α-helix (from the names of three scientists who described its structure) * 3.613-helix because there are 3.6 amino acids in one ring, with 13 atoms being involved in the ring formed by the hydrogen bond (starting with amidic hydrogen and ending with carbonyl oxygen) Discovery In the early 1930s, William Astbury showed that there were dras ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Xenopus Laevis
The African clawed frog (''Xenopus laevis''), also known as simply xenopus, African clawed toad, African claw-toed frog or the ''platanna'') is a species of African aquatic frog of the family Pipidae. Its name is derived from the short black claws on its feet. The word ''Xenopus'' means 'strange foot' and ''laevis'' means 'smooth'. The species is found throughout much of Sub-Saharan Africa (Nigeria and Sudan to South Africa), and in isolated, introduced populations in North America, South America, Europe, and Asia. All species of the family Pipidae are tongueless, toothless and completely aquatic. They use their hands to shove food in their mouths and down their throats and a hyobranchial pump to draw or suck things in their mouth. Pipidae have powerful legs for swimming and lunging after food. They also use the claws on their feet to tear pieces of large food. They have no external eardrums, but instead subcutaneous cartilaginous disks that serve the same function. They use ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
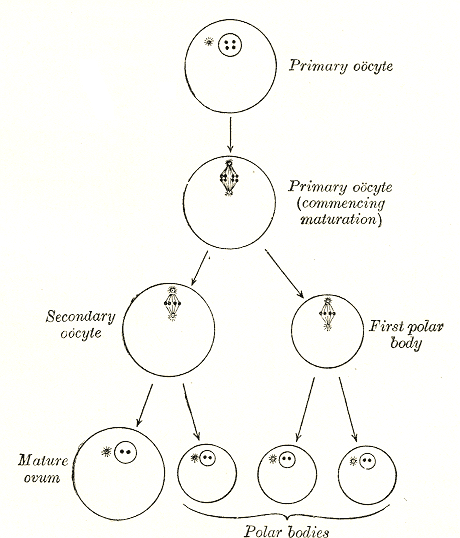
Oocyte
An oocyte (, oöcyte, or ovocyte) is a female gametocyte or germ cell involved in reproduction. In other words, it is an immature ovum, or egg cell. An oocyte is produced in a female fetus in the ovary during female gametogenesis. The female germ cells produce a primordial germ cell (PGC), which then undergoes mitosis, forming oogonia. During oogenesis, the oogonia become primary oocytes. An oocyte is a form of genetic material that can be collected for cryoconservation. Formation The formation of an oocyte is called oocytogenesis, which is a part of oogenesis. Oogenesis results in the formation of both primary oocytes during fetal period, and of secondary oocytes after it as part of ovulation. Characteristics Cytoplasm Oocytes are rich in cytoplasm, which contains yolk granules to nourish the cell early in development. Nucleus During the primary oocyte stage of oogenesis, the nucleus is called a germinal vesicle. The only normal human type of secondary oocyte has the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
KCNQ3
Kv7.3 (KvLQT3) is a potassium channel protein coded for by the gene KCNQ3. It is associated with benign familial neonatal epilepsy. The M channel is a slowly activating and deactivating potassium channel that plays a critical role in the regulation of neuronal excitability. The M channel is formed by the association of the protein encoded by this gene and one of two related proteins encoded by the KCNQ2 and KCNQ5 genes, both integral membrane proteins. M channel currents are inhibited by M1 muscarinic acetylcholine receptors and activated by retigabine, a novel anti-convulsant drug. Defects in this gene are a cause of benign familial neonatal convulsions type 2 (BFNC2), also known as epilepsy, benign neonatal type 2 (EBN2). Interactions KvLQT3 has been shown to interact with KCNQ5 Potassium voltage-gated channel subfamily KQT member 5 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''KCNQ5'' gene. This gene is a member of the KCNQ potassium channel gene family that is differen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
KCNQ5
Potassium voltage-gated channel subfamily KQT member 5 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''KCNQ5'' gene. This gene is a member of the KCNQ potassium channel gene family that is differentially expressed in subregions of the brain and in skeletal muscle. The protein encoded by this gene yields currents that activate slowly with depolarization and can form heteromeric channels with the protein encoded by the KCNQ3 gene. Currents expressed from this protein have voltage dependences and inhibitor sensitivities in common with M-currents. They are also inhibited by M1 muscarinic receptor activation. Three alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding distinct isoforms have been found for this gene, but the full-length nature of only one has been determined. Interactions KCNQ5 has been shown to interact with KvLQT3. See also * Voltage-gated potassium channel Voltage-gated potassium channels (VGKCs) are potassium channel, transmembrane channels specific for potas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gene
In biology, the word gene has two meanings. The Mendelian gene is a basic unit of heredity. The molecular gene is a sequence of nucleotides in DNA that is transcribed to produce a functional RNA. There are two types of molecular genes: protein-coding genes and non-coding genes. During gene expression (the synthesis of Gene product, RNA or protein from a gene), DNA is first transcription (biology), copied into RNA. RNA can be non-coding RNA, directly functional or be the intermediate protein biosynthesis, template for the synthesis of a protein. The transmission of genes to an organism's offspring, is the basis of the inheritance of phenotypic traits from one generation to the next. These genes make up different DNA sequences, together called a genotype, that is specific to every given individual, within the gene pool of the population (biology), population of a given species. The genotype, along with environmental and developmental factors, ultimately determines the phenotype ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |