|
Japan National Route 280
is a national highway of Japan that traverses the prefectures, Aomori and Hokkaido as well as the Tsugaru Strait that separates them. It currently is made up of two sections that travel from Aomori, north across the Tsugaru Peninsula to Sotogahama where the first section ends at the site of a former ferry to across the Tsugaru Strait to the town, Fukushima. The other section begins at the corresponding former ferry terminal in Fukushima. The road then travels alongside the southern coast of Hokkaido concurrently with National Route 228 to Hakodate where the route meets its northern terminus. National Route 280's path across Aomori and Hokkaido follows one of the oldest roads in northern Japan, the Matsumaedō. It was established by Tokugawa Ieyasu for government officials traveling through the area as a branch of the Edo Five Routes and it had some defensive importance to the Japanese who feared a Russian incursion into Ezo, which was ruled by the Matsumae clan. Route de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Minmaya, Aomori
was a village located in Higashitsugaru District in northern Aomori Prefecture, Japan. Minmaya Village was located on the north coast of Tsugaru Peninsula bordering on Tsugaru Strait. The area was part of Hirosaki Domain during the Edo period. After the Meiji Restoration, Minmaya Village was created on April 1, 1889. On March 28, 2005, Minmaya, along with the neighboring town of Kanita, and the village of Tairadate (all from Higashitsugaru District), was merged to create the town of Sotogahama, and thus no longer exists as an independent municipality. At the time of its merger, Minmaya had an estimated population of 2,364 and a population density of 36.19 persons per km2. The total area was 65.34 km2. The village economy was dominated by commercial fishing. Minmaya was served by Route 339 (Japan) highway, and by Minmaya Station on the Tsugaru Line of JR East The is a major passenger railway company in Japan and is the largest of the seven Japan Railways Gro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tokugawa Ieyasu
was the founder and first ''shōgun'' of the Tokugawa Shogunate of Japan, which ruled Japan from 1603 until the Meiji Restoration in 1868. He was one of the three "Great Unifiers" of Japan, along with his former lord Oda Nobunaga and fellow Oda subordinate Toyotomi Hideyoshi. The son of a minor daimyo, Ieyasu once lived as a hostage under daimyo Imagawa Yoshimoto on behalf of his father. He later succeeded as daimyo after his father's death, serving as a vassal and general of the Oda clan, and building up his strength under Oda Nobunaga. After Oda Nobunaga's death, Ieyasu was briefly a rival of Toyotomi Hideyoshi, before declaring his allegiance and fighting on his behalf. Under Toyotomi, Ieyasu was relocated to the Kanto plains in eastern Japan, away from the Toyotomi power base in Osaka. He built his castle in the fishing village of Edo (now Tokyo). He became the most powerful daimyo and the most senior officer under the Toyotomi regime. Ieyasu preserved his strengt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
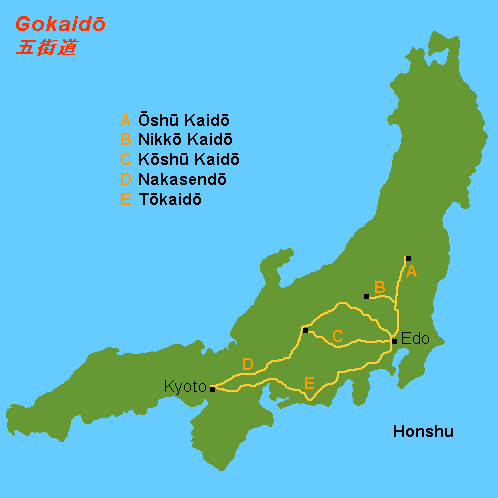
Ōshū Kaidō
The was one of the five routes of the Edo period. It was built to connect Edo (modern-day Tokyo) with Mutsu Province and the present-day city of Shirakawa, Fukushima Prefecture, Japan. It was established by Tokugawa Ieyasu for government officials traveling through the area. Subroutes In addition to the established use of traveling from Edo to Mutsu Province, there were also many roads that connected from the Ōshū Kaidō. One such sub-route was the Sendaidō (仙台道), which connected Mutsu Province with Sendai. The terminus for the Sendaidō is in Aoba-ku in modern Sendai. From there, the Matsumaedō (松前道) connected Sendai with Hakodate, Hokkaidō. Though the Ōshū Kaidō has only 27 post stations,Ōshū Kaidō Map Yumekaidō. Accessed September 4, 2007. there were over 100 designated post stations when the subroutes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Edo Period
The or is the period between 1603 and 1867 in the history of Japan, when Japan was under the rule of the Tokugawa shogunate and the country's 300 regional '' daimyo''. Emerging from the chaos of the Sengoku period, the Edo period was characterized by economic growth, strict social order, isolationist foreign policies, a stable population, perpetual peace, and popular enjoyment of arts and culture. The period derives its name from Edo (now Tokyo), where on March 24, 1603, the shogunate was officially established by Tokugawa Ieyasu. The period came to an end with the Meiji Restoration and the Boshin War, which restored imperial rule to Japan. Consolidation of the shogunate The Edo period or Tokugawa period is the period between 1603 and 1867 in the history of Japan, when Japan was under the rule of the Tokugawa shogunate and the country's regional '' daimyo''. A revolution took place from the time of the Kamakura shogunate, which existed with the Tennō's court, t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Japan National Route 5
is a major highway on the island and prefecture of Hokkaido in northern Japan. The highway begins at an intersection with National Routes 279 and 278 in Hakodate. It travels north across the southern half of the island, traveling through Otaru where it curves to the east toward its endpoint at an intersection with National Route 12 in Chūō-ku, Sapporo. Route description Overlapping sections *In Oshamanbe, from Kunnui intersection to Asahihama intersection: Route 230 *From Kutchan (North-4 West-1 intersection) to Kyōwa (Kunitomi intersection): Route 276 *From Yoichi (Yoichi Station intersection) to Otaru (Inaho 2-18 intersection): Route 229 Municipalities passed through *Oshima Subprefecture **Hakodate - Nanae - Mori - Yakumo - Oshamanbe *Shiribeshi Subprefecture ** Kuromatsunai - Rankoshi - Niseko - Kyōwa - Niki - Yoichi - Otaru * Ishikari Subprefecture **Sapporo History National Route 5 traces its origin to the , a road designed by Horace Capron, in 1872 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hakodate Station
is a railway station on the Hakodate Main Line in Hakodate, Hokkaido, Japan, operated by the Hokkaido Railway Company (JR Hokkaido). Lines *South Hokkaido Railway Company Dōnan Isaribi Tetsudō Line (Normally ends at Goryōkaku, but trains generally serve Hakodate as well) *Hakodate Main Line *Tsugaru-Kaikyō Line (Former) Hakodate Station is the terminus of the Hakodate Main Line and the former Tsugaru-Kaikyō Line; Hakodate Municipal Transit streetcars stop at the adjacent Hakodate Eki-mae Station. Train services In addition to local services, the following long-distance trains serve Hakodate Station. *''Hokuto'' and ''Super Hokuto'' limited express to Sapporo The following services ended in March 2016 due to the Hokkaido Shinkansen's opening From Shin-Hakodate-Hokuto Station to Shin-Aomori Station, which is takes a similar route of the Hakuchō\Super Hakuchō. All services go through to Tokyo station, which means the two former sleeper trains had to be discontinued due ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Japan National Route 339
is a national highway of Japan that traverses the western side of Aomori Prefecture, traveling south to north. The highway begins as a concurrent route with National Route 7 in central Hirosaki, it then leaves National Route 7 in Fujisaki and travels north through the municipalities of Itayanagi, Tsuruta, Goshogawara, and Nakadomari before ending at an intersection with National Route 280 in Sotogahama. In a unique feature, a section of the route on Cape Tappi is a staircase. Route description National Route 339 begins as a concurrent route with National Route 7 in central Hirosaki, northeast of Undōkōenmae Station. Shortly after, the highway has an interchange with National Routes 102, 394, and Aomori Route 109. After passing through the city and entering the town of Fujisaki, it leaves National Route 7 and turns northwest, paralleling the downstream path of the Iwaki River. In Itayanagi, the route curves to the north again, heading directly towards central ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aomori Bay
The is a bay located north of the island of Honshu, in Japan. It is considered to be part of the larger Mutsu Bay. Geography Aomori Bay is an inner bay located to the west of Natsudomari Peninsula that protrudes in the center of the southern coast of Mutsu Bay. The bay is bordered by the Tsugaru Peninsula to the west and the harbor of Aomori to the south. Animal and plant life '' Emplectonema kandai'' is a bioluminescent marine ribbon worm found in Aomori Bay at a depth of 35–40 meters, and coiled up on '' Chelyosoma'' sea squirts. Human history The bay provided resources for the Jōmon people living at the settlements along its coastline, such as the Sannai-Maruyama Site The is an archaeological site and museum located in the Maruyama and Yasuta neighborhoods to the southwest of central Aomori in Aomori Prefecture in northern Japan, containing the ruins of a very large Jōmon period settlement. The ruins of a .... References {{Authority control Bays of Japan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aburakawa Station
is a railway station on the East Japan Railway Company (JR East) Tsugaru Line located in the city of Aomori, Aomori Prefecture, Japan. Lines Aburakawa Station is served by the Tsugaru Line and is located from the starting point of the line at . Station layout Aburakawa Station has one side platform serving a single bi-directional track. The station is a kan'i itaku station, ''kan'i itaku'' station, administered by Aomori Station, and operated by the local Jaster Corporation, with point-of-sales terminal installed. The short platform requires that trains longer than seven carriages use a Selective door operation, door cut system. History Aburakawa Station was opened on December 5, 1951, as a station on the Japanese National Railways (JNR). Freight operations were discontinued from July 1970. The station became a ''kan'i itaku'' station on April 1, 1971, operated by the Japan Travel Bureau. With the privatization of the JNR on April 1, 1987, it came under the operational control ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aomori Station
is a railway station in the city of Aomori in Aomori Prefecture, Japan. The station has been operating since September 1891, though the most recent station building, which consists of three island platforms connected to the station building by a footbridge, was completed in March 2021. Since 1987 the station has been used by the East Japan Railway Company (JR East) which operates various services to destinations throughout the Tōhoku region. Since 2010 the station's operations have been jointly run by JR East and the Aoimori Railway Company, a third sector, regional rail operator. Location Aomori Station is located at the western terminus of Aomori Prefecture Route 16, a road that provides access to the station from Japan National Route 4 in central Aomori. The station is situated within the urban core of central Aomori and is in close proximity to the city hall, prefectural hall, the city library, and several landmarks and museums including the Aomori Bay Bridge, A-Facto ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Japan National Route 7
is a major north-south national highway on the Sea of Japan side of the island of Honshū, Japan. It traverses four prefectures, with Niigata at its southern end, then Yamagata, Akita, and finally, Aomori at its northern end. The long highway begins at an intersection with national routes 8, 17, 113, 116, 289, 350, and 402 in the capital of Niigata, Niigata. Travelling north, the highway links the prefectural capitals Akita and Aomori. In central Aomori the highway ends at the northern terminus of National Route 4 and National Route 45. Route description The main line of National Route 7 has a length of . When bypasses signed as National Route 7 are included, its total distance increases to . The highway's origin and southern terminus lies in Chuo-ku, Niigata at junction with national routes 8, 17, 113, 116, 289, 350, and 402. The highway passes through Shibata, Murakami, Tsuruoka, Sakata, Yurihonjō, Akita, Noshiro, Ōdate, and Hirosaki. Its endpoint and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Southern Terminus Of Japan National Route 280
Southern may refer to: Businesses * China Southern Airlines, airline based in Guangzhou, China * Southern Airways, defunct US airline * Southern Air, air cargo transportation company based in Norwalk, Connecticut, US * Southern Airways Express, Memphis-based passenger air transportation company, serving eight cities in the US * Southern Company, US electricity corporation * Southern Music (now Peermusic), US record label * Southern Railway (other), various railways * Southern Records, independent British record label * Southern Studios, recording studio in London, England * Southern Television, defunct UK television company * Southern (Govia Thameslink Railway), brand used for some train services in Southern England Media * ''Southern Daily'' or ''Nanfang Daily'', the official Communist Party newspaper based in Guangdong, China * ''Southern Weekly'', a newspaper in Guangzhou, China * Heart Sussex, a radio station in Sussex, England, previously known as "Southern FM" * 8 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.png)
.png)

