|
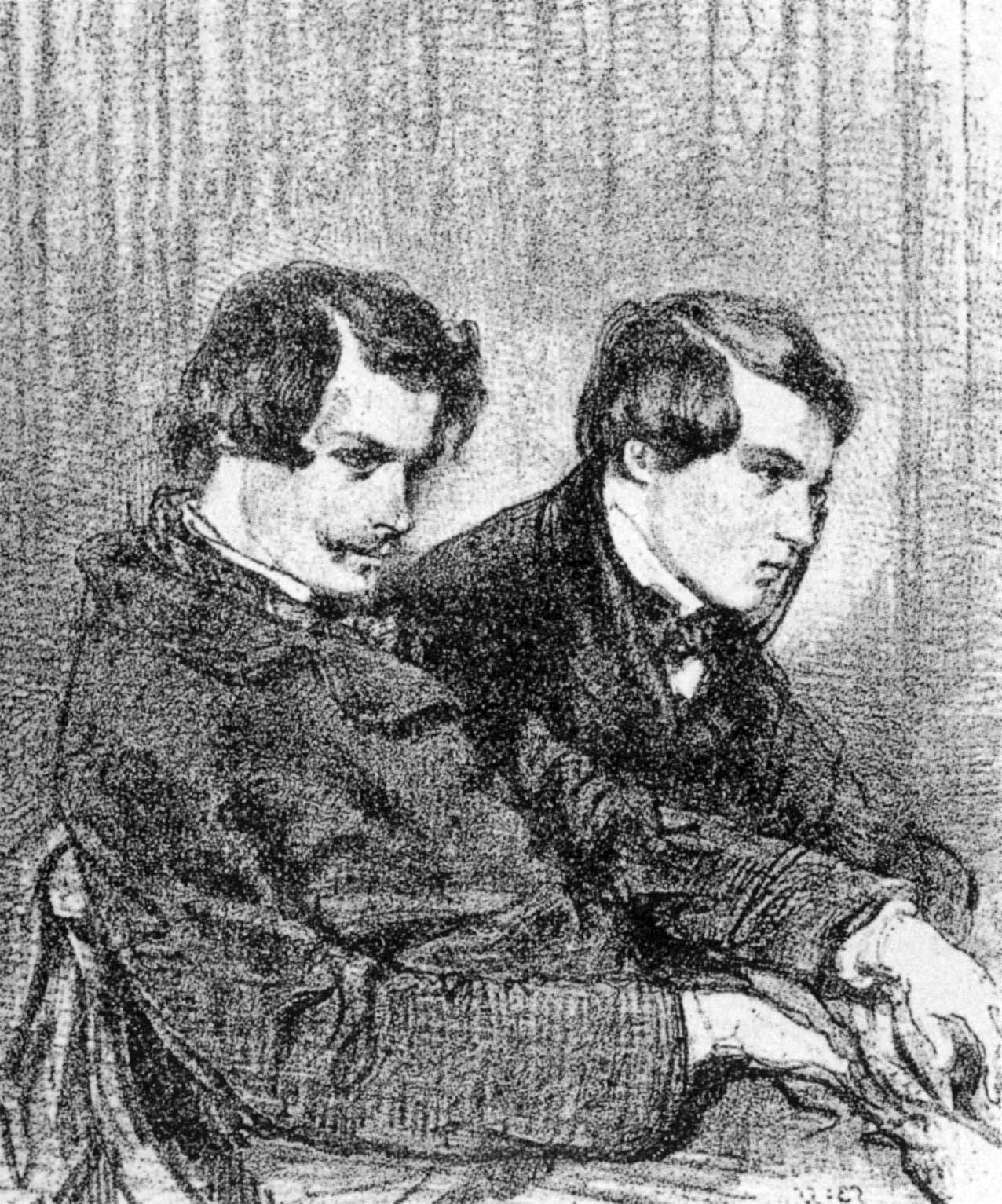
Jules De Goncourt
Jules Alfred Huot de Goncourt (; 17 December 183020 June 1870) was a French writer, who published books together with his brother Edmond. Jules was born and died in Paris. His death at the age of 39 was at Auteuil of a stroke brought on by syphilis. The Prix Goncourt is awarded annually in his honor. Biography Background Jules de Goncourt was born in Paris, the fourth child of a former cavalry officer and squadron leader in the Grande Armée of Napoléon I, Marc-Pierre Huot de Goncourt, and his wife Annette-Cécile de Goncourt (née Guérin). Between Jules and his older brother Edmond were born two sisters who died at young ages, Nephtalie (1824–1825) and Émilie (1829–1832). Jules' paternal grandfather, Huot de Goncourt, sat as a deputy in the National Assembly of 1789. At the Lycée Condorcet, which he attended from 1842 to 1848, he was a strong student, obtaining two ''accessits'' in Greek and Latin in the Concours général. Both parents died while their sons were sti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
George Moore (novelist)
George Augustus Moore (24 February 1852 – 21 January 1933) was an Irish novelist, short-story writer, poet, art critic, memoirist and dramatist. Moore came from a landed family of Catholics who lived at Moore Hall in Carra, County Mayo. He originally wanted to be a painter, and studied art in Paris during the 1870s. There, he befriended many of the leading French artists and writers of the day. As a naturalistic writer, he was amongst the first English-language authors to absorb the lessons of the French realists, and was particularly influenced by the works of Émile Zola. His writings influenced James Joyce, according to the literary critic and biographer Richard Ellmann,Gilcher, Edwin (September 2004; online edn, May 2006"Moore, George Augustus (1852–1933)" ''Oxford Dictionary of National Biography'', Oxford University Press, , retrieved 7 January 2008 (Subscription required) and, although Moore's work is sometimes seen as outside the mainstream of both Irish and B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Goncourt Brothers
The Goncourt brothers (, , ) were Edmond de Goncourt (1822–1896) and Jules de Goncourt (1830–1870), both French naturalism writers who, as collaborative sibling authors, were inseparable in life. Background Edmond and Jules were born to minor aristocrats Marc-Pierre Huot de Goncourt and his second wife Annette-Cécile de Goncourt (née Guérin). Marc-Pierre was a retired cavalry officer and squadron leader in the Grande Armée of Napoléon I. The brothers' great-grandfather, Antoine Huot de Goncourt, purchased the '' seigneurie'' of the village of Goncourt in the Meuse Valley in 1786, and their grandfather Huot sat as a deputy in the National Assembly of 1789. The brothers' uncle, Pierre Antoine Victor Huot de Goncourt, was a deputy for the Vosges in the National Assembly between 1848 and 1851. In 1860, the brothers applied to the Keeper of the Seals for the exclusive use of the noble title "de Goncourt", but their claim was refused. They are buried together (in the same ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
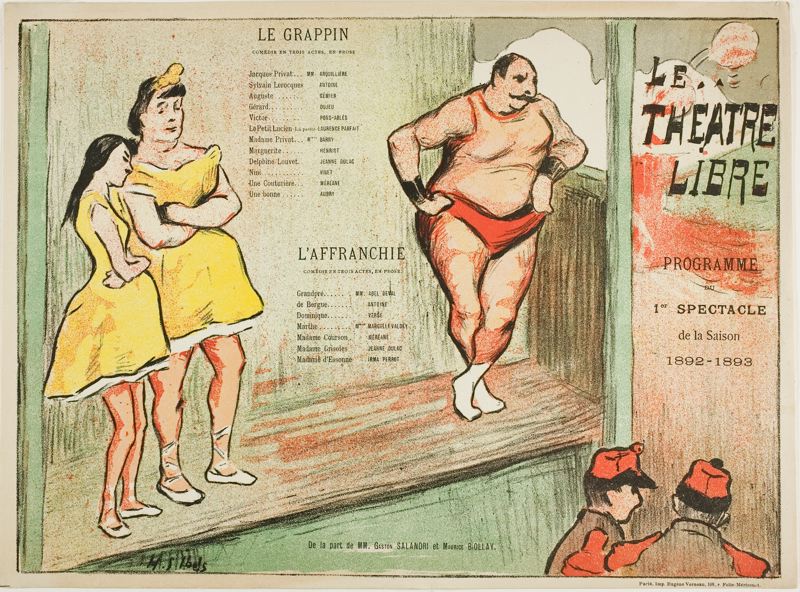
Théâtre Libre
The Théâtre Libre (; "Free Theatre") was a theatre company that operated from 1887 to 1896 in Paris, France. Origins and History Théâtre Libre was founded on 30 March 1887 by André Antoine (actor), André Antoine. The primary goal of the theatre was to present new plays that were untried and unproduced by the commercial houses. Antoine was driven to open his own theatre company to create a dramatization of an Émile Zola novel, ''Thérèse Raquin'', after the theater group for which he previously worked had refused. In order to ensure that the Théâtre Libre was exempt from censorship and could produce plays that other theaters would not, the theatre was supported solely by subscribers. This allowed the Théâtre Libre to collect no money at the door meaning it was not legally considered a theatre. Being a "free" theatre, in the case of Théâtre Libre, meant being a theatre that presented naturalism and was dedicated to producing plays in any and all genres that had not b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Comédie-Française
The Comédie-Française () or Théâtre-Français () is one of the few state theatres in France. Founded in 1680, it is the oldest active theatre company in the world. Established as a French state-controlled entity in 1995, it is the only state theatre in France to have its own permanent troupe of actors. The company's primary venue is the Salle Richelieu, which is a part of the Palais-Royal complex and located at 2, Rue de Richelieu on Place André-Malraux in the 1st arrondissement of Paris. The theatre has also been known as the Théâtre de la République and popularly as "La Maison de Molière" (The House of Molière). It acquired the latter name from the troupe of the best-known playwright associated with the Comédie-Française, Molière. He was considered the patron of French actors. He died seven years before his troupe became known as the Comédie-Française, but the company continued to be known as "La Maison de Molière" even after the official change of name. Hist ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Goncourt Journal
The Goncourt Journal was a diary written in collaboration by the brothers Edmond de Goncourt, Edmond and Jules de Goncourt from 1850 up to Jules' death in 1870, and then by Edmond alone up to a few weeks before his own death in 1896. It forms an unrivalled and entirely candid chronicle of the literary and artistic Parisian world in which they lived; "a world", it has been said, "of bitter rivalries and bitterer friendships, in which every gathering around a café table on the Boulevards of Paris#The grands boulevards, Grands Boulevards [was] a chance to raise one's status in the byzantine literary hierarchy". Fear of lawsuits by the Goncourts' friends and their heirs prevented publication of anything but carefully chosen selections from the Journal for many years, but a complete edition of the original French text appeared in the 1950s in 22 volumes, and there have been several selective translations into English. The process of collaboration The Goncourt brothers formed a ver ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Montmartre Cemetery
The Cemetery of Montmartre () is a cemetery in the 18th arrondissement of Paris, France, that dates to the early 19th century. Officially known as the Cimetière du Nord, it is the third largest necropolis in Paris, after the Père Lachaise Cemetery and the Montparnasse Cemetery. History In the mid-18th century, overcrowding in the cemeteries of Paris had created numerous problems, from impossibly high funeral costs to unsanitary living conditions in the surrounding neighborhoods. In the 1780s, the Cimetière des Innocents was officially closed and citizens were banned from burying corpses within the city limits of Paris. During the early 19th century, new cemeteries were constructed outside the precincts of the capital: Montmartre in the north, Père Lachaise Cemetery in the east, Passy Cemetery in the west and Montparnasse Cemetery in the south. The Montmartre Cemetery was opened on 1 January 1825. It was initially known as le Cimetière des Grandes Carrières (Cemetery of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Journal Des Goncourt
The Goncourt Journal was a diary written in collaboration by the brothers Edmond and Jules de Goncourt from 1850 up to Jules' death in 1870, and then by Edmond alone up to a few weeks before his own death in 1896. It forms an unrivalled and entirely candid chronicle of the literary and artistic Parisian world in which they lived; "a world", it has been said, "of bitter rivalries and bitterer friendships, in which every gathering around a café table on the Grands Boulevards asa chance to raise one's status in the byzantine literary hierarchy". Fear of lawsuits by the Goncourts' friends and their heirs prevented publication of anything but carefully chosen selections from the Journal for many years, but a complete edition of the original French text appeared in the 1950s in 22 volumes, and there have been several selective translations into English. The process of collaboration The Goncourt brothers formed a very close literary partnership. Not only were all of their novels, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
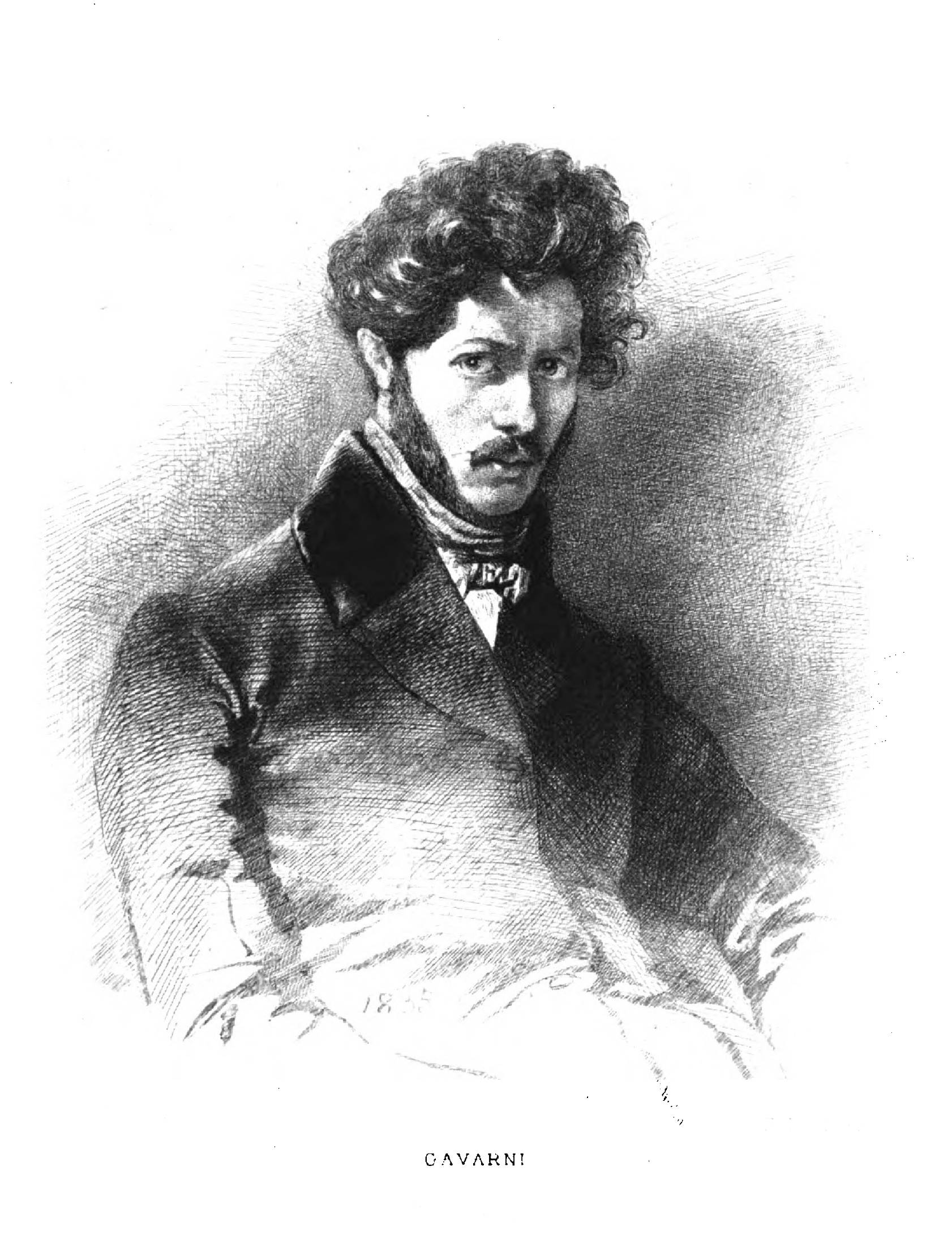
Paul Gavarni
Paul Gavarni was the pen name of Sulpice Guillaume Chevalier (13 January 1804 – 24 November 1866), a French illustrator, born in Paris. Early career Gavarni's father, Sulpice Chevalier, was from a family line of coopers from Burgundy. Paul began work as a mechanical worker in a machine factory but he saw that to make any progress in his profession, he had to be able to draw; accordingly in his spare time in the evenings, he took classes in drawing. He devoted his special attention to architectural and mechanical drawing and worked at land surveying and mapping which led to his obtaining a position with the Government Ordnance Department as a draughtsman.''Frank Leslie's Popular Monthly'' Vol. 20 (1885) pp. 615–619, Frank Leslie's Publishing House, New York It wasn't until his early thirties that he turned his ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marie Anne De Mailly-Nesle
Marie Anne de Mailly-Nesle, duchesse de Châteauroux (; 5 October 1717 – 8 December 1744) was the youngest of the five famous ''de Nesle'' sisters, four of whom would become the mistress of King Louis XV of France. She was his mistress from 1742 until 1744. Early life, family and marriage Marie Anne was born the youngest daughter of Louis de Mailly, Marquis de Nesle et de Mailly, Prince d'Orange (1689 - 1767), and Armande Félice de La Porte Mazarin (1691 - 1729). Her parents had been married in 1709. Her mother was the daughter of Paul Jules de La Porte, duc Mazarin et de La Meilleraye (1666 - 1731), the son of the famous adventuress, Hortense Mancini, the niece of Cardinal Mazarin. Her mother was a lady-in-waiting in service to the queen, and her father reportedly "wasted his substance on actresses and the capacious requirements of Court life".Latour, Louis Therese, Princesses Ladies And Salonnieres of The Reign of Louis XV', 1927 Marie Anne had four older full sisters: ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Madame Du Barry
Jeanne Bécu, comtesse du Barry (; 28 August 1744 – 8 December 1793) was the last ''maîtresse-en-titre'' of King Louis XV of France. She was executed by guillotine during the French Revolution on accusations of treason—particularly being suspected of assisting ''émigrés'' to flee from the Revolution. She is also known as "Mademoiselle Vaubernier" (). In 1768, when the king wished to make Jeanne ''maîtresse-en-titre'', etiquette required her to be the wife of a high courtier, so she was hastily married on 1 September 1768 to Comte Guillaume du Barry. The wedding ceremony was accompanied by a false birth certificate created by Jean-Baptiste du Barry, the comte's older brother. The certificate made Jeanne appear younger by three years and obscured her poor background. Henceforth, she was recognised as the king's official paramour. Her arrival at the French royal court scandalised some, as she had been a courtesan and came from humble beginnings. She was shunned by many i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Madame De Pompadour
Jeanne Antoinette Poisson, Marquise de Pompadour (, ; 29 December 1721 – 15 April 1764), commonly known as Madame de Pompadour, was a member of the French court. She was the official chief mistress of King Louis XV from 1745 to 1751, and remained influential as court favourite until her death. Pompadour took charge of the king's schedule and was a valued aide and advisor, despite her frail health and many political enemies. She secured titles of nobility for herself and her relatives, and built a network of clients and supporters. She was particularly careful not to alienate the popular Queen, Marie Leszczyńska. On 8 February 1756, the Marquise de Pompadour was named as the thirteenth lady-in-waiting to the queen, a position considered the most prestigious at the court, which accorded her with honors. Pompadour was a major patron of architecture and decorative arts, especially porcelain. She was a patron of the '' philosophes'' of the Enlightenment, including Voltaire. H ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |