|
Joint Probability Distribution
A joint or articulation (or articular surface) is the connection made between bones, ossicles, or other hard structures in the body which link an animal's skeletal system into a functional whole.Saladin, Ken. Anatomy & Physiology. 7th ed. McGraw-Hill Connect. Webp.274/ref> They are constructed to allow for different degrees and types of movement. Some joints, such as the knee, elbow, and shoulder, are self-lubricating, almost frictionless, and are able to withstand compression and maintain heavy loads while still executing smooth and precise movements. Other joints such as suture (joint), sutures between the bones of the skull permit very little movement (only during birth) in order to protect the brain and the sense organs. The connection between a tooth and the jawbone is also called a joint, and is described as a fibrous joint known as a gomphosis. Joints are classified both structurally and functionally. Joints play a vital role in the human body, contributing to movement, sta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Synovial Joint
A synovial joint, also known as diarthrosis, joins bones or cartilage with a fibrous joint capsule that is continuous with the periosteum of the joined bones, constitutes the outer boundary of a synovial cavity, and surrounds the bones' articulating surfaces. This joint unites long bones and permits free bone movement and greater mobility. The synovial cavity/joint is filled with synovial fluid. The joint capsule is made up of an outer layer of fibrous membrane, which keeps the bones together structurally, and an inner layer, the synovial membrane, which seals in the synovial fluid. They are the most common and most movable type of joint in the body. As with most other joints, synovial joints achieve movement at the point of contact of the articulating bones. They originated 400 million years ago in the first jawed vertebrates. Structure Synovial joints contain the following structures: * Synovial cavity: all diarthroses have the characteristic space between the bones that is f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fibrous Joint
In anatomy, fibrous joints are joints connected by Fibrous connective tissue, fibrous tissue, consisting mainly of collagen. These are fixed joints where bones are united by a layer of white fibrous tissue of varying thickness. In the skull, the joints between the bones are called Suture (anatomy), sutures. Such immovable joints are also referred to as synarthrosis, synarthroses. Types Most fibrous joints are also called "fixed" or "immovable". These joints have no joint cavity and are connected via fibrous connective tissue. * Suture (anatomy), Sutures: The skull bones are connected by fibrous joints called ''#Sutures, sutures''. In fetus, fetal skulls, the sutures are wide to allow slight movement during birth. They later become rigid (synarthrosis, synarthrodial). * Syndesmosis: Some of the long bones in the body such as the radius (bone), radius and ulna in the forearm are joined by a ''#Syndesmosis, syndesmosis'' (along the interosseous membrane of forearm, interosseous mem ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pivot Joint
In animal anatomy, a pivot joint (trochoid joint, rotary joint or lateral ginglymus) is a type of synovial joint whose movement axis is parallel to the long axis of the proximal bone, which typically has a convex articular surface. According to one classification system, a pivot joint like the other synovial joint—the hinge joint has one degree of freedom.Platzer, Werner (2008) ''Color Atlas of Human Anatomy'', Volume 1p.28/ref> Note that the degrees of freedom of a joint is not the same as a joint's range of motion. Movements Pivot joints allow rotation Rotation or rotational/rotary motion is the circular movement of an object around a central line, known as an ''axis of rotation''. A plane figure can rotate in either a clockwise or counterclockwise sense around a perpendicular axis intersect ..., which can be external (for example when rotating an arm outward), or internal (as in rotating an arm inward). When rotating the forearm, these movements are typically ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hinge Joint
A hinge joint (ginglymus or ginglymoid) is a bone joint where the articular surfaces are molded to each other in such a manner as to permit motion only in one plane. According to one classification system they are said to be uniaxial (having one degree of freedom).Platzer, Werner (2008) ''Color Atlas of Human Anatomy', Volume 1p.28/ref> The direction which the distal bone takes in this motion is rarely in the same plane as that of the axis of the proximal bone; there is usually a certain amount of deviation from the straight line during flexion. The articular surfaces of the bones are connected by strong collateral ligaments. Examples of ginglymoid joints are the interphalangeal joints of the hand and those of the foot and the joint between the humerus and ulna. The knee joints and ankle joints are less typical, as they allow a slight degree of rotation or side-to-side movement in certain positions of the limb. The knee is the largest hinge joint in the human body ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
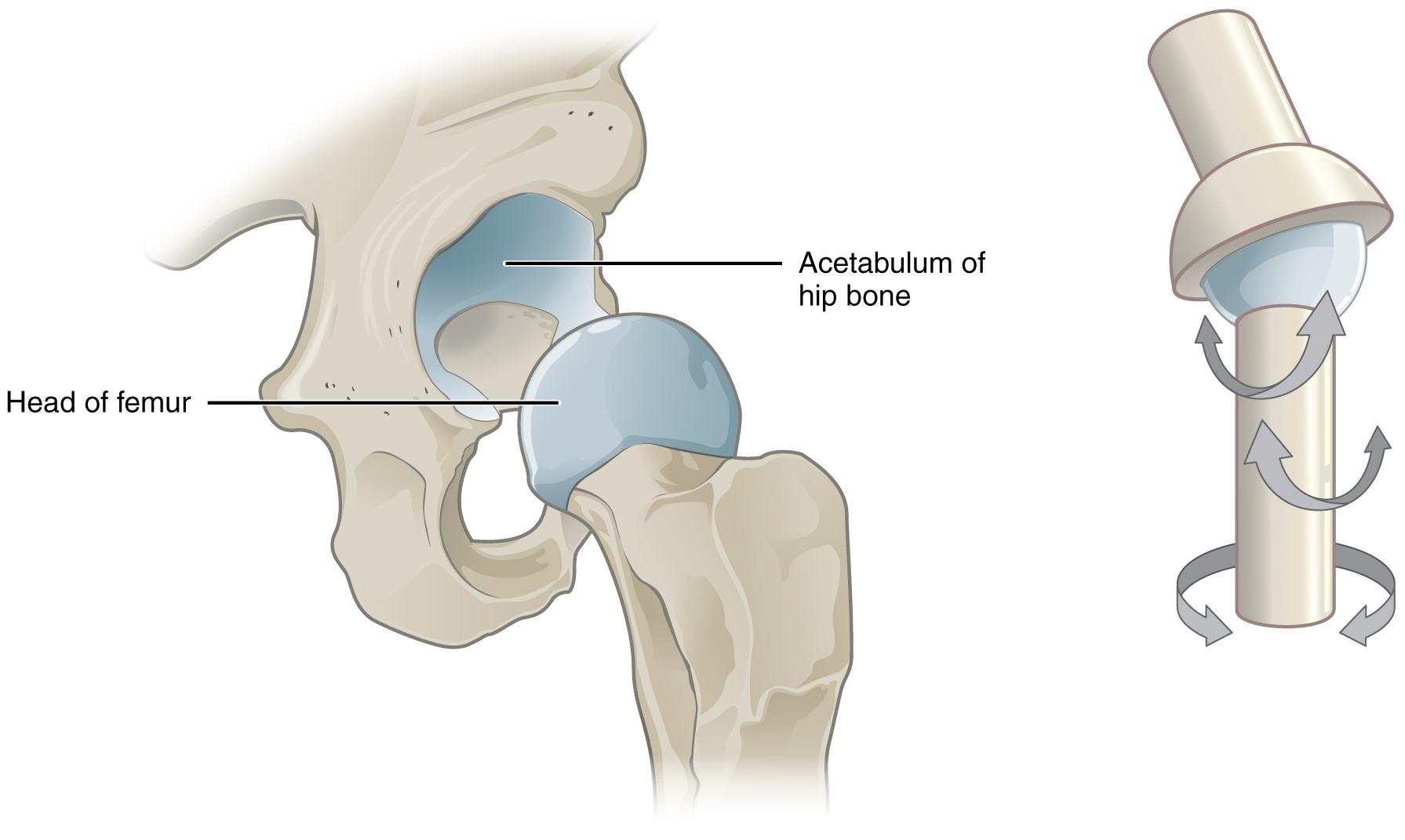
Ball And Socket Joint
The ball-and-socket joint (or spheroid joint) is a type of synovial joint in which the ball-shaped surface of one rounded bone fits into the cup-like depression of another bone. The distal bone is capable of motion around an indefinite number of axes, which have one common center. This enables the joint to move in many directions. An enarthrosis is a special kind of spheroidal joint in which the socket covers the sphere beyond its equator.Platzer, Werner (2008) ''Color Atlas of Human Anatomy'', Volume 1p.28/ref> Examples of joints Examples of this form of articulation are found in the hip, where the round head of the femur (ball) rests in the cup-like acetabulum (socket) of the pelvis The pelvis (: pelves or pelvises) is the lower part of an Anatomy, anatomical Trunk (anatomy), trunk, between the human abdomen, abdomen and the thighs (sometimes also called pelvic region), together with its embedded skeleton (sometimes also c ...; and in the shoulder joint, where the rou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plane Joint
A plane joint (arthrodial joint, gliding joint, plane articulation) is a synovial joint A synovial joint, also known as diarthrosis, joins bones or cartilage with a fibrous joint capsule that is continuous with the periosteum of the joined bones, constitutes the outer boundary of a synovial cavity, and surrounds the bones' articulati ... which, under physiological conditions, allows only gliding movement. Plane joints permit sliding movements in the plane of articular surfaces. The opposed surfaces of the bones are flat or almost flat, with movement limited by their tight joint capsules. Based only on their shape, plane joints can allow multiple movements, including rotation. Thus plane joints can be functionally classified as multiaxial joints. Plane joints are numerous and are nearly always small, such as the acromioclavicular joint between the acromion of the scapula and the clavicle. Typically, they are found in the wrists, ankles, the 2nd through 7th sternocostal j ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amphiarthrosis
Amphiarthrosis is a type of continuous, slightly movable joint. Most amphiarthroses are held together by cartilage, as a result of which limited movements between the bones are made possible. An example is the joints of the vertebral column, which only allow for small movements between adjacent vertebrae. However, when combined, these movements provide the flexibility that allows the body to twist, bend forward, backwards, or to the side. Types In amphiarthroses, the contiguous bony surfaces can be: * A symphysis: connected by broad flattened disks of fibrocartilage, of a more or less complex structure, which adhere to the ends of each bone, as in the articulations between the bodies of the vertebrae or the inferior articulation of the two hip bones (aka the pubic symphysis). The strength of the pubic symphysis is important in conferring weight-bearing stability to the pelvis. * An interosseous membrane - the sheet of connective tissue joining neighboring bones (e.g. tibia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Synarthrosis
A synarthrosis is a type of joint which allows no movement under normal conditions. Sutures and gomphoses are both synarthroses. Joints which allow more movement are called amphiarthroses or diarthroses. Syndesmoses are considered to be amphiarthrotic, because they allow a small amount of movement. Types They can be categorised by how the bones are joined together: *'' Gomphosis'' is the type of joint in which a conical peg fits into a socket, for example, the socket of a tooth. Normally, there is very little movement of the teeth in the mandible or maxilla. *'' Synostosis'' is where two bones that are initially separated eventually fuse, essentially becoming one bone. In humans, as in other animals, the plates of the cranium fuse with dense fibrous connective tissue as a child approaches adulthood.Principles of Anatomy & Physiology, 12th Edition, Tortora & Derrickson, Pub: Wiley & Sons Children whose cranial plates fuse too early may suffer deformities and brain damage as th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anatomical Planes
An anatomical plane is a hypothetical plane used to transect the body, in order to describe the location of structures or the direction of movements. In human anatomy and non-human anatomy, four principal planes are used: the median plane, sagittal plane, coronal plane, and transverse plane. * The median plane or midsagittal plane passes through the middle of the body, dividing it into left and right halves. * A para sagittal plane is any plane that runs parallel to the median plane, also dividing the body into left and right sections. * The dorsal plane divides the body into dorsal (towards the backbone) and ventral (towards the belly) parts. In human anatomy coronal plane is preferred, or sometimes the frontal plane, and the description may reference splitting the body into front and back parts, but this phrasing is not as clear for animals with a horizontal spine like quadrupeds or fish. * The transverse plane, also called the axial plane or horizontal plane, is perpe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Process (anatomy)
In anatomy, a process () is a projection or outgrowth of tissue from a larger body. For instance, in a vertebra, a process may serve for muscle attachment and leverage (as in the case of the transverse and spinous processes), or to fit (forming a synovial joint A synovial joint, also known as diarthrosis, joins bones or cartilage with a fibrous joint capsule that is continuous with the periosteum of the joined bones, constitutes the outer boundary of a synovial cavity, and surrounds the bones' articulati ...), with another vertebra (as in the case of the articular processes).Moore, Keith L. et al. (2010) ''Clinically Oriented Anatomy'', 6th Ed, p.442 fig. 4.2 The word is also used at the microanatomic level, where cells can have processes such as cilia or pedicels. Depending on the tissue, processes may also be called by other terms, such as ''apophysis'', '' tubercle'', or ''protuberance''. Examples Examples of processes include: *The many processes of the human skull: ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
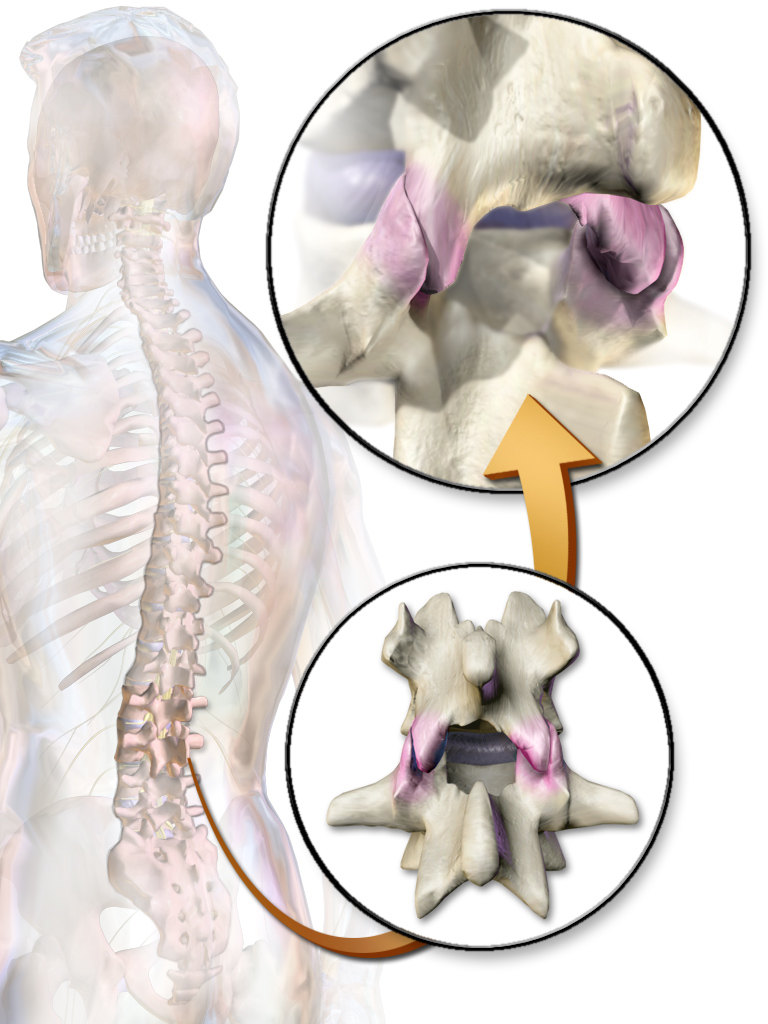
Facet Joint
The facet joints (also zygapophysial joints, zygapophyseal, apophyseal, or Z-joints) are a set of synovial joint, synovial, plane joints between the articular processes of two adjacent vertebrae. There are two facet joints in each functional spinal unit, spinal motion segment and each facet joint is innervated by the Meningeal branches of spinal nerve, recurrent meningeal nerves. Innervation Innervation to the facet joints vary between segments of the spinal, but they are generally innervated by medial branch nerves that come off the dorsal rami. It is thought that these nerves are for primary sensory input, though there is some evidence that they have some motor input local musculature. Within the cervical spine, most joints are innervated by the medial branch nerve (a branch of the dorsal rami) from the same levels. In other words, the facet joint between C4 and C5 vertebral segments is innervated by the C4 and C5 medial branch nerves. However, there are two exceptions: # T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fibrocartilage
Fibrocartilage consists of a mixture of white fibrous tissue and cartilaginous tissue in various proportions. It owes its inflexibility and toughness to the former of these constituents, and its elasticity to the latter. It is the only type of cartilage that contains type I collagen in addition to the normal type II. Structure The extracellular matrix of fibrocartilage is mainly made from type I collagen secreted by chondroblasts. Locations of fibrocartilage in the human body * secondary cartilaginous joints: ** pubic symphysis ** annulus fibrosis of intervertebral discs ** manubriosternal joint * glenoid labrum of shoulder joint * acetabular labrum of hip joint * medial and lateral menisci of the knee joint * location where tendons and ligaments attach to bone * triangular fibrocartilage complex (UTFCC) Function Repair If hyaline cartilage is torn all the way down to the bone, the blood supply from inside the bone is sometimes enough to start some heal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |