|
Ji (surname 纪)
Jǐ (or Jì) is the Mandarin pinyin romanization of the Chinese surname written in simplified Chinese and in traditional Chinese. It is romanized as Chi in Wade–Giles, and Kei in Cantonese. Ji is the 136th most common surname in China, with a population of 1.1 million. It is listed 122nd in the Song dynasty classic text ''Hundred Family Surnames''. It is 42nd in the Hundred Family Surnames, contained in the verse 熊紀舒屈 ( Xiong, Ji, Shu, Qu). Demographics As of 2008, Ji is the 136th most common surname in China, shared by 1.1 million people, or 0.088% of the Chinese population. It is concentrated in Beijing, Anhui, Jiangsu, and Shandong, which together account for 48% of the total. Origin Ji originated from the ancient state of Ji in present-day Shouguang, Shandong province. In 690 BC, Ji was conquered and annexed by Duke Xiang of the neighbouring state of Qi, and the people of Ji adopted the name of their former state as their surname. The Ji surname is a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Old Chinese
Old Chinese, also called Archaic Chinese in older works, is the oldest attested stage of Chinese, and the ancestor of all modern varieties of Chinese. The earliest examples of Chinese are divinatory inscriptions on oracle bones from around 1250 BC, in the late Shang dynasty. Bronze inscriptions became plentiful during the following Zhou dynasty. The latter part of the Zhou period saw a flowering of literature, including classical works such as the '' Analects'', the '' Mencius'', and the '' Zuo zhuan''. These works served as models for Literary Chinese (or Classical Chinese), which remained the written standard until the early twentieth century, thus preserving the vocabulary and grammar of late Old Chinese. Old Chinese was written with several early forms of Chinese characters, including Oracle Bone, Bronze, and Seal scripts. Throughout the Old Chinese period, there was a close correspondence between a character and a monosyllabic and monomorphemic word. Although the s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beijing
} Beijing ( ; ; ), alternatively romanized as Peking ( ), is the capital of the People's Republic of China. It is the center of power and development of the country. Beijing is the world's most populous national capital city, with over 21 million residents. It has an administrative area of , the third in the country after Guangzhou and Shanghai. It is located in Northern China, and is governed as a municipality under the direct administration of the State Council with 16 urban, suburban, and rural districts.Figures based on 2006 statistics published in 2007 National Statistical Yearbook of China and available online at archive. Retrieved 21 April 2009. Beijing is mostly surrounded by Hebei Province with the exception of neighboring Tianjin to the southeast; together, the three divisions form the Jingjinji megalopolis and the national capital region of China. Beijing is a global city and one of the world's leading centres for culture, diplomacy, politics, finance, busine ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eastern Han
The Han dynasty (, ; ) was an imperial dynasty of China (202 BC – 9 AD, 25–220 AD), established by Liu Bang (Emperor Gao) and ruled by the House of Liu. The dynasty was preceded by the short-lived Qin dynasty (221–207 BC) and a warring interregnum known as the ChuHan contention (206–202 BC), and it was succeeded by the Three Kingdoms period (220–280 AD). The dynasty was briefly interrupted by the Xin dynasty (9–23 AD) established by usurping regent Wang Mang, and is thus separated into two periods—the Western Han (202 BC – 9 AD) and the Eastern Han (25–220 AD). Spanning over four centuries, the Han dynasty is considered a golden age in Chinese history, and it has influenced the identity of the Chinese civilization ever since. Modern China's majority ethnic group refers to themselves as the " Han people", the Sinitic language is known as "Han language", and the written Chinese is referred to as " Han characters". The emperor was at the pinnacle o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yuan Shu
Yuan Shu () (died July or August 199), courtesy name Gonglu, was a Chinese military general, politician, and warlord who lived during the late Eastern Han dynasty. He rose to prominence following the collapse of the Han central government in 189. He declared himself Emperor of China in 197 under the short-lived Zhong dynasty, two years before his death in 199. Life Early life Yuan Shu was from Ruyang County (), Runan Commandery, which is in present-day Shangshui County, Henan. His family had for over four generations been a prominent force in the Han civil service, having produced numerous members in high positions since the first century CE. Descended from Yuan An, who served during the reign of Emperor Zhang, Yuan Shu was a son of the Minister of Works Yuan Feng () and his principal wife. Yuan Shu is sometimes described to be a younger cousin(绍之从弟也) ''Sanguozhi'' vol. 6. of the warlord Yuan Shao, but was actually Yuan Shao's younger half-brother. As a young ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ji Ling
Ji Ling ( 196) was a military general serving under the warlord Yuan Shu during the late Eastern Han dynasty of China. In historical records In late 196, Yuan Shu sent Ji Ling to lead 30,000 troops to attack a rival warlord Liu Bei. When Liu Bei requested aid from another warlord Lü Bu, Lü's subordinates said, "General, you've been wanting to kill Liu Bei. Now you can make use of Yuan Shu to help you kill him." Lü Bu replied, "No. If Yuan Shu eliminates Liu Bei, he'll be able to build a network with the warlords in the north and I'll end up being encircled by them." He then sent 1,000 foot soldiers and 200 riders to help Liu Bei. Ji Ling withdrew his forces and did not dare to make any move when he heard of Lü Bu's approach. Lü Bu set up a camp one '' li'' southwest of Xiaopei (小沛; present-day Pei County, Jiangsu) and invited Ji Ling to his camp. Ji Ling also hosted a feast in his camp and invited Lü Bu to attend. Lü Bu went there and brought Liu Bei along with him. H ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
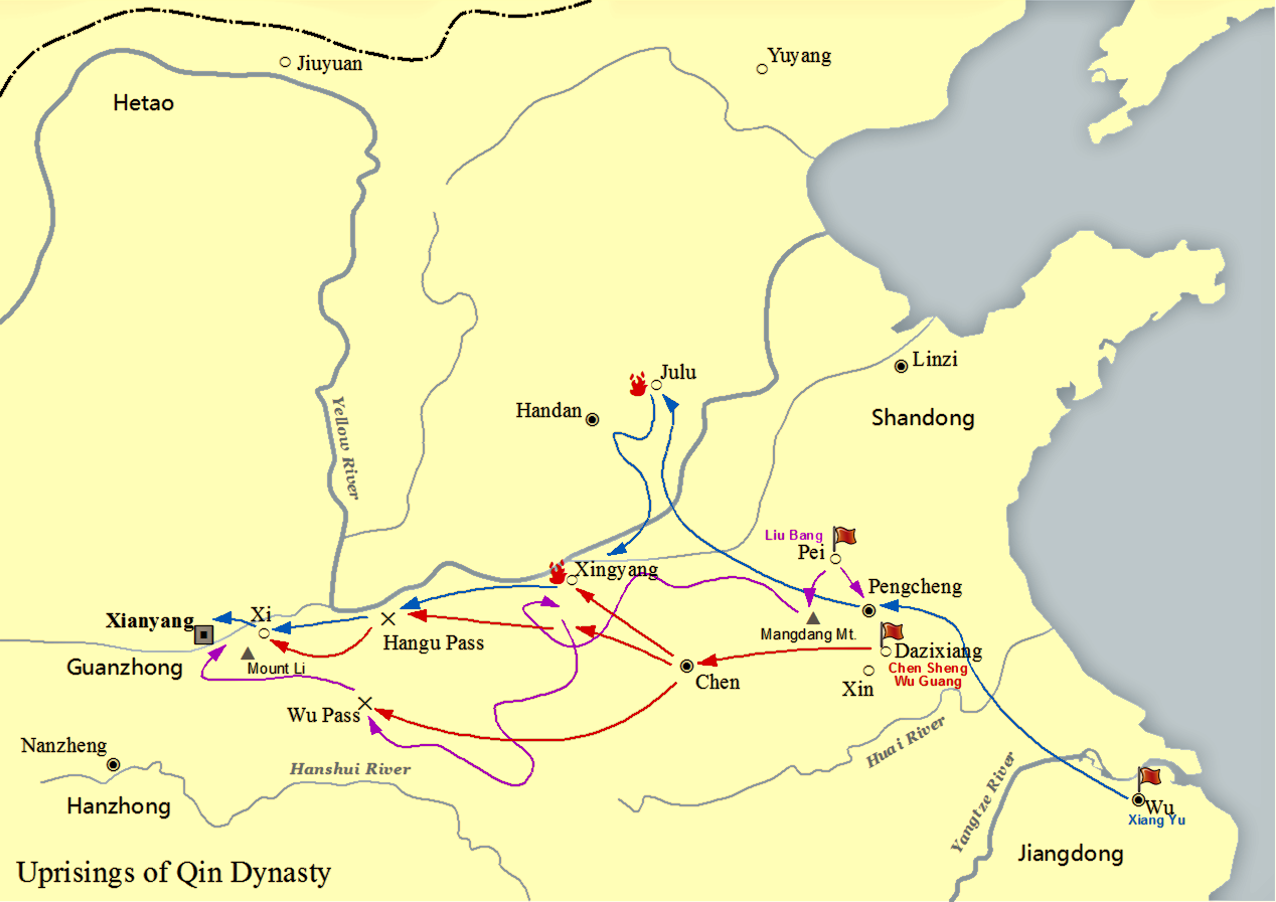
Chu–Han Contention
The Chu–Han Contention ( zh, , lk=on) or Chu–Han War () was an interregnum period in ancient China between the fallen Qin dynasty and the subsequent Han dynasty. After the third and last Qin ruler, Ziying, unconditionally surrendered to rebel forces in 206 BCE, the former Qin Empire was divided by rebel leader Xiang Yu into the Eighteen Kingdoms, which were ruled by various rebel leaders and surrendered Qin generals. A civil war soon broke out, most prominently between two major contending powers – Xiang Yu's Western Chu and Liu Bang's Han. Some of the other kingdoms also waged war among themselves but these were largely insignificant compared to the main conflict between Chu and Han. The war ended in 202 BCE with a total Han victory at the Battle of Gaixia, where Xiang Yu fled to Wujiang and committed suicide after a violent last stand. Liu Bang subsequently proclaimed himself Emperor and established the Han dynasty as the ruling dynasty of China. Background ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Liu Bang
Emperor Gaozu of Han (256 – 1 June 195 BC), born Liu Bang () with courtesy name Ji (季), was the founder and first emperor of the Han dynasty, reigning in 202–195 BC. His temple name was "Taizu" while his posthumous name was Emperor Gao, or Gaodi; "Gaozu of Han", derived from the ''Records of the Grand Historian'', is the common way of referring to this sovereign even though he was not accorded the temple name "Gaozu", which literally means "High Founder". Liu Bang was one of the few dynasty founders in Chinese history who was born into a peasant family. Prior to coming to power, Liu Bang initially served for the Qin dynasty as a minor law enforcement officer in his home town Pei County, within the conquered state of Chu. With the First Emperor's death and the Qin Empire's subsequent political chaos, Liu Bang renounced his civil service position and became an anti-Qin rebel leader. He won the race against fellow rebel leader Xiang Yu to invade the Qin heartl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ji Xin
Ji Xin (; died 204 BC) was a general serving Liu Bang (later Emperor Gaozu of Han) during the Chu–Han contention. In the summer of 204 BC, Liu Bang was besieged in the city of Xingyang by the much larger forces of Xiang Yu. After a month in the seemingly desperate situation, Ji Xin came up with a plan and volunteered to act as a decoy to help his lord escape. Ji Xin rode out of the city in Liu Bang's distinctive chariot, pretended to be Liu and offered to surrender. It took Xiang Yu some time to realize that he had been fooled, and when he discovered that the real Liu Bang had already escaped, had Ji Xin burnt to death. He was later enshrined as the City God of Zhengzhou and Xingyang which was the town he saved. See also * , the temple dedicated to him in Zhengzhou City, built no later than 1501(14th year of Hongzhi era, Ming dynasty The Ming dynasty (), officially the Great Ming, was an imperial dynasty of China, ruling from 1368 to 1644 following the coll ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jiang (surname 姜) , in Shanxi, China
{{disambig ...
Jiang may refer to: * ''Jiang'' (rank), rank held by general officers in the military of China * Jiang (surname), several Chinese surnames **Jiang Zemin (1926–2022), as general secretary of the Chinese Communist Party *Jiang River, an ancient river of China *Jiang County Jiang County or Jiangxian () is a county in the south of Shanxi Shanxi (; ; formerly romanised as Shansi) is a landlocked province of the People's Republic of China and is part of the North China region. The capital and largest city of the pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Qi (state)
Qi, or Ch'i in Wade–Giles romanization, was a state of the Zhou dynasty-era in ancient China, variously reckoned as a march, duchy, and independent kingdom. Its capital was Linzi, located in present-day Shandong. Qi was founded shortly after the Zhou overthrow of Shang in the 11th centuryBC. Its first marquis was Jiang Ziya, minister of King Wen and a legendary figure in Chinese culture. His family ruled Qi for several centuries before it was replaced by the Tian family in 386BC. In 221BC, Qi was the final major state annexed by Qin during its unification of China. History Foundation During the Zhou conquest of Shang, Jiang Ziya, a native of Ju County served as the chief minister to King Wu. After King Wu's death, Ziya remained loyal to the Duke of Zhou during the Three Guards' failed rebellion against his regency. The Shang prince Wu Geng had joined the revolt along with the Dongyi states of Yan, Xu, and Pugu. These were suppressed by 1039 BC a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Duke Xiang Of Qi
Duke Xiang of Qi (; died 686 BC) was from 697 to 686 BC the fourteenth recorded ruler of the State of Qi, a major power during the Spring and Autumn period of ancient China. His personal name was Lü Zhu'er (呂諸兒), ancestral name Jiang ( 姜), and Duke Xiang was his posthumous title. Although under Duke Xiang the state of Qi conquered the neighbouring state of Ji, its traditional enemy, Duke Xiang is best known for his depravity, having had an incestuous relationship with his sister Wen Jiang and murdered his brother-in-law Duke Huan of Lu. At the end Duke Xiang was himself murdered by his cousin Wuzhi, who subsequently usurped the Qi throne. Murdering Duke Huan of Lu Duke Xiang succeeded his father Duke Xi of Qi, who died in 698 BC after 33 years of reign. Duke Xiang had had an incestuous relationship with his younger half-sister Wen Jiang, who in 709 BC married Duke Huan, ruler of the neighbouring State of Lu. In 694 BC, Duke Huan of Lu visited Qi with his wife, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shouguang
Shouguang () is a county-level city in the north-central part of Shandong Province, China, situated on the southwest shore of the Laizhou Bay. Under the administration of the prefecture-level city of Weifang, it has people residing within the municipality and its surrounding towns and villages as of the 2010 Census, even though the built-up (''or metro'') area is much smaller. Administrative divisions As 2012, this city is divided to 5 subdistricts and 9 towns. ;Subdistricts ;Towns Climate Economy Shouguang is a major hub for vegetables and produce in China. Sports The Shouguang Chengtou Stadium Shouguang () is a county-level city in the north-central part of Shandong Province, China, situated on the southwest shore of the Laizhou Bay Laizhou Bay () is a bay on the southern shore of the Bohai Sea (also known as the ''Bohai Gulf'', or ... is located in Shouguang. The 25,000-capacity stadium is used mostly for association football matches and also sometimes for athlet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |