|
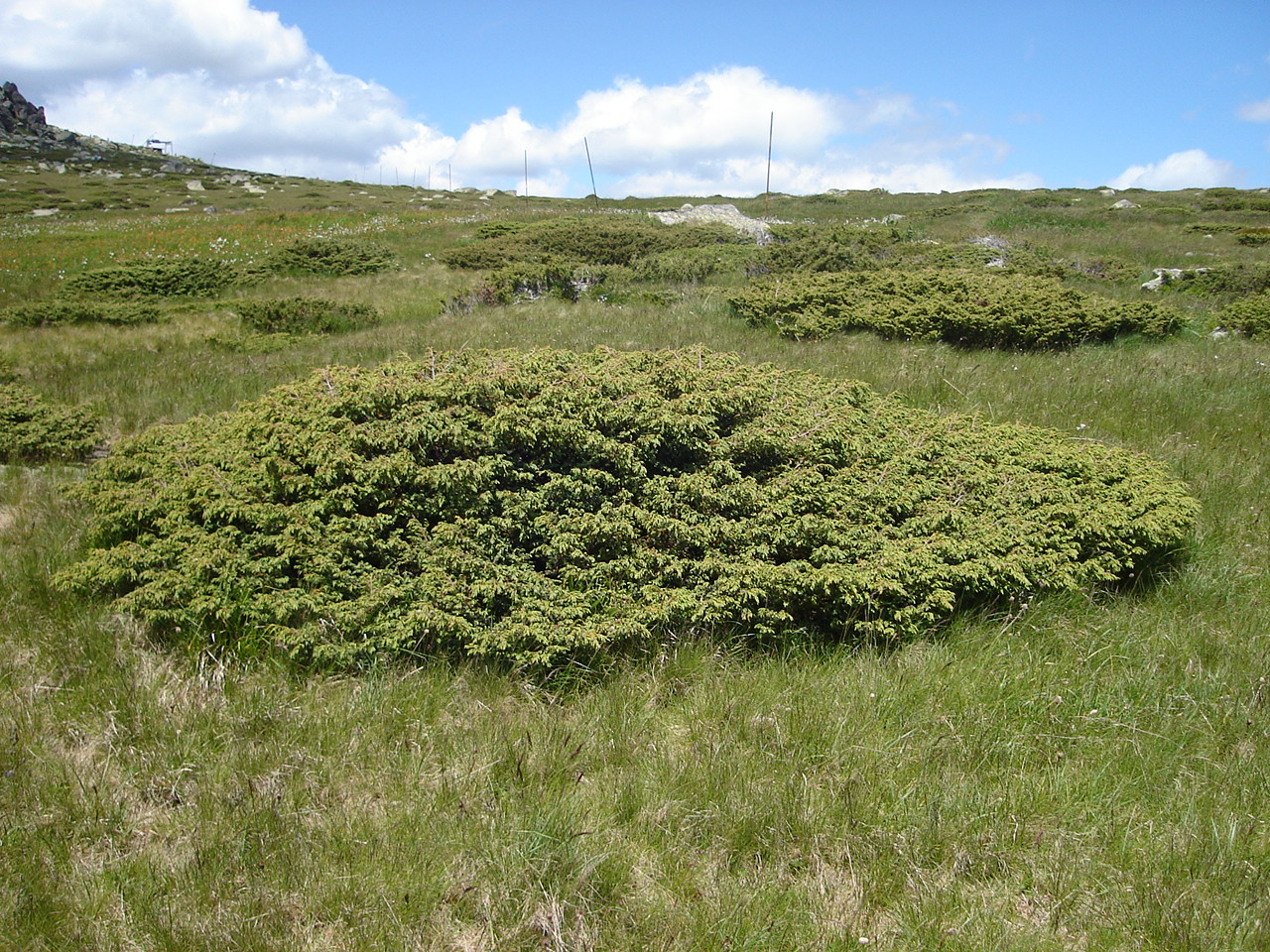
Juniperus Communis
''Juniperus communis'', the common juniper, is a species of small tree or shrub in the cypress family Cupressaceae. An evergreen conifer, it has the largest geographical range of any woody plant, with a circumpolar distribution throughout the cool temperate Northern Hemisphere. Description ''Juniperus communis'' is very variable in form, ranging from —rarely —tall to a low, often prostrate spreading shrub in exposed locations. It has needle-like leaves in whorls of three; the leaves are green, with a single white stomatal band on the inner surface. It never attains the scale-like adult foliage of other members of the genus. It is dioecious, with male and female cones (both of which are wind pollinated) on separate plants. The male cones are yellow, long, and fall soon after shedding their pollen in March–April. The fruit are berry-like cones known as juniper berries. They are initially green, ripening in 18 months to purple-black with a blue waxy coating; they are spheri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Conifer Cone
A conifer cone (in formal botanical usage: strobilus, plural strobili) is a seed-bearing organ on gymnosperm plants. It is usually woody, ovoid to globular, including scales and bracts arranged around a central axis, especially in conifers and cycads. The cone of Pinophyta (conifer clade) contains the reproductive structures. The woody cone is the female cone, which produces seeds. The male cone, which produces pollen, is usually herbaceous and much less conspicuous even at full maturity. The name "cone" derives from Greek ''konos'' (pine cone), which also gave name to the geometric cone. The individual plates of a cone are known as ''scales''. The ''umbo'' of a conifer cone refers to the first year's growth of a seed scale on the cone, showing up as a protuberance at the end of the two-year-old scale. The male cone (microstrobilus or pollen cone) is structurally similar across all conifers, differing only in small ways (mostly in scale arrangement) from species to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Juniper Berries
A juniper berry is the female seed cone produced by the various species of junipers. It is not a true berry, but a cone with unusually fleshy and merged scales, which gives it a berry-like appearance. The cones from a handful of species, especially '' Juniperus communis'', are used as a spice, particularly in European cuisine, and also give gin its distinctive flavour. Juniper berries are among the only spices derived from conifers,Chapter 8: Seeds, Fruits, and Cones Retrieved July 27, 2006. along with buds. Description '' Juniperus communis'' berries vary from in diameter; other species ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
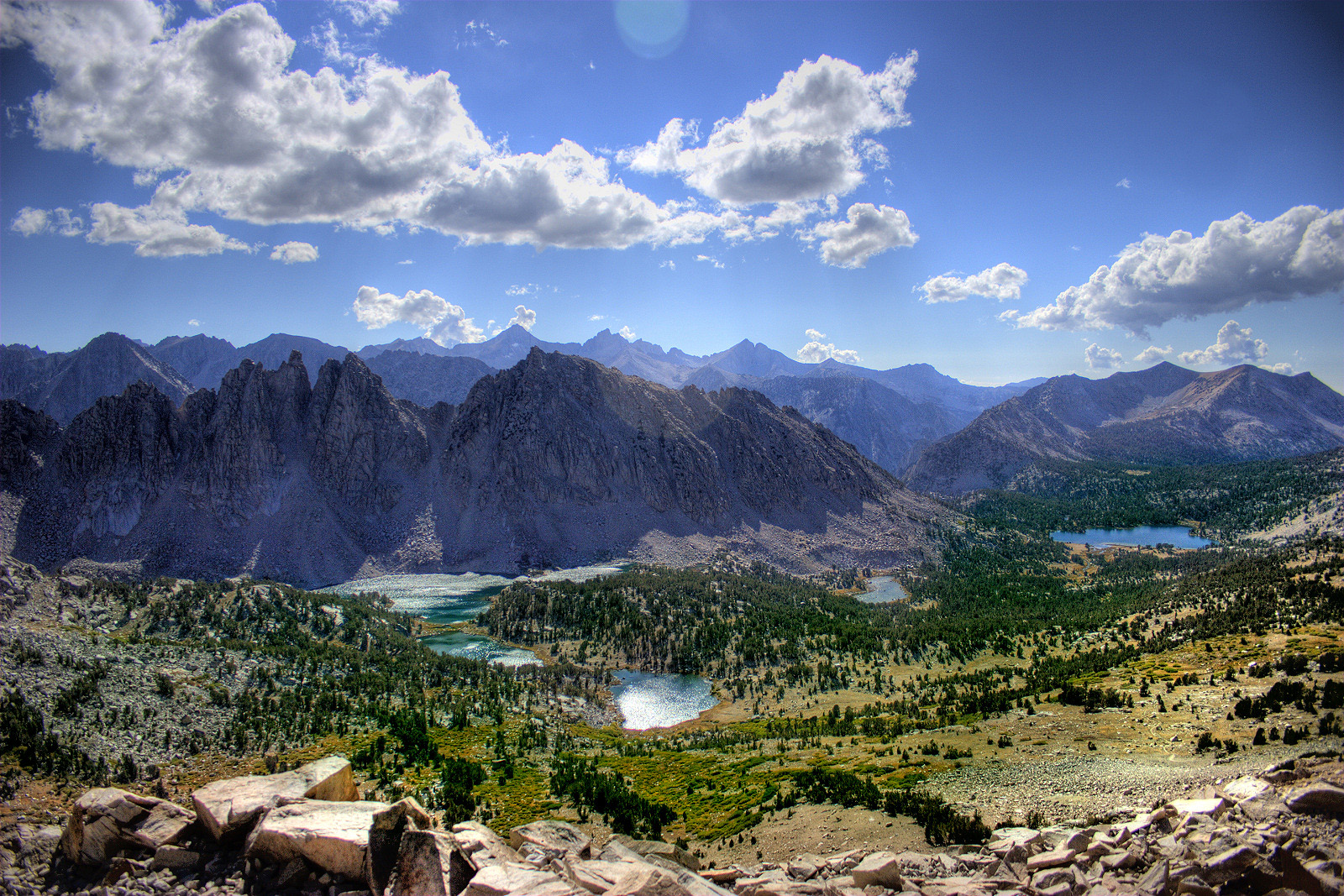
Sierra Nevada (U
The Sierra Nevada () is a mountain range in the Western United States, between the Central Valley (California), Central Valley of California and the Great Basin. The vast majority of the range lies in the state of California, although the Carson Range spur lies primarily in Nevada. The Sierra Nevada is part of the American Cordillera, an almost continuous chain of mountain ranges that forms the western "backbone" of the Americas. The Sierra runs north-south and its width ranges from to across east–west. Notable features include General Sherman (tree), General Sherman, the largest tree in the world by volume; Lake Tahoe, the largest alpine lake in North America; Mount Whitney at , the highest point in the contiguous United States; and Yosemite Valley sculpted by glaciers from one-hundred-million-year-old granite, containing List of waterfalls in Yosemite National Park, high waterfalls. The Sierra is home to three national parks, twenty wilderness areas, and two national mon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Limonene
Limonene is a colorless liquid aliphatic hydrocarbon classified as a cyclic monoterpene, and is the major component in the oil of citrus fruit peels. The -isomer, occurring more commonly in nature as the fragrance of oranges, is a flavoring agent in food manufacturing. It is also used in chemical synthesis as a precursor to carvone and as a renewables-based solvent in cleaning products. The less common -isomer has a piny, turpentine-like odor, and is found in the edible parts of such plants as caraway, dill, and bergamot orange plants. Limonene takes its name from Italian ''limone'' ("lemon"). Limonene is a chiral molecule, and biological sources produce one enantiomer: the principal industrial source, citrus fruit, contains -limonene ((+)-limonene), which is the (''R'')-enantiomer. Racemic limonene is known as dipentene. -Limonene is obtained commercially from citrus fruits through two primary methods: centrifugal separation or steam distillation. Chemical reactions ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
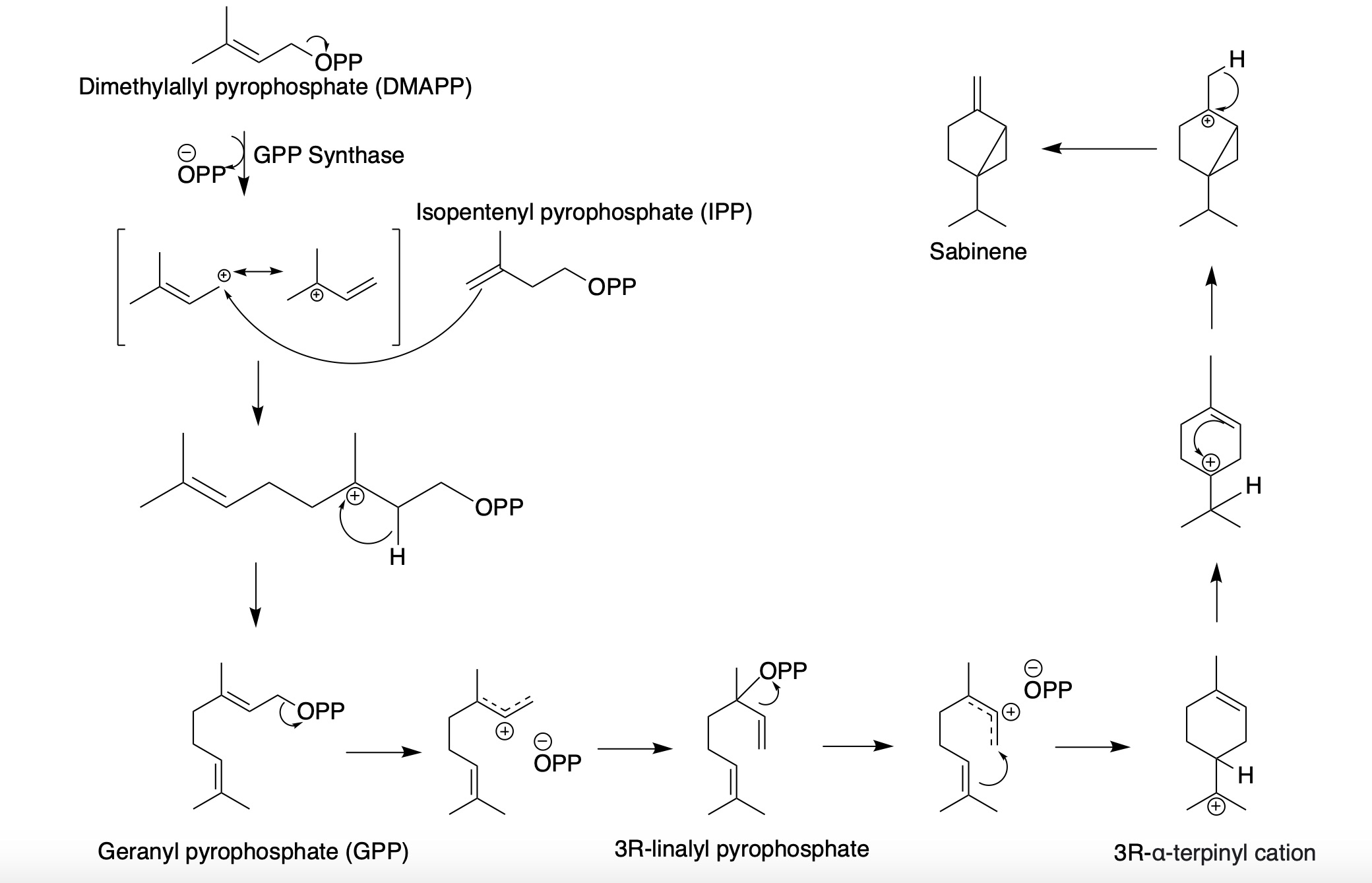
Sabinene
Sabinene is a natural bicyclic monoterpene with the molecular formula C10H16. It is isolated from the essential oils of a variety of plants including Marjoram, holm oak (''Quercus ilex'') and Norway spruce (''Picea abies''). It has a strained ring system with a cyclopentane ring fused to a cyclopropane ring. Sabinene is one of the chemical compounds that contributes to the spiciness of black pepper and is a major constituent of carrot seed oil. It also occurs in tea tree oil at a low concentration. It is also present in the essential oil obtained from nutmeg, '' Laurus nobilis'', and '' Clausena anisata''. Biosynthesis Sabinene, a bicyclic monoterpene, is present in the (+) and (-) enantiomers. It is biosynthesized from the common terpenoid precursor, geranyl pyrophosphate (GPP) that undergoes polycyclization catalyzed by sabinene synthase (SabS). GPP is formed from the terpenoid synthesis pathway with the starter units, isopentenyl pyrophosphate Isopentenyl pyrophospha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Myrcene
Myrcene, or β-myrcene, is a monoterpene. A colorless oil, it occurs widely in essential oils. It is produced mainly semi-synthetically from '' Myrcia'', from which it gets its name. It is an intermediate in the production of several fragrances. α-Myrcene is the name for the isomer 2-methyl-6-methylene-1,7-octadiene, which has not been found in nature. Production Myrcene is often produced commercially by the pyrolysis (400 °C) of β-pinene, which is obtained from turpentine. It is rarely obtained directly from plants. Plants biosynthesize myrcene via geranyl pyrophosphate (GPP), which isomerizes into linalyl pyrophosphate. The release of the pyrophosphate (OPP) and a proton completes the conversion. Occurrence It could in principle be extracted from any number of plants, such as verbena or wild thyme, the leaves of which contain up to 40% by weight of myrcene. Many other plants contain myrcene, sometimes in substantial amounts. Some of these include cannabis, hops, ' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
α-pinene
α-Pinene is an organic compound of the terpene class, one of two isomers of pinene. It is an alkene and it contains a reactive four-membered ring. It is found in the oils of many species of many coniferous trees, notably the pine. It is also found in the essential oil of rosemary (''Rosmarinus officinalis'') and '' Satureja myrtifolia'' (also known as ''Zoufa'' in some regions). Both enantiomers are known in nature; (1''S'',5''S'')- or (−)-α-pinene is more common in European pines, whereas the (1''R'',5''R'')- or (+)-α-isomer is more common in North America. The racemic mixture is present in some oils such as eucalyptus oil and orange peel oil. Reactivity : Commercially important derivatives of alpha-pinene are linalool, geraniol, nerol, a-terpineol, and camphene. α-Pinene 1 is reactive owing to the presence of the four-membered ring adjacent to the alkene. The compound is prone to skeletal rearrangements such as the Wagner–Meerwein rearrangement. Acids ty ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monoterpene
Monoterpenes are a class of terpenes that consist of two isoprene units and have the molecular formula C10H16. Monoterpenes may be linear (acyclic) or contain rings (monocyclic and bicyclic). Modified terpenes, such as those containing oxygen functionality or missing a methyl group, are called monoterpenoids. Monoterpenes and monoterpenoids are diverse. They have relevance to the pharmaceutical, cosmetic, agricultural, and food industries. Biosynthesis Monoterpenes are derived biosynthetically from units of isopentenyl pyrophosphate, which is formed from acetyl-CoA via the intermediacy of mevalonic acid in the HMG-CoA reductase pathway. An alternative, unrelated biosynthesis pathway of IPP is known in some bacterial groups and the plastids of plants, the so-called MEP-(2-methyl-D-erythritol-4-phosphate) pathway, which is initiated from C5 sugars. In both pathways, IPP is isomerized to DMAPP by the enzyme isopentenyl pyrophosphate isomerase. Geranyl pyrophosphate is the precu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lüneburg Heath
Lüneburg Heath (german: Lüneburger Heide) is a large area of heath, geest, and woodland in the northeastern part of the state of Lower Saxony in northern Germany. It forms part of the hinterland for the cities of Hamburg, Hanover and Bremen and is named after the town of Lüneburg. Most of the area is a nature reserve. Northern Low Saxon is still widely spoken in the region. Lüneburg Heath has extensive areas, and the most yellow of heathland, typical of those that covered most of the North German countryside until about 1800, but which have almost completely disappeared in other areas. The heaths were formed after the Neolithic period by overgrazing of the once widespread forests on the poor sandy soils of the geest, as this slightly hilly and sandy terrain in northern Europe is called. Lüneburg Heath is therefore a historic cultural landscape. The remaining areas of heath are kept clear mainly through grazing, especially by a North German breed of moorland sheep calle ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Estonia
Estonia, formally the Republic of Estonia, is a country by the Baltic Sea in Northern Europe. It is bordered to the north by the Gulf of Finland across from Finland, to the west by the sea across from Sweden, to the south by Latvia, and to the east by Lake Peipus and Russia. The territory of Estonia consists of the mainland, the larger islands of Saaremaa and Hiiumaa, and over 2,200 other islands and islets on the eastern coast of the Baltic Sea, covering a total area of . The capital city Tallinn and Tartu are the two largest urban areas of the country. The Estonian language is the autochthonous and the official language of Estonia; it is the first language of the majority of its population, as well as the world's second most spoken Finnic language. The land of what is now modern Estonia has been inhabited by '' Homo sapiens'' since at least 9,000 BC. The medieval indigenous population of Estonia was one of the last " pagan" civilisations in Europe to adopt Ch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |