|
Juansher
Juansher was the Mihranids, Mihranid prince of Caucasian Albania, ruling the principality from 637 to 669. He was the son and successor of Varaz Grigor (). During his reign, Juansher changed his allegiance thrice. He started out as a subject to the Sasanian Empire, under which he fought against the Muslim conquest of Persia, Arab-Islamic invasion of Iran (632–654). Realizing the impending downfall of the Sasanians, he withdrew to Albania, where he rebelled. Although he briefly lost control over the Albanian lowlands and its capital, Barda, Azerbaijan, Partaw, his guerrilla warfare forced the Sasanians to grant him more autonomy. Following the fall of the Sasanian Empire in 651, Juansher's father seemingly became the leader of Albania once more, due to his seniority. He took the safe route by acknowledging the suzerainty of the Rashidun Caliphate, but also instructed Juansher to establish contact with the Byzantine Empire, Byzantine emperor Constans II () and offer his services ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Davtak Kertogh
Davtak Kertogh () was a 7th-century Armenian poet who authored the first known work of Armenian poetry on a secular subject. He is the author of "Elegy on the Death of the Great Prince Jevansher" (""), dedicated to Juansher, a 7th-century prince of Caucasian Albania who was murdered by a traitor, The only information that has survived about Davtak comes from the history History is the systematic study of the past, focusing primarily on the Human history, human past. As an academic discipline, it analyses and interprets evidence to construct narratives about what happened and explain why it happened. Some t ... attributed to Movses Kaghankatvatsi, in which Davtak's elegy for Juansher—his only known work—is recorded. According to Movses, Davtak was a guest at the royal court in Partav, the capital of Caucasian Albania, when Juansher was assassinated (669). This indicates that Davtak was a figure of some renown in Caucasian Albania. Movses praises Davtak, but gives no ot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
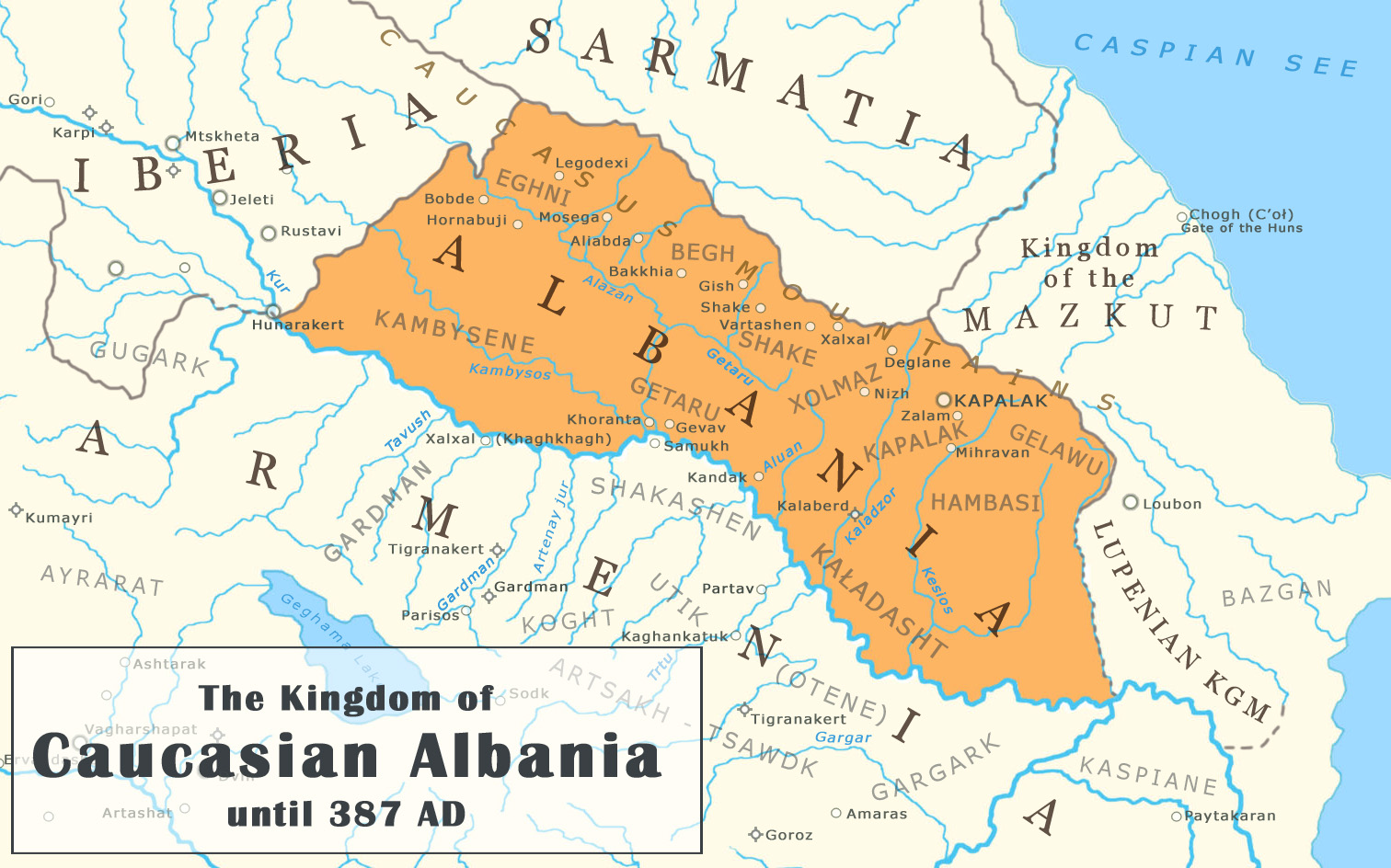
Caucasian Albania
Caucasian Albania is a modern exonym for a former state located in ancient times in the Caucasus, mostly in what is now Azerbaijan (where both of its capitals were located). The modern endonyms for the area are ''Aghwank'' and ''Aluank'', among the Udi people, who regard themselves as descended from the inhabitants of Caucasian Albania. However, its original endonym is unknown. The name Albania is derived from the Ancient Greek name and Latin , created from Greek sources that incorrectly translated the Armenian language. The prefix "Caucasian" is used to avoid confusion with Albania in the Balkans, which has no geographical or historical connections to Caucasian Albania. Little is known of the region's prehistory, including the origins of Caucasian Albania as a geographical and/or ethnolinguistic concept. In the 1st century BC and the 1st century AD, the area south of the Greater Caucasus and north of the Lesser Caucasus was divided between Caucasian Albania in the east, Kingd ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Varaz Grigor
Varaz Grigor () was the first known Mihranid king of Caucasian Albania from 628 until at least 654. The last holder of the title was Vachagan III. Before reign Although mentioned in '' The History of the Country of Albania'' numerously, almost nothing prior to his reign is known. He was son of Vard II, the Prince of Gardman and had a sister called Shushik. He succeeded his father before his accession to the throne of Albania in 628. Like other Gardman rulers, he was of the Mihranid stock and according to Movses Kaghankatvatsi he was baptized by Catholicos Viro. Cyril Toumanoff believes that it was simply a rebaptism from monophysite doctrine to Chalcedonian doctrine. According to Constantin Zuckerman, however, his Zoroastrian name may have been Gadvšnasp prior to his conversion to Christianity, and he used the opportunity to become the ruler of the kingdom. Reign He rose to prominence during Byzantine–Sasanian War of 602–628, gaining the trust of Byzantine emperor Her ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Khosrow II
Khosrow II (spelled Chosroes II in classical sources; and ''Khosrau''), commonly known as Khosrow Parviz (New Persian: , "Khosrow the Victorious"), is considered to be the last great Sasanian King of Kings (Shahanshah) of Iran, ruling from 590 to 628, with an interruption of one year. Khosrow II was the son of Hormizd IV (reigned 579–590), and the grandson of Khosrow I (reigned 531–579). He was the last king of Iran to have a lengthy reign before the Muslim conquest of Iran, which began five years after his execution. He lost his throne, then recovered it with the help of the Byzantine emperor Maurice, and, a decade later, went on to emulate the feats of the Achaemenids, conquering the rich Roman provinces of the Middle East; much of his reign was spent in wars with the Byzantine Empire and struggling against usurpers such as Bahram Chobin and Vistahm. Khosrow II began a war against the Byzantines in 602, ostensibly to avenge the murder of his ally Maurice. Persian fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Museum Of History Of Azerbaijan
The National Museum of History of Azerbaijan () is the largest museum in Azerbaijan. It is located in Baku, in the former residential house of Azerbaijani oil magnate and philanthropist Haji Zeynalabdin Taghiyev. The museum was founded in 1920, following the Russian takeover of Baku, and opened to visitors in 1921. History The museum's building was constructed between 1895 and 1901, originally as a residence for the Taghiyev family. It was designed by Polish architect Józef Gosławski, in imitation of the Italian Renaissance style. It is large, stretching over an entire block and reaching four floors in some parts. Since 1914, Baku Commercial Bank, which was headed by Taghiyev, had been situated in the mansion. When the Red Army entered Baku in April 1920, Taghiyev's residence was immediately confiscated. Under a resolution of the USSR People's Commissariat, the residence was established as the State Historical Museum in June 1920, just two months after the Bolsheviks took B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Siwnik
Syunik (, ) is the southernmost administrative divisions of Armenia, province of Armenia. It is bordered by the Vayots Dzor Province to the north, Azerbaijan's Nakhchivan Autonomous Republic exclave to the west, Azerbaijan to the east, and Iran to the south. Its capital and largest city is the town of Kapan. The Statistical Committee of Armenia reported its population was 141,771 in the 2011 census, down from 152,684 at the 2001 census. Etymology Syunik (historical province), Syunik was one of the 15 provinces of the Kingdom of Armenia (Antiquity), Kingdom of Armenia. The early Armenian historian Movses Khorenatsi connected the name of the province with Sisak (eponym), Sisak, a descendant of the legendary Armenian patriarch Hayk and supposed progenitor of the ancient Siunia dynasty, Siunia (or Syunik) dynasty, which ruled Syunik from the first century BC. However, historian Robert H. Hewsen, Robert Hewsen considered Sisak to be a later eponym. Historian Armen Petrosyan sugges ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arabic
Arabic (, , or , ) is a Central Semitic languages, Central Semitic language of the Afroasiatic languages, Afroasiatic language family spoken primarily in the Arab world. The International Organization for Standardization (ISO) assigns language codes to 32 varieties of Arabic, including its standard form of Literary Arabic, known as Modern Standard Arabic, which is derived from Classical Arabic. This distinction exists primarily among Western linguists; Arabic speakers themselves generally do not distinguish between Modern Standard Arabic and Classical Arabic, but rather refer to both as ( "the eloquent Arabic") or simply ' (). Arabic is the List of languages by the number of countries in which they are recognized as an official language, third most widespread official language after English and French, one of six official languages of the United Nations, and the Sacred language, liturgical language of Islam. Arabic is widely taught in schools and universities around the wo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Medieval Greek
Medieval Greek (also known as Middle Greek, Byzantine Greek, or Romaic; Greek: ) is the stage of the Greek language between the end of classical antiquity in the 5th–6th centuries and the end of the Middle Ages, conventionally dated to the Ottoman conquest of Constantinople in 1453. From the 7th century onwards, Greek was the only language of administration and government in the Byzantine Empire. This stage of language is thus described as Byzantine Greek. The study of the Medieval Greek language and literature is a branch of Byzantine studies, the study of the history and culture of the Byzantine Empire. The conquests of Alexander the Great, and the ensuing Hellenistic period, had caused Greek to spread throughout Anatolia and the Eastern Mediterranean. The beginning of Medieval Greek is occasionally dated back to as early as the 4th century, either to 330 AD, when the political centre of the Roman Empire was moved to Constantinople, or to 395 AD, the division o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Caucasian Albanian Language
Caucasian Albanian (also called Old Udi, Aluan or Aghwan) is an extinct member of the Northeast Caucasian languages. It was spoken in Caucasian Albania, which stretched from current day south Dagestan to Azerbaijan. Linguists believe it is an early linguistic predecessor to the endangered Northeast Caucasian Udi language. The distinct Caucasian Albanian alphabet used 52 letters. Caucasian Albanian possibly corresponds to the "Gargarian" language identified by medieval Armenian historians. Despite its name, Caucasian Albanian bears no linguistic relationship whatsoever with the Albanian language spoken in Albania, which belongs to the Indo-European family. Discovery and decipherment The existence of the Caucasian Albanian literature was known only indirectly before the late 20th century. Koryun's ''Life of Mashtots'', written in the 5th century but only surviving in much later corrupted manuscripts, and Movses Kaghankatvatsi's ''History of the Caucasian Albanians'', written i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Armenian Language
Armenian (endonym: , , ) is an Indo-European languages, Indo-European language and the sole member of the independent branch of the Armenian language family. It is the native language of the Armenians, Armenian people and the official language of Armenia. Historically spoken in the Armenian highlands, today Armenian is also widely spoken throughout the Armenian diaspora. Armenian is written in its own writing system, the Armenian alphabet, introduced in 405 AD by Saint Mesrop Mashtots. The estimated number of Armenian speakers worldwide is between five and seven million. History Classification and origins Armenian is an independent branch of the Indo-European languages. It is of interest to linguists for its distinctive phonological changes within that family. Armenian exhibits Centum and satem languages, more satemization than centumization, although it is not classified as belonging to either of these subgroups. Some linguists tentatively conclude that Armenian, Greek ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Middle Persian
Middle Persian, also known by its endonym Pārsīk or Pārsīg ( Inscriptional Pahlavi script: , Manichaean script: , Avestan script: ) in its later form, is a Western Middle Iranian language which became the literary language of the Sasanian Empire. For some time after the Sasanian collapse, Middle Persian continued to function as a prestige language. It descended from Old Persian, the language of the Achaemenid Empire and is the linguistic ancestor of Modern Persian, the official language of Iran (also known as Persia), Afghanistan ( Dari) and Tajikistan ( Tajik). Name "Middle Iranian" is the name given to the middle stage of development of the numerous Iranian languages and dialects. The middle stage of the Iranian languages begins around 450 BCE and ends around 650 CE. One of those Middle Iranian languages is Middle Persian, i.e. the middle stage of the language of the Persians, an Iranian people of Persia proper, which lies in the south-western Iran highlands on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gardman
Gardman (), also known as Gardmank' or Gardmanadzor, was one of the eight cantons of the ancient province of Utik' in the Kingdom of Armenia and simultaneously, together with the canton of Tuch'katak, an Armenian principality. It roughly corresponded within the Gazakh, Shamkir, Aghstafa, Dashkasan, Goygol, Tovuz, Gadabay districts of modern-day Azerbaijan and the original Tavush Region of Armenia. Gardman was also the name of the central fortress of the canton. History In the view of historian Robert H. Hewsen, the name Gardman might be of Georgian origin. Many contemporary Armenian authors referred to Gardman as a part of the ('province, land') of Artsakh. During the reign of the Arsacid kings of Armenia (66–428 A.D.), Gardman was the seat of the of Utik'. For this reason, Utik' was sometimes called , or the principality of the Gardmanians. Gardman was acquired by Caucasian Albania in 387 following the partition of Armenia. In the seventh century, the local hou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |