|
Japan–Korea Treaty Of 1876
The Japan–Korea Treaty of 1876 (also known as the Japan-Korea Treaty of Amity in Japan and the Treaty of Ganghwa Island in Korea) was made between representatives of the Empire of Japan and the Korean Kingdom of Joseon in 1876.Chung, Young-lob. (2005). ; excerpt, "''... the initial opening of Korea's borders to the outside world came in the form of the Korea-Japan Treaty of Amity (the so-called Ganghwa Treaty)''." Negotiations were concluded on February 26, 1876.Korean Mission to the Conference on the Limitation of Armament, Washington, D.C., 1921–1922. (1922). ; excerpt, "Treaty between Japan and Korea, dated February 26, 1876." In Korea, Heungseon Daewongun, who instituted a policy of increased isolationism against the European powers, was forced into retirement by his son King Gojong and Gojong's wife, Empress Myeongseong. France and the United States had already made several unsuccessful attempts to begin commerce with the Joseon dynasty during the Daewongun's era. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Treaty Of Kanagawa
The Convention of Kanagawa, also known as the Kanagawa Treaty (, ''Kanagawa Jōyaku'') or the Japan–US Treaty of Peace and Amity (, ''Nichibei Washin Jōyaku''), was a treaty signed between the United States and the Tokugawa Shogunate on March 31, 1854. Signed under threat of force, it effectively meant the end of Japan's 220-year-old policy of national seclusion (''sakoku'') by opening the ports of Shimoda and Hakodate to American vessels. It also ensured the safety of American castaways and established the position of an American consul in Japan. The treaty precipitated the signing of similar treaties establishing diplomatic relations with other Western powers. Isolation of Japan Since the beginning of the 17th century, the Tokugawa Shogunate pursued a policy of isolating the country from outside influences. Foreign trade was maintained only with the Dutch and the Chinese and was conducted exclusively at Nagasaki under a strict government monopoly. This "Pax Tokugawa" per ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Second Opium War
The Second Opium War (), also known as the Second Anglo-Sino War, the Second China War, the Arrow War, or the Anglo-French expedition to China, was a colonial war lasting from 1856 to 1860, which pitted the British Empire#Britain's imperial century (1815–1914), British Empire and the Second French Empire, French Empire against the Qing dynasty of China. It was the second major conflict in the Opium Wars, which were fought over the right to import opium to China, and resulted in a second defeat for the Qing dynasty and the forced legalisation of the opium trade. It caused many Chinese officials to believe that conflicts with the Western powers were no longer traditional wars, but part of a looming national crisis. In 1860, British and French troops landed near Beijing and fought their way into the city. Peace negotiations quickly broke down and the British High Commissioner to China ordered the foreign troops to loot and destroy the Old Summer Palace, Imperial Summer Palace ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
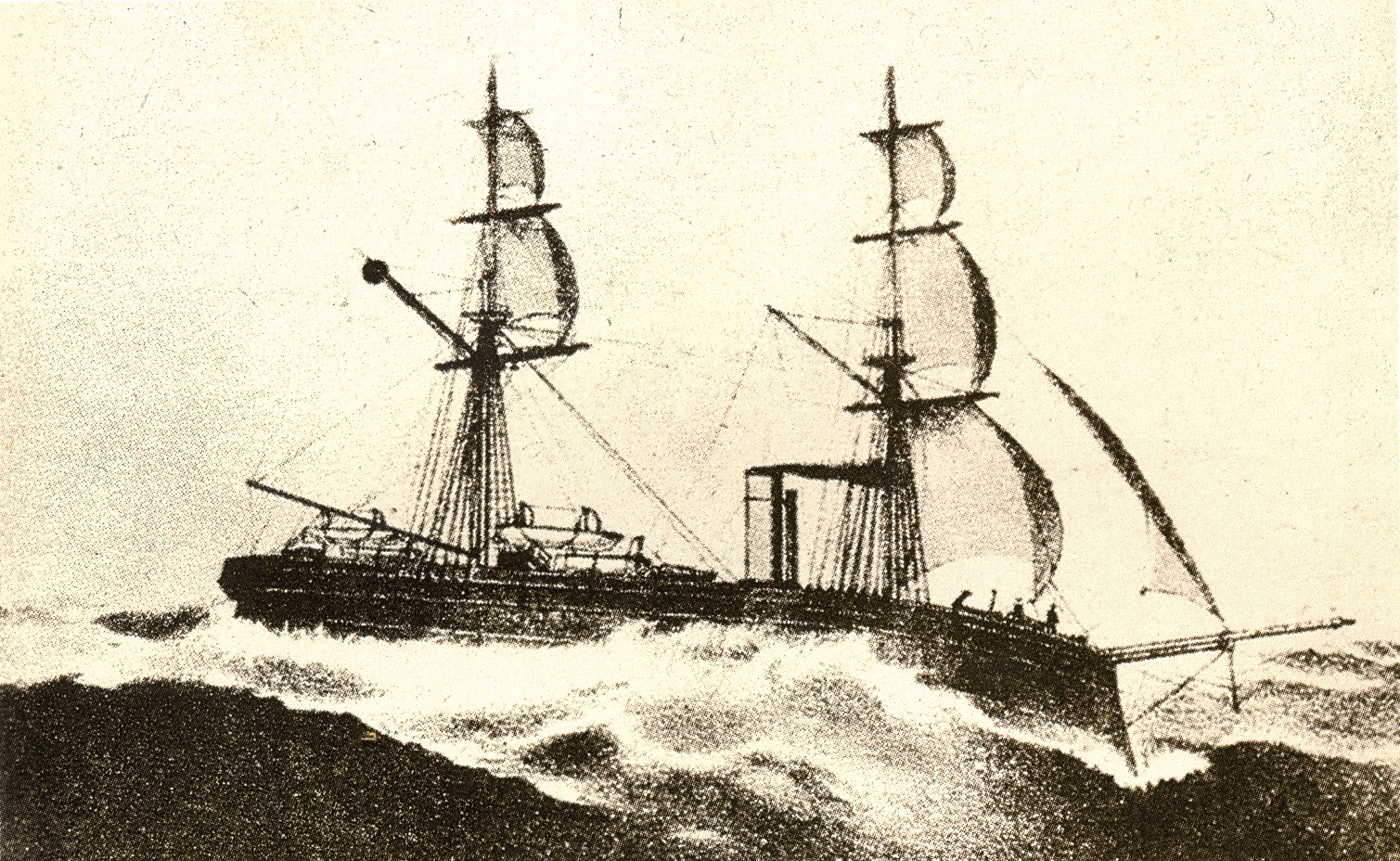
United States Expedition To Korea
The United States expedition to Korea, known in Korea as the ''Shinmiyangyo'' () or simply the Korean Expedition, was the first American military action in Korea and took place predominantly on and around Ganghwa Island in 1871. The reason for the presence of the American land and naval force in Korea was to support an American diplomatic delegation sent to negotiate trade and political relations with the peninsular nation led by the American ambassador to China, Frederick Low, to ascertain the fate of the merchant ship ''General Sherman'', which had gone missing while visiting Korea in 1866. However, according to a ''National Interest'' article, Low's own records indicated the punitive campaign was motivated by a need to demonstrate American power over what he considered to be a weaker nation. Previously, the American commanders had felt entitled to be able to "peacefully" enter Korean waters for survey and trade using heavily armed warships and had ignored repeated diplo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
French Campaign Against Korea
The French expedition to Korea (french: Expédition française en Corée, ) was an 1866 punitive expedition undertaken by the Second French Empire against Joseon Korea in retaliation for the execution of seven French Catholic missionaries. The encounter over Ganghwa Island lasted nearly six weeks. The result was an eventual French retreat, and a check on French influence in the region. The encounter also confirmed Korea in its isolationism for another decade, until Japan forced it to open up to trade in 1876 through the Treaty of Ganghwa. In contemporary South Korea it is known as the ''Byeong-in yangyo'', or "Western disturbance of the ''byeong-in'' year". Background Throughout the history of the Joseon dynasty, Korea maintained a policy of strict isolationism from the outside world (with the exceptions being interaction with the Qing dynasty and occasional trading with Japan through the island of Tsushima). However, it did not succeed entirely in sealing itself off from f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bak Gyusu
Bak Gyusu ( ko, 박규수, 朴珪壽; 1807–1877) was a scholar-bureaucrat, teacher, politician, and a diplomat of the Joseon Dynasty. He was known as a pioneer of the enlightenment group. Bak Gyusu was the grandson of Park Ji-won, the great Silhak scholar of the Joseon. He was also known by the names of Hwanjae (환재, 瓛齋), Hwanjae (환재, 桓齋) en Heonjae (헌재, 獻齋), and Hwanjaegeosa (환재거사 瓛齋居士). Life In 1827, Bak Gyusu met Crown Prince Hyomyeong who quickly became a trusted friend. The Crown Prince would often ask Gyusu for his thoughts on delicate political and social issues. When the Crown Prince died three years later at the age of 20, Gyusu fell into a deep state of mourning. Due to this, Gyusu isolated himself from the outside world for twenty years. In 1848, he successfully passed the Gwageo civil service exam, a test required for government work. Doing well on this test allowed Bak Gyusu to acquire a well-paid job early on. Later in h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Taedong River
The Taedong River (Chosŏn'gŭl: ) is a large river in North Korea. The river rises in the Rangrim Mountains of the country's north where it then flows southwest into Korea Bay at Namp'o.Suh, Dae-Sook (1987) "North Korea in 1986: Strengthening the Soviet Connection" ''Asian Survey'' 27(1): pp. 56-63, page 62 In between, it runs through the country's capital, Pyongyang. Along the river are landmarks such as the Juche Tower and Kim Il-sung Square. The river is 439 km or 272.7 mi in length, and is generally deep. It is the fifth-longest river on the Korean peninsula and the second-longest in North Korea. Pyongyang is approximately 110 km upstream from the mouth, Sunchon 192 km upstream, and Taehŭng 414 km upstream. Because of its depth, it is widely used for river transport; it is navigable by large ships up to 65 km inland, although most commercial traffic stops at Songrim. History The kingdom of Koguryo was founded on its shores. Many archeological site ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pyongan Province
Pyeong-an Province (, ) was one of Eight Provinces of Korea during the Joseon Dynasty. Pyeong'an was located in the northwest of Korea. The provincial capital was Pyeongyang (now Pyongyang, North Korea). History Pyeong'an Province was formed in 1413. Its name derived from the names of two of its principal cities, Pyeongyang () and Anju (). In 1895, the province was replaced by the Districts of Ganggye () in the northeast, Uiju County () in the northwest, and Pyeongyang () in the south. In 1896, Kanggye and Ŭiju Districts were reorganized into North Pyongan Province, and Pyeongyang District was reorganized as South Pyongan Province. North and South Pyongan Provinces are part of North Korea. Geography Pyeong'an was bounded on the east by Hamgyeong Province, on the south by Hwanghae Province, on the west by the Yellow Sea, and on the north by Qing China. The regional name for the province was Gwanseo Kwansŏ is the name of a region that coincides with the former Pyongan P ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
USS General Sherman (1864)
USS ''General Sherman'' was acquired from the U.S. War Department by the Union Navy during the American Civil War as a gunboat in waterways of the Confederate South. She was named after Gen. William T. Sherman. Service history ''General Sherman'', a 187-ton side-wheel "tinclad" river gunboat, was one of four light wooden gunboats built at Chattanooga, Tennessee, for the War Department in 1864. She commissioned at Bridgeport, Alabama, 27 July 1864, Acting Master Joseph W. Morehead in command. Turned over to the Navy and commissioned in July 1864, ''General Sherman'' spent most of her service on the Upper Tennessee River. ''General Sherman'' was assigned to the 11th District, Mississippi Squadron, and became part of Lt. Moreau Forrest's gunboat fleet on the upper Tennessee River. Leaving Bridgeport, Alabama, 22 August, she patrolled with other gunboats between Decatur, Alabama, and Muscle Shoals, Alabama, controlling guerrilla attacks and working to prevent major elements ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ernst Oppert
Ernst Jakob Oppert (5 December 1832 – 19 September 1903) was a Jewish businessman from Germany best known for his unsuccessful attempt in 1867 to remove the remains of the father of regent Yi Ha-eung from their grave in order to use them to blackmail the regent into removing Korean trade barriers. Life Oppert was born into a wealthy banker family in Hamburg. Two of his brothers, Julius and Gustav, became leading German orientalists,Bräsel, S.: Ernst Jakob Oppert: "Ein verschlossenes Land" - Die erste Reisebeschreibung eines Deutschen über Korea'', project description, University of Erfurt, 2002. URL last accessed April 26, 2006. while Ernst opened a trading business in 1851 in Hong Kong. When that company went bankrupt in 1867, he became interested in trading with Korea, which at that time followed a strict isolationist policy and was a hermit kingdom, and a closed market to westerners. Oppert visited the country clandestinely several times.Lankov, A. A Grave enterprise', ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hamgyong Province
Hamgyong Province () was one of the Eight Provinces of Korea during the Joseon Dynasty. Hamgyŏng was located in the northeast of Korea. The provincial capital was Hamhŭng. Names The province was first established as Yonggil ( ko, 영길, , ''Yŏnggil'') in 1413. It was renamed Hamgil (, ) three years later. In 1470, it was renamed Yongan (, , ''Yŏngan''). In 1509, it was renamed Hamgyong after its two principal cities, Hamhung (, , ''Hamhŭng'', "Complete Success") and Kyongsong (, , ''Kyŏngsŏng'', "Mirror," "Clear," or "Perceptive City"). In the 18th century, this was transcribed via Chinese as Kyen-king and glossed as meaning "the Happy". In the 19th century, it was transcribed as Ham-kieng. Within Korea, the province was also referred to by the regional name Dongbuk ("Northeast"). the southern half of the province was also referred as " Kwannam", the northern half of the province was also referred as "Kwanbuk". History Korea's northeastern frontier was first organi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chungcheong Province
Chungcheong (''Chungcheong-do''; ) was one of the eight provinces of Korea during the Joseon Dynasty. Chungcheong was located in the southwest of Korea. The provincial capital was located at Gongju, which had been the capital of the kingdom of Baekje from 475 to 538. History Chungcheong Province was formed in 1356—during the Goryeo Dynasty—from the southern portion of the former province of Yanggwang. Its name derived from the names of the principal cities of Chungju (충주; 忠州) and Cheongju (청주; 淸州). In 1895, the province was replaced by the Districts of Chungju (''Chungju-bu;'' 충주부; 忠州府) in the east, Gongju (''Gongju-bu;'' 공주부; 公州府) in the centre, and Hongju (''Hongju-bu;'' 홍주부; 洪州府; modern-day Hongseong County) in the west. In 1896, Chungju and eastern Gongju Districts were reorganized into North Chungcheong Province, and Hongju and western Gongju Districts were reorganized into South Chungcheong Province. No ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chŏlla
Jeolla Province (, ) was one of the historical Eight Provinces of Korea during the Kingdom of Joseon in today Southwestern Korea. It consisted of the modern South Korean provinces of North Jeolla, South Jeolla and Gwangju Metropolitan City as well as the Jeju Province. The provincial capital was Jeonju, the current capital of North Jeolla. The entire inland region was called Honam ("South of the Lake"), which is still commonly used today. History Samhan and Samguk During the Samhan era of Korean history, the area of Jeolla was controlled by the Mahan confederacy and the Tamna kingdom on Jeju. Fifteen of the 45 Korean tribes had their bases in this region. When Baekje overtook Mahan by the 5th century, the Three Kingdoms era began and the region became part of southern Baekje. Jungbang was the center of the province during this period. Unified Silla When Silla conquered Baekje with the help of Tang China in 660, it became a territory of Later Silla during the 16th year of the r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




.jpg)