|
Ji Kangzi
Ji or JI may refer to: Names and titles * Ji (surname), the pinyin romanization of a number of distinct Chinese surnames * Ji (Korean name), a Korean surname and element in given names (including lists of people with the name) * -ji, an honorific used as a suffix in many languages of India * J.I the Prince of N.Y, American rapper also known as J.I. * Ji (or Hou Ji), legendary founder of Zhou dynasty Places in China * Jì (冀), pinyin abbreviation for the province of Hebei * Jí (吉), pinyin abbreviation for the province of Jilin * Ji (state), an ancient Chinese state * Ji City (other), several places * Ji County (other), several places * Ji Prefecture (Shandong), a prefecture in imperial China * Ji Province, one of the Nine Provinces of ancient China * Ji River, either of two former rivers Organizations * Jamaat-e-Islami (other), several organizations * Jemaah Islamiyah (JI), a Southeast Asian militant Islamist rebel group * Jurong Institute ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ji (surname)
Ji is the pinyin romanization of a number of distinct Chinese surnames that are written with different characters in Chinese. Depending on the character, it may be spelled Jī, Jí, Jǐ, or Jì when tone diacritics are used. In Wade–Giles they are romanized as Chi. Languages using the Latin alphabet do not distinguish among the different Chinese surnames, rendering them all as Ji or Chi. Chi (池) is also a Chinese surname; it is the surname of Wuhan author Chi Li. Surnames romanized as Ji Ancient clan names * Jī 姬 (first tone), Gei or Kei in Cantonese, the royal surname of the Zhou dynasty, the 207th most common surname in modern China * Jí 姞 (second tone), Gat or Kat in Cantonese, the royal surname of the states of Southern Yan (南燕), Mixu (密须), and Bi (偪) * Jǐ 己 (third tone), Gei or Kei in Cantonese, the royal surname of the states of Ju, Tan (郯), and Wen (温) Other surnames * Jǐ (or Jì) 紀/纪 (third tone (or fourth tone)), Gei or Kei in Cantonese, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ji (film)
''Ji'' () is a 2005 Indian Tamil-language political action film written and directed by N. Lingusamy and produced by S.S. Chakravarthy. The film stars Ajith Kumar and Trisha, while the score and soundtrack are composed by Vidyasagar. ''Ji'' was released on 11 February 2005 following a series of delays. It received mixed reviews from the critics. Plot Vasu is a happy-go-lucky final-year college student who is forced to contest elections in the college after being persuaded by his friends Arun and Uma Shankar. He incurs the wrath of the local MLA Varadharajan, whose son is studying in the same college and is also contesting the elections. In the course of events, Varadharajan's gang attacks Vasu and his friends. Vasu's father Seenu, a tea shop owner, advises the students to take a plunge in politics and teach bad apples like Varadharajan a lesson. Taking cue from his words, Vasu does take the plunge in politics with the backing of college students and files a nomination for th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tsurumi Line
The Tsurumi Line ( ja, 鶴見線,) is a group of 3 railway lines operated by East Japan Railway Company (JR East) in Kanagawa Prefecture, Japan. Originally built to service the port and adjacent industrial area, the lines provide passenger services (especially for local workers) along a line between Tsurumi Station in Tsurumi-ku, Yokohama and Ōgimachi Station in Kawasaki-ku, Kawasaki, and 2 short branches with a total length of track to 9.7 km. The gauge is , two sections of the line have double track and the line is electrified at 1,500 V DC. Japan Freight Railway Company (JR Freight) operates on three segments of the line, often to carry petroleum and other chemicals from the numerous refineries and factories in the area. The line is also used to carry jet fuel from the US Navy fuel depot near Anzen Station through the Musashino Line to Yokota Air Base in west Tokyo. Station list * All stations are located in Kanagawa Prefecture. * All trains stop at every station ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
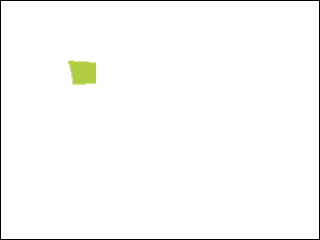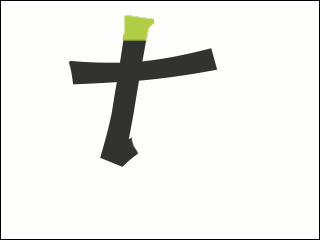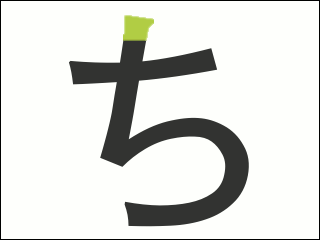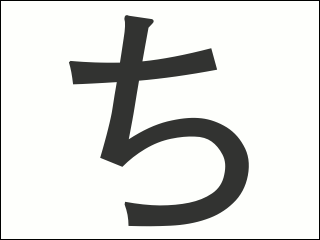
Chi (kana)
ち, in hiragana, or チ in katakana, is one of the Japanese kana, which each represent one mora. Both are phonemically , although, for phonological reasons, the actual pronunciation is . The kanji for one thousand (千, ''sen''), appears similar to チ, and at one time they were related, but today チ is used as phonetic, while the kanji carries an entirely unrelated meaning. Many onomatopoeic words beginning with ち pertain to things that are small or quick.Hiroko Fukuda, ''Jazz Up Your Japanese with Onomatopoeia: For All Levels'', trans. Tom Gally. New York: Kodansha International (2003): 19 - 20, Introduction, Words Beginning with ち Chi, Indicating Smallness or Quickness. The dakuten forms ぢ, ヂ, pronounced the same as the dakuten forms of the shi kana in most dialects (see yotsugana), are uncommon. They are primarily used for indicating a voiced consonant in the middle of a compound word (see rendaku), and they can never begin a word, although some people will writ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dakuten
The , colloquially , is a diacritic most often used in the Japanese kana syllabaries to indicate that the consonant of a syllable should be pronounced voiced, for instance, on sounds that have undergone rendaku (sequential voicing). The , colloquially , is a diacritic used with the kana for syllables starting with ''h'' to indicate that they should instead be pronounced with . History The ''kun'yomi'' pronunciation of the character is ''nigori''; hence the ''daku-ten'' may also be called the ''nigori-ten''. This character, meaning ''muddy'' or ''turbid'', stems from historical Chinese phonology, where consonants were traditionally classified as ''clear'' ( "voiceless"), ''lesser-clear'' ( " aspirated") and ''muddy'' ( "voiced"). (See: Middle Chinese § Initials) ''Dakuten'' were used sporadically since the start of written Japanese; their use tended to become more common as time went on. The modern practice of using dakuten in all cases of voicing in all writing only ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shi (kana)
し, in hiragana, or シ in katakana, is one of the Japanese kana, which each represent one mora. Both represent the phonemes although for phonological reasons, the actual pronunciation is . The shapes of these kana have origins in the character 之. The katakana form has become increasingly popular as an emoticon in the Western world due to its resemblance to a smiling face. This character may be combined with a dakuten, forming じ in hiragana, ジ in katakana, and ''ji'' in Hepburn romanization; the pronunciation becomes (phonetically or in the middle of words). The dakuten form of this character is used when transliterating "di" occasionally, as opposed to チ's dakuten form, or a de assigned to a small i; for example, ''Aladdin'' is written as アラジン ''Arajin'', and radio is written as ラジオ. In the Ainu language Ainu (, ), or more precisely Hokkaido Ainu, is a language spoken by a few elderly members of the Ainu people on the northern Japanese is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yotsugana
are a set of four specific kana, じ, ぢ, ず, づ (in the Nihon-shiki romanization system: ''zi'', ''di'', ''zu'', ''du''), used in the Japanese writing system. They historically represented four distinct voiced morae (syllables) in the Japanese language. However, most dialects, such as Standard Japanese-speakers, have undergone mergers and now pronounce two sounds. Modern sound usage in various dialects Most of the far northern dialects (Tōhoku dialects and Hokkaidō) and far southern dialects (notably Okinawan Japanese) and the Ryukyuan languages (the other Japonic languages) have also mostly merged the four sounds to one sound. However, a few dialects, mainly around Shikoku and Kyushu in the southwest, still distinguish three or even all four sounds. In the current Tokyo dialect, the base of the modern standard language, as well as in the widely spoken Kansai dialect, only two sounds are distinguished, as is represented in the Hepburn (''ji'', ''ji'', ''zu'', ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Joint Implementation
Joint Implementation (JI) is one of three flexibility mechanisms set out in the Kyoto Protocol to help countries with binding greenhouse gas emissions targets (the Annex I countries) meet their treaty obligations. Under Article 6, any Annex I country can invest in a project to reduce greenhouse gas emissions in any other Annex I country (referred to as a "Joint Implementation Project") as an alternative to reducing emissions domestically. In this way countries can lower the costs of complying with their Kyoto targets by investing in projects where reducing emissions may be cheaper and applying the resulting Emission Reduction Units (ERUs) towards their commitment goal. A JI project might involve, for example, replacing a coal-fired power plant with a more efficient combined heat and power plant. Most JI projects are expected to take place in the economies in transition (the EIT Parties) noted in Annex B of the Kyoto Protocol. Currently Russia and Ukraine are slated to host the gr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
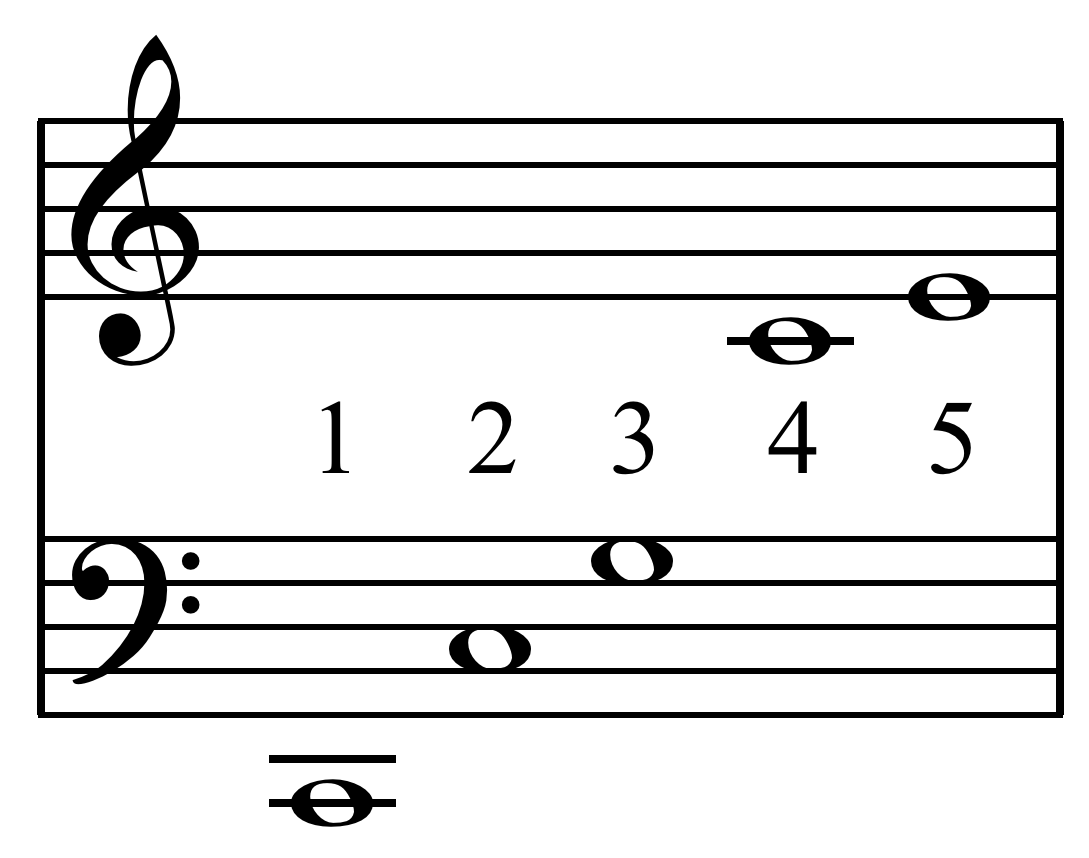
Just Intonation
In music, just intonation or pure intonation is the tuning of musical intervals as whole number ratios (such as 3:2 or 4:3) of frequencies. An interval tuned in this way is said to be pure, and is called a just interval. Just intervals (and chords created by combining them) consist of tones from a single harmonic series of an implied fundamental. For example, in the diagram, if the notes G3 and C4 (labelled 3 and 4) are tuned as members of the harmonic series of the lowest C, their frequencies will be 3 and 4 times the fundamental frequency. The interval ratio between C4 and G3 is therefore 4:3, a just fourth. In Western musical practice, instruments are rarely tuned using only pure intervals—the desire for different keys to have identical intervals in Western music makes this impractical. Some instruments of fixed pitch, such as electric pianos, are commonly tuned using equal temperament, in which all intervals other than octaves consist of irrational-number freq ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ji Koizumi
is a Japanese manga series by Satomi Ikezawa about a Labrador puppy, named Ponta, who turns into a human and falls in love with Mirai Iwaki, who's very popular in his school. In 2000, it won the Kodansha Manga Award for shōjo. It was published in the United States by Del Rey Manga. Plot Ponta, the Koizumi family's labrador retriever puppy one day eats the 'talking bone' that the grandfather invented to allow an animal who licks it the power of speech. Instead of just being able to talk however, she transforms into a human girl. When she rushes out into traffic as a girl, she is saved by the most popular boy at school and falls in love with him. To be near him she enrolls in school and tries to learn how to live as a human. Characters * Ponta Koizumi — The lead character of the series. Grandpa Koizumi's invention transformed her from a puppy into a small child. * Mirai Iwaki — A popular and attractive boy at school. * Go Fujinaga — A boy who loves animals and is a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ji (polearm)
The ''ji'' (pronunciation: , English approximation: , ) was a Chinese polearm, sometimes translated into English as spear or halberd, though they are fundamentally different weapons. They were used in one form or another for over 3000 years, from at least as early as the Zhou dynasty, until the end of the Qing dynasty. They are still used for training purposes in many Chinese martial arts. History The ''ji'' was initially a hybrid between a spear and a dagger-axe. It was a relatively common infantry weapon in Ancient China, and was also used by cavalry and charioteers. In the Song dynasty, several weapons were referred to as ''ji'', but they were developed from spears, not from ancient ''ji''. One variety was called the ''qinglong ji'' (), and had a spear tip with a crescent blade on one side. Another type was the ''fangtian ji'' (), which had a spear tip with crescent blades on both sides. They had multiple means of attack: the side blade or blades, the spear tip, plus of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ji (monk)
Kuījī (; 632–682), also known as Ji (), an exponent of Yogācāra, was a Chinese monk and a prominent disciple of Xuanzang.Lusthaus, Dan (undated). ''Quick Overview of the Faxiang School'' (). Source(accessed: December 12, 2007) His posthumous name was Cí'ēn dàshī (), The Great Teacher of Cien Monastery, after the Daci'en Temple or Great Monastery of Compassionate Grace, which was located in Chang'an, the main capital of the Tang Dynasty. The Giant Wild Goose Pagoda was built in Daci'en Temple in 652. According to biographies, he was sent to the imperial translation bureau headed by Xuanzang, from whom he later would learn Sanskrit, Abhidharma, and Yogācāra. Kuiji collaborated closely with Xuanzang on the '' Cheng weishi lun'', a redacted translation of commentaries on Vasubandhu's Triṃśikā-vijñaptimātratā. Kuiji's commentaries on the former text, the ''Cheng weishi lun shuji'', along with his original treatise on Yogācāra, the '' Dasheng Fayuan yilin chang'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)