|
James Brown (Louisiana)
James Brown (September 11, 1766April 7, 1835) was a Virginia-born American lawyer, planter and politician who served as a Secretary of State for the new state of Kentucky, and later as U.S. Senator from Louisiana, and Minister to France (1823-1829) before his retirement and death in Philadelphia. Early and family life Born near Staunton, Virginia, to John Brown and his wife, young James Brown had brothers John and Samuel Brown and sisters Mary and Elizabeth who either survived him or had children who survived him, unlike his brother Preston. His brother John Brown became the U.S. Senator from Kentucky and active in its gaining statehood. Well-connected among the southern elite, they were also cousins of John Breckinridge, James Breckinridge and Francis Preston. James Brown attended Washington College (later Washington and Lee University) in Lexington, Virginia, and the College of William & Mary in Williamsburg. James Brown read law, was admitted to the Virginia bar, and commenc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United States Ambassador To France
The United States ambassador to France is the official representative of the president of the United States to the president of France. The United States has maintained diplomatic relations with France since the American Revolution. Relations were upgraded to the higher Diplomatic rank, rank of Ambassador in 1893. The diplomatic relationship has continued through France's two empires, three monarchies, and five republics. Since 2006 the ambassador to France has also served as the List of ambassadors of the United States to Monaco, ambassador to Monaco. List of United States chiefs of mission in France Ministers to the Court of Versailles (1778–1792) Relations between the United States and the French Court of Versailles were established in 1778 with the signing of the Treaty of Amity and Commerce (United States–France), Treaty of Amity and Commerce. As a republic, the United States was not entitled to send an ambassador. Instead, relations were maintained at the lower d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The College Of William & Mary
The College of William & Mary (officially The College of William and Mary in Virginia, abbreviated as William & Mary, W&M) is a public research university in Williamsburg, Virginia. Founded in 1693 by letters patent issued by King William III and Queen Mary II, it is the second-oldest institution of higher education in the United States and the ninth-oldest in the English-speaking world. Institutional rankings have placed it among the best public universities in the United States. The college educated American presidents Thomas Jefferson, James Monroe, and John Tyler. It also educated other key figures pivotal to the development of the United States, including the first President of the Continental Congress Peyton Randolph, the first U.S. Attorney General Edmund Randolph, the fourth U.S. Supreme Court Chief Justice John Marshall, Speaker of the House of Representatives Henry Clay, Commanding General of the U.S. Army Winfield Scott, sixteen members of the C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
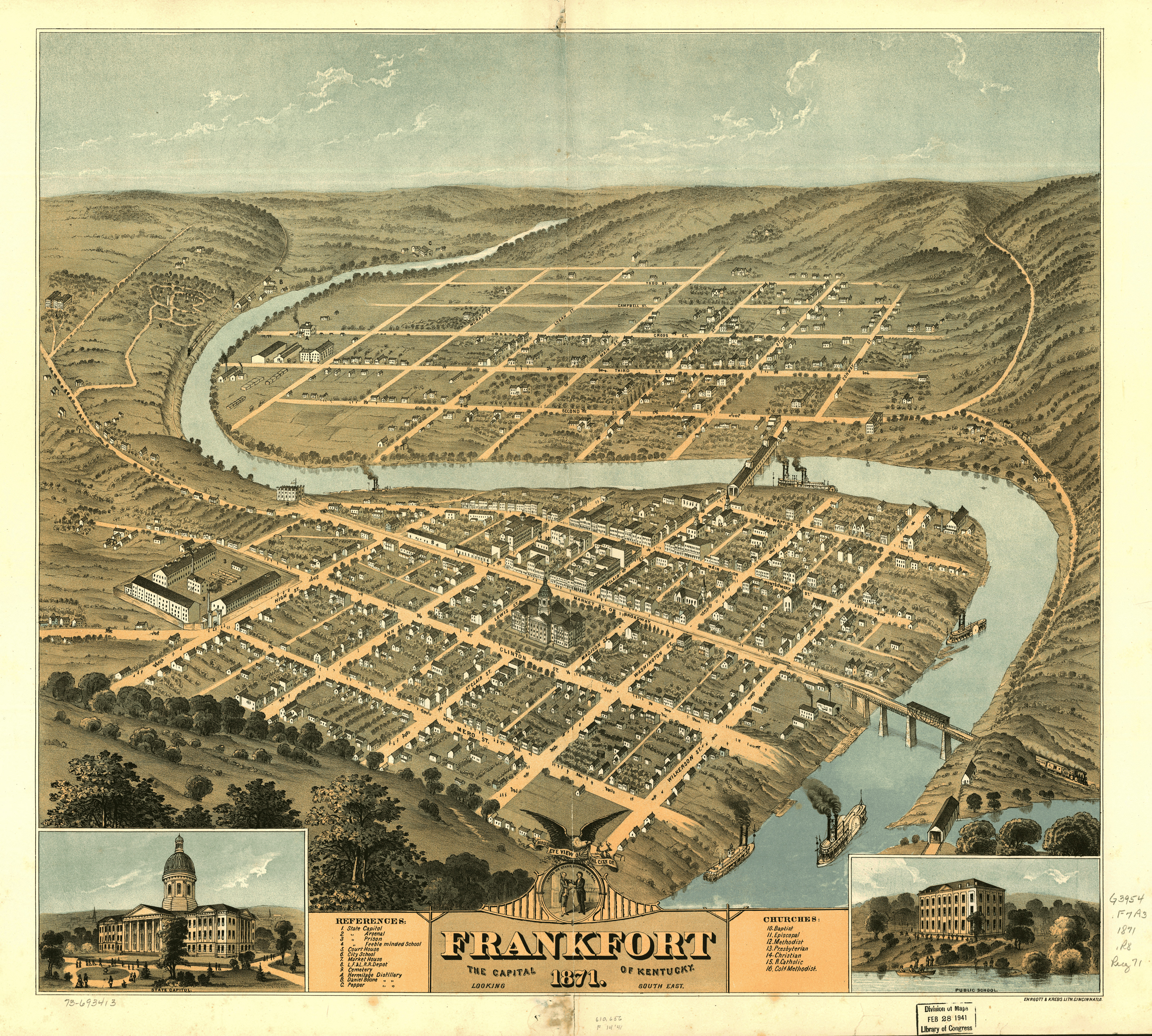
Frankfort, Kentucky
Frankfort is the capital city of the Commonwealth of Kentucky, United States, and the seat of Franklin County. It is a home rule-class city; the population was 28,602 at the 2020 census. Located along the Kentucky River, Frankfort is the principal city of the Frankfort, Kentucky Micropolitan Statistical Area, which includes all of Franklin and Anderson counties. History Pre-1900 The town of Frankfort likely received its name from an event that took place in the 1780s. Native Americans attacked a group of early European colonists from Bryan Station, who were on their way to make salt at Mann's Lick in Jefferson County. Pioneer Stephen Frank was killed at the Kentucky River and the settlers thereafter called the crossing "Frank's Ford". This name was later elided to Frankfort. In 1786, James Wilkinson purchased a tract of land on the north side of the Kentucky River, which developed as downtown Frankfort. He was an early promoter of Frankfort as the state capital. Wilki ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Practice Of Law
In its most general sense, the practice of law involves giving legal advice to clients, drafting legal documents for clients, and representing clients in legal negotiations and court proceedings such as lawsuits, and is applied to the professional services of a lawyer or attorney at law, barrister, solicitor, or civil law notary. However, there is a substantial amount of overlap between the practice of law and various other professions where clients are represented by agents. These professions include real estate, banking, accounting, and insurance. Moreover, a growing number of legal document assistants (LDAs) are offering services which have traditionally been offered only by lawyers and their employee paralegals. Many documents may now be created by computer-assisted drafting libraries, where the clients are asked a series of questions that are posed by the software in order to construct the legal documents. In addition, regulatory consulting firms also provid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reading Law
Reading law was the method used in common law countries, particularly the United States, for people to prepare for and enter the legal profession before the advent of law schools. It consisted of an extended internship or apprenticeship under the tutelage or mentoring of an experienced lawyer. The practice largely died out in the early 20th century. A few U.S. states still permit people to become lawyers by reading law instead of attending law school, although the practice is rare. In this sense, "reading law" specifically refers to a means of entering the profession, although in England it is still customary to say that a university undergraduate is "reading" a course, which may be law or any other. __TOC__ History United States In colonial America, as in Britain in that day, law schools did not exist at all until Litchfield Law School was founded in 1773. Within a few years following the American Revolution, some universities such as the College of William and Mary and th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Williamsburg, Virginia
Williamsburg is an independent city in the Commonwealth of Virginia. As of the 2020 census, it had a population of 15,425. Located on the Virginia Peninsula, Williamsburg is in the northern part of the Hampton Roads metropolitan area. It is bordered by James City County on the west and south and York County on the east. English settlers founded Williamsburg in 1632 as Middle Plantation, a fortified settlement on high ground between the James and York rivers. The city functioned as the capital of the Colony and Commonwealth of Virginia from 1699 to 1780 and became the center of political events in Virginia leading to the American Revolution. The College of William & Mary, established in 1693, is the second-oldest institution of higher education in the United States and the only one of the nine colonial colleges in the South. Its alumni include three U.S. presidents as well as many other important figures in the nation's early history. The city's tourism-based economy is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
College Of William & Mary
The College of William & Mary (officially The College of William and Mary in Virginia, abbreviated as William & Mary, W&M) is a public research university in Williamsburg, Virginia. Founded in 1693 by letters patent issued by King William III and Queen Mary II, it is the second-oldest institution of higher education in the United States and the ninth-oldest in the English-speaking world. Institutional rankings have placed it among the best public universities in the United States. The college educated American presidents Thomas Jefferson, James Monroe, and John Tyler. It also educated other key figures pivotal to the development of the United States, including the first President of the Continental Congress Peyton Randolph, the first U.S. Attorney General Edmund Randolph, the fourth U.S. Supreme Court Chief Justice John Marshall, Speaker of the House of Representatives Henry Clay, Commanding General of the U.S. Army Winfield Scott, sixteen members of the C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lexington, Virginia
Lexington is an independent city in the Commonwealth of Virginia. At the 2020 census, the population was 7,320. It is the county seat of Rockbridge County, although the two are separate jurisdictions. The Bureau of Economic Analysis combines the city of Lexington (along with nearby Buena Vista) with Rockbridge County for statistical purposes. Lexington is about east of the West Virginia border and is about north of Roanoke, Virginia. It was first settled in 1778. Lexington is the location of the Virginia Military Institute (VMI) and of Washington and Lee University (W&L). City Council History Lexington was named in 1778. It was the first of what would be many American places named after Lexington, Massachusetts, known for being the place at which the first shot was fired in the American Revolution. The Union General David Hunter led a raid on Virginia Military Institute during the American Civil War. Robert E. Lee and Thomas "Stonewall" Jackson are buried in the ci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Francis Preston
Francis Preston (August 2, 1765 – May 26, 1835) was an American lawyer and politician from Abingdon, Virginia. He was the son of Col. William Preston of Virginia, served in both houses of the state legislature, and represented Virginia in the U.S. House of Representatives from 1793 to 1797. Preston had a house built in Abingdon, now called the Martha Washington Inn. In 1795, while residing at Saltville, he constructed the Preston House. Preston was the father of Isaac Trimble Preston, William Campbell Preston, and John S. Preston and the uncle of William Ballard William is a male given name of Germanic origin.Hanks, Hardcastle and Hodges, ''Oxford Dictionary of First Names'', Oxford University Press, 2nd edition, , p. 276. It became very popular in the English language after the Norman conquest of Engl ... and William Preston. Electoral history *1793; Preston was elected to the U.S. House of Representatives defeating Abram Trigg. *1795; Preston was re-elected uno ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
James Breckinridge
James Breckinridge (March 7, 1763May 13, 1833) was a Virginia lawyer and politician and a member of the Breckinridge family. He served in the Virginia House of Delegates, as well as the U.S. House of Representatives. He also fought in the American Revolutionary War and served as a brigadier-general during the War of 1812. Family and early life Breckinridge was born near Fincastle in Botetourt County in the Colony of Virginia. He was the son of Robert Breckinridge whose father had immigrated from Ireland. His mother was the former Leticia Preston.Dictionary of American Biography'' Vol. 2, p 5 His brother was John Breckinridge and he was the great-great-great-uncle of John Bayne Breckinridge. He married Ann Cary Selden (daughter of Wilson Cary Selden & Elizabeth Jennings) born 1770 died 1843. He studied under private tutors and during the Revolutionary War, he served in Colonel Preston's rifle regiment under General Nathanael Greene. He attended Washington College (now Was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Breckinridge (1760-1806)
John Breckinridge (December 2, 1760 – December 14, 1806) was a lawyer, slave-owning planter, soldier, and politician in the U.S. states of Virginia and Kentucky. He served several terms each in the state legislatures of Virginia and Kentucky before legislators elected him to the U.S. Senate. He also served as United States Attorney General during the second term of President Thomas Jefferson. He is the progenitor of Kentucky's Breckinridge political family and the namesake of Breckinridge County, Kentucky. Breckinridge's father was landowner and colonel in the local Virginia militia who married into the Preston political family. Breckinridge attended the William and Mary College intermittently between 1780 and 1784; his attendance was interrupted by the Revolutionary War and he three times won election to the Virginia House of Delegates. One of the youngest members of that (part-time) body, this allowed him to meet many prominent politicians. In 1785, he married "Polly" Cabe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Brown (Kentucky Politician, Born 1757)
John Brown (September 12, 1757August 29, 1837) was an American lawyer and statesman who participated in the development and formation of the State of Kentucky after the American Revolutionary War. Brown represented Virginia in the Continental Congress (1777–1778) and the U.S. Congress (1789–1791). While in Congress, he introduced the bill granting Statehood to Kentucky. Once that was accomplished, he was elected by the new state legislature as a U.S. Senator for Kentucky. From 1803 to 1804, Brown served as President pro tempore of the United States Senate. Early life John Brown was born in Augusta County in the Colony of Virginia, on September 12, 1757. He was a son of Reverend John Brown and Margaret Preston Brown, immigrants from northern Ireland. The son of a Presbyterian minister and schoolmaster, John was well educated, first at his father's Liberty Hall Academy (now Washington and Lee University), and then at the College of New Jersey (now Princeton University). His ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |