|
Joseph Antoine Ferdinand Plateau
Joseph Antoine Ferdinand Plateau (14 October 1801 – 15 September 1883) was a Belgian physicist and mathematician. He was one of the first people to demonstrate the illusion of a moving image. To do this, he used counterrotating disks with repeating drawn images in small increments of motion on one and regularly spaced slits in the other. He called this device of 1832 the phenakistiscope. Biography Plateau was born in Brussels. His father, Antoine Plateau ( fr) born in Tournai, was a talented flower painter. At the age of six, the younger Plateau already could read, making him a child prodigy in those times. While attending primary school, he was particularly impressed by a lesson of physics; enchanted by the experiments he observed, he vowed to discover their secrets someday. Plateau spent his school holidays in Marche-les-Dames, with his uncle and his family; his cousin and playfellow was Auguste Payen, who later became an architect and the principal designer of the Belgian ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brussels
Brussels (french: Bruxelles or ; nl, Brussel ), officially the Brussels-Capital Region (All text and all but one graphic show the English name as Brussels-Capital Region.) (french: link=no, Région de Bruxelles-Capitale; nl, link=no, Brussels Hoofdstedelijk Gewest), is a region of Belgium comprising 19 municipalities, including the City of Brussels, which is the capital of Belgium. The Brussels-Capital Region is located in the central portion of the country and is a part of both the French Community of Belgium and the Flemish Community, but is separate from the Flemish Region (within which it forms an enclave) and the Walloon Region. Brussels is the most densely populated region in Belgium, and although it has the highest GDP per capita, it has the lowest available income per household. The Brussels Region covers , a relatively small area compared to the two other regions, and has a population of over 1.2 million. The five times larger metropolitan area of Bruss ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marche-les-Dames
Marche-les-Dames (; wa, Måtche-les-Dames) is a village of Wallonia and a district of the city of Namur, located in the province of Namur, Belgium. It is located on the bank of the Meuse river. Because of the high cliffs this place is popular with rock climbers. History King Albert I died here in a 1934 mountaineering accident. The King fell from a rock face and his dead body was found later. At this site a memorial was erected to honour the king. Movies shot at Marche-les-Dames * 2009 : Sister Smile (film) de Stijn Coninx * 2012 : La Marque Des Anges de Sylvain White * 2015: Public Enemy (TV series) de Matthieu Frances Matthieu is a given name or surname. It comes from French Matthieu, which is from Latin Matthaeus, derived from Greek Ματθαῖος (''Matthaios'') from Hebrew מתתיהו (''Matatyahu''), מתיתיהו (''Matityahu''), meaning "gift of the ... et Gary Seghers References Former municipalities of Namur (province) {{Namur-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Surface Tension
Surface tension is the tendency of liquid surfaces at rest to shrink into the minimum surface area possible. Surface tension is what allows objects with a higher density than water such as razor blades and insects (e.g. water striders) to float on a water surface without becoming even partly submerged. At liquid–air interfaces, surface tension results from the greater attraction of liquid molecules to each other (due to cohesion) than to the molecules in the air (due to adhesion). There are two primary mechanisms in play. One is an inward force on the surface molecules causing the liquid to contract. Second is a tangential force parallel to the surface of the liquid. This ''tangential'' force is generally referred to as the surface tension. The net effect is the liquid behaves as if its surface were covered with a stretched elastic membrane. But this analogy must not be taken too far as the tension in an elastic membrane is dependent on the amount of deformation of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Capillary Action
Capillary action (sometimes called capillarity, capillary motion, capillary rise, capillary effect, or wicking) is the process of a liquid flowing in a narrow space without the assistance of, or even in opposition to, any external forces like gravity. The effect can be seen in the drawing up of liquids between the hairs of a paint-brush, in a thin tube, in porous materials such as paper and plaster, in some non-porous materials such as sand and liquefied carbon fiber, or in a biological cell. It occurs because of intermolecular forces between the liquid and surrounding solid surfaces. If the diameter of the tube is sufficiently small, then the combination of surface tension (which is caused by cohesion within the liquid) and adhesive forces between the liquid and container wall act to propel the liquid. Etymology Capillary comes from the Latin word capillaris, meaning "of or resembling hair." The meaning stems from the tiny, hairlike diameter of a capillary. While capil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Film
A film also called a movie, motion picture, moving picture, picture, photoplay or (slang) flick is a work of visual art that simulates experiences and otherwise communicates ideas, stories, perceptions, feelings, beauty, or atmosphere through the use of moving images. These images are generally accompanied by sound and, more rarely, other sensory stimulations. The word "cinema", short for cinematography, is often used to refer to filmmaking and the film industry, and to the art form that is the result of it. Recording and transmission of film The moving images of a film are created by photography, photographing actual scenes with a movie camera, motion-picture camera, by photographing drawings or miniature models using traditional animation techniques, by means of computer-generated imagery, CGI and computer animation, or by a combination of some or all of these techniques, and other visual effects. Before the introduction of digital production, series of still imag ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stroboscope
A stroboscope, also known as a strobe, is an instrument used to make a cyclically moving object appear to be slow-moving, or stationary. It consists of either a rotating disk with slots or holes or a lamp such as a flashtube which produces brief repetitive flashes of light. Usually, the rate of the stroboscope is adjustable to different frequencies. When a rotating or vibrating object is observed with the stroboscope at its vibration frequency (or a submultiple of it), it appears stationary. Thus stroboscopes are also used to measure frequency. The principle is used for the study of rotating, reciprocating, oscillating or vibrating objects. Machine parts and vibrating string are common examples. A stroboscope used to set the ignition timing of internal combustion engines is called a timing light. Mechanical In its simplest mechanical form, a stroboscope can be a rotating cylinder (or bowl with a raised edge) with evenly spaced holes or slots placed in the line of si ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anorthoscope
An anorthoscope is a device that demonstrates an optical illusion that turns an anamorphic picture on a disc into a normal image through fast rotation behind a counter-rotating disk with four radial slits. It was invented in 1829 by Joseph Plateau, before further studies into similar principles led to his invention of animation through the phénakisticope in 1832. Anorthoscopes with a black background have a translucent picture and need a luminous slit revolving behind the image disc. To make them translucent, the discs were impregnated with oil on the back and varnished on both sides. History As a university student, Plateau noticed in some early experiments that when looking from a small distance at two concentric cogwheels, which turned fast in opposite directions, an optical illusion of a motionless wheel appeared. He later read Peter Mark Roget's 1824 article ''Explanation of an optical deception in the appearance of the spokes of a wheel when seen through vertical apertures ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Locus (mathematics)
In geometry, a locus (plural: ''loci'') (Latin word for "place", "location") is a set of all points (commonly, a line, a line segment, a curve or a surface), whose location satisfies or is determined by one or more specified conditions.. In other words, the set of the points that satisfy some property is often called the ''locus of a point'' satisfying this property. The use of the singular in this formulation is a witness that, until the end of the 19th century, mathematicians did not consider infinite sets. Instead of viewing lines and curves as sets of points, they viewed them as places where a point may be ''located'' or may move. History and philosophy Until the beginning of the 20th century, a geometrical shape (for example a curve) was not considered as an infinite set of points; rather, it was considered as an entity on which a point may be located or on which it moves. Thus a circle in the Euclidean plane was defined as the ''locus'' of a point that is at a given d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phenakistiscope Snakes 16 Sections - Animated
The phenakistiscope (also known by the spellings phénakisticope or phenakistoscope) was the first widespread animation device that created a fluent illusion of motion. Dubbed and ('stroboscopic discs') by its inventors, it has been known under many other names until the French product name became common (with alternative spellings). The phenakistiscope is regarded as one of the first forms of moving media entertainment that paved the way for the future motion picture and film industry. Like a GIF animation, it can only show a short continuous loop. Etymology and spelling When it was introduced in the French newspaper ''Le Figaro'' in June 1833, the term 'phénakisticope' was explained to be from the root Greek word ''phenakistikos'' (or rather from φενακίζειν ''phenakizein''), meaning "deceiving" or "cheating", and ὄψ ''óps'', meaning "eye" or "face", so it was probably intended loosely as 'optical deception' or 'optical illusion'. The term phénakisticope ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atheneum (school)
Atheneum, named after the ancient school founded by Roman Emperor Hadrian, is the name used for one of the Dutch educational courses aimed at preparation for scientific education at university with a strong emphasis on academic learning. The VWO (voorbereidend wetenschappelijk onderwijs) which translates to 'preparatory scientific education', consists of two substreams, the gymnasium and atheneum. The latter does not require finals in Greek or Latin Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic languages, Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area (then known as Latium) around present-day Rome, but through ... language and culture, unlike the former. Atheneum is a six-year course. Successful completion allows the candidate to enroll in a bachelor program at a Dutch university. The first three years of Atheneum are the same for every student. During the six years the mandatory subjects are: ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Royal Netherlands Academy Of Arts And Sciences
The Royal Netherlands Academy of Arts and Sciences ( nl, Koninklijke Nederlandse Akademie van Wetenschappen, abbreviated: KNAW) is an organization dedicated to the advancement of science and literature in the Netherlands. The academy is housed in the Trippenhuis in Amsterdam. In addition to various advisory and administrative functions it operates a number of research institutes and awards many prizes, including the Lorentz Medal in theoretical physics, the Dr Hendrik Muller Prize for Behavioural and Social Science and the Heineken Prizes. Main functions The academy advises the Dutch government on scientific matters. While its advice often pertains to genuine scientific concerns, it also counsels the government on such topics as policy on careers for researchers or the Netherlands' contribution to major international projects. The academy offers solicited and unsolicited advice to parliament, ministries, universities and research institutes, funding agencies and internatio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
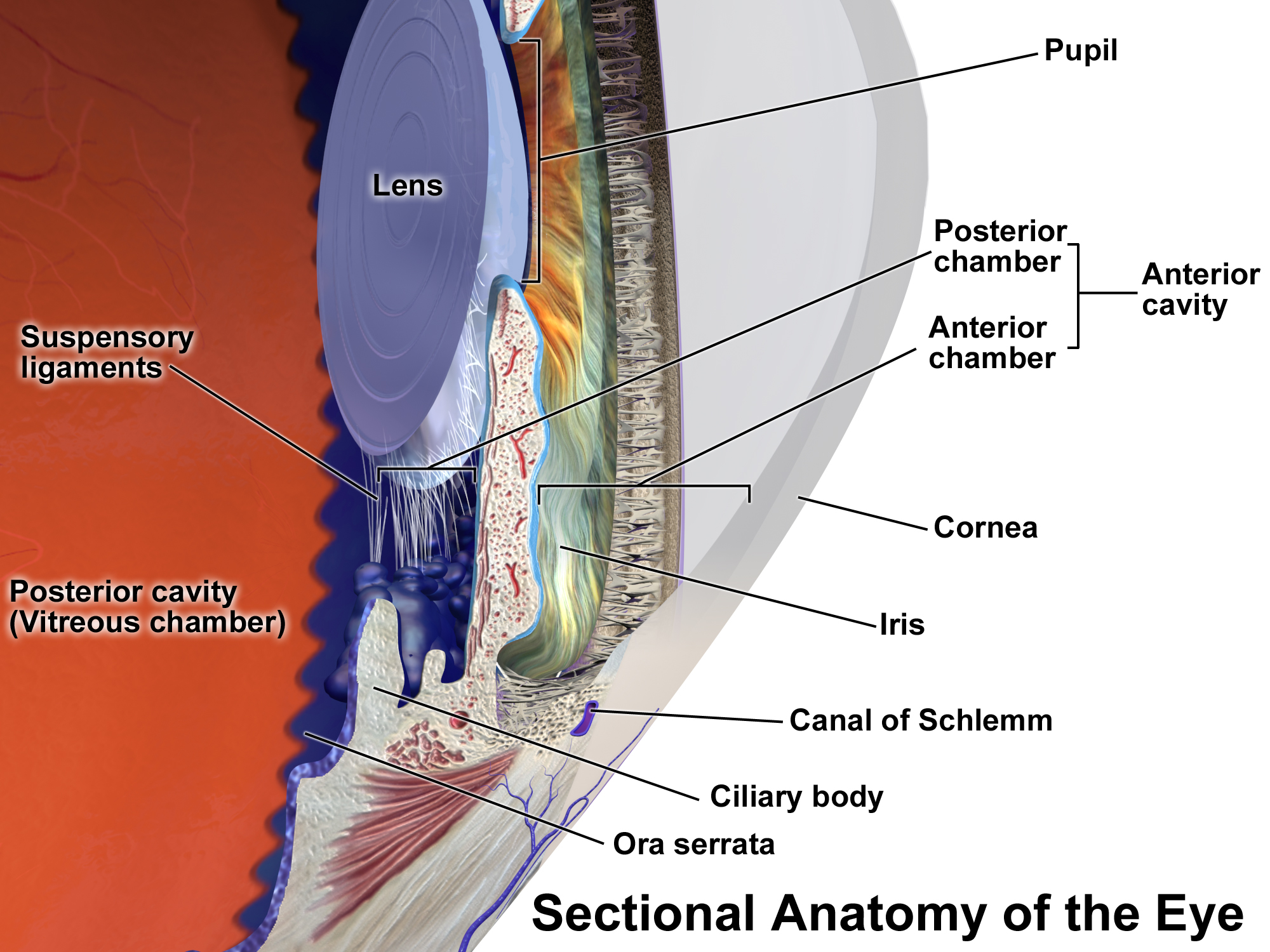
Uveitis
Uveitis () is inflammation of the uvea, the pigmented layer of the eye between the inner retina and the outer fibrous layer composed of the sclera and cornea. The uvea consists of the middle layer of pigmented vascular structures of the eye and includes the Iris (anatomy), iris, ciliary body, and choroid. Uveitis is described anatomically, by the part of the eye affected, as anterior, intermediate uveitis, intermediate or posterior, or panuveitic if all parts are involved. Anterior uveitis (iridocyclytis) is the most common, with the incidence of uveitis overall affecting approximately 1:4500, most commonly those between the ages of 20-60. Symptoms include eye pain, eye redness, floaters and blurred vision, and ophthalmic examination may show dilated ciliary body, ciliary blood vessels and the presence of cells in the Anterior chamber of eyeball, anterior chamber. Uveitis may arise spontaneously, have a genetic component, or be associated with an autoimmune disease or infection. Wh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |