|
Johannes De Sacrobosco
Johannes de Sacrobosco, also written Ioannes de Sacro Bosco, later called John of Holywood or John of Holybush ( 1195 – 1256), was a scholar, Catholic monk, and astronomer who taught at the University of Paris. He wrote a short introduction to the Hindu-Arabic numeral system. Judging from the number of manuscript copies that survive today, for the next 400 years it became the most widely read book on that subject. He also wrote a short textbook which was widely read and influential in Europe during the later medieval centuries as an introduction to astronomy. In his longest book, on the computation of the date of Easter, Sacrobosco correctly described the defects of the then-used Julian calendar, and recommended a solution similar to the modern Gregorian calendar three centuries before its implementation. Very little is known about the education and biography of Sacrobosco. For one thing, his year of death has been guessed at 1236, 1244, and 1256, each of which is pl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nithsdale
Nithsdale (), also known as Strathnith, Stranith or Stranit, is the strath or dale (landform), dale of the River Nith in southern Scotland. Nithsdale was one of the medieval provinces of Scotland. The provinces gradually lost their administrative importance to the shires of Scotland, shires created from the twelfth century, with Nithsdale forming part of Dumfriesshire. A Nithsdale districts of Scotland, district covering a similar area to the medieval province was created in 1975, based in the area's main town of Dumfries. The district was abolished in 1996, since when the area has been directly administered by Dumfries and Galloway Council. History The name ''Strath Nid'' may represent the Cumbric ''Ystrad Nidd''; Cumbric (a variety of Common Brittonic) was the dominant language in this area from before Roman times until the 11th or 12th century, whereas Gaelic influence here was late and transient. The River Nith flows north to south through the Southern Uplands in south-wes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Of Oxford
The University of Oxford is a collegiate university, collegiate research university in Oxford, England. There is evidence of teaching as early as 1096, making it the oldest university in the English-speaking world and the List of oldest universities in continuous operation, second-oldest continuously operating university globally. It expanded rapidly from 1167, when Henry II of England, Henry II prohibited English students from attending the University of Paris. When disputes erupted between students and the Oxford townspeople, some Oxford academics fled northeast to Cambridge, where they established the University of Cambridge in 1209. The two English Ancient university, ancient universities share many common features and are jointly referred to as ''Oxbridge''. The University of Oxford comprises 43 constituent colleges, consisting of 36 Colleges of the University of Oxford, semi-autonomous colleges, four permanent private halls and three societies (colleges that are depar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
County Wicklow
County Wicklow ( ; ) is a Counties of Ireland, county in Republic of Ireland, Ireland. The last of the traditional 32 counties, having been formed as late as 1606 in Ireland, 1606, it is part of the Eastern and Midland Region and the Provinces of Ireland, province of Leinster. It is bordered by the Irish Sea to the east and the counties of County Wexford, Wexford to the south, County Carlow, Carlow to the southwest, County Kildare, Kildare to the west, and South Dublin and Dún Laoghaire–Rathdown to the north. Wicklow is named after its county town of Wicklow, which derives from the name (Old Norse for "Vikings' Meadow"). Wicklow County Council is the Local government in the Republic of Ireland, local authority for the county, which had a population of 155,258 at the 2022 census of Ireland, 2022 census. Colloquially known as the "Garden of Ireland" for its scenerywhich includes extensive woodlands, nature trails, beaches, and ancient ruins while allowing for a multitude of w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Olaf Pedersen
Olaf Pedersen (8 April 1920 – 3 December 1997) was a Danish historian of science who was "leading authority on astronomy in classical antiquity and the Latin middle ages."Michael Hoskin (October 1998Obituary: Olaf Pedersen Astronomy and Geophysics 39(5):33,4 Pedersen was active in the journal Centaurus, the Steno Museum, the International Union of History and Philosophy of Science, and the International Academy of the History of Science. Biography Olaf Pedersen was born in Egtved, Jutland, Denmark. At the University of Copenhagen he studied in Niels Bohr’s institute, graduating in 1943 when the country was occupied by German forces. He began his teaching career in Randers, Jutland, teaching physics. He entered scholarship studying the philosophy and history of ideas. After the war he studied with Etienne Gilson in Paris. Returning to Denmark, he obtained a doctorate for work on Nicole Oresme in 1956, when he became a lecturer at Aarhus University. In 1965 a departmen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Holywood, County Down
Holywood ( ; ) is a town in the metropolitan area of Belfast in County Down, Northern Ireland. It is a Holywood, County Down (civil parish), civil parish and townland of lying on the shore of Belfast Lough, between Belfast and Bangor, County Down, Bangor. Holywood Exchange and Belfast City Airport are nearby. Toponymy The English name ''Holywood'' comes . This was the name the Normans gave to the woodland surrounding the monastery of St Laiseran, son of Nasca. The monastery was founded by Laiseran before 640 and was on the site of the present Holywood Priory. The earliest Anglicised form appears as ''Haliwode'' in a 14th-century document. The Irish language, Irish name for Holywood is ''Ard Mhic Nasca'' meaning "high ground of Mac Nasca". History In the early 19th century, Holywood, like many other coastal villages throughout Ireland, became popular as a Seaside resort, resort for bathing, sea-bathing. Many wealthy Belfast merchants chose the town and the surrounding area to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Richard Stanihurst
Richard Stanyhurst (or Stanihurst) (1547–1618) was an Anglo-Irish alchemist, translator, poet and historian, who was born in Dublin. Life His father, James Stanyhurst, was Recorder of Dublin, and Speaker of the Irish House of Commons in 1557, 1560 and 1568. His grandfather was Nicholas Stanihurst, Mayor of Dublin in 1543. His mother was Anne Fitzsimon, daughter of Thomas Fitzsimon, Recorder of Dublin. Richard was sent to Peter White's Kilkenny College after which, in 1563, he continued to University College, Oxford, where he took his degree five years later. At Oxford, he became intimate with Edmund Campion. After leaving the university he studied law at Furnival's Inn and Lincoln's Inn. He contributed in 1587 to ''Holinshed's Chronicles'' "a playne and perfecte description" of Ireland, and a ''History of Ireland during the reign of Henry VIII'', which were severely criticized in Barnabe Rich's ''New Description of Ireland'' (1610) as a misrepresentation of Irish affair ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William Blackwood And Sons
William Blackwood and Sons was a Scottish publishing house and printer founded by William Blackwood in 1804. It played a key role in literary history, publishing many important authors, for example John Buchan, George Tomkyns Chesney, Joseph Conrad, George Eliot, E. M. Forster, John Galt, John Neal, Thomas De Quincey, Charles Reade, Margaret Oliphant, John Hanning Speke and Anthony Trollope, both in books and in the monthly ''Blackwood’s Magazine''. History In 1804 William Blackwood opened a shop in South Bridge Street, Edinburgh, for the sale of old, rare and curious books. He undertook the Scottish agency for John Murray and other London publishers, and gradually drifted into publishing on his own account, moving in 1816 to Princes Street. On 1 April 1817 the first number of the ''Edinburgh Monthly Magazine'' was published, which on its seventh number became ''Blackwood's Edinburgh Magazine''. "''Maga''," as this magazine soon came to be called, was the organ of the Sc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dryburgh Abbey
Dryburgh Abbey, near Dryburgh on the banks of the River Tweed in the Scottish Borders, was nominally founded on 10 November (Martinmas) 1150 in an agreement between Hugh de Morville, Constable of Scotland, and the Premonstratensian canons regular from Alnwick Abbey in Northumberland. The arrival of the canons along with their first abbot, Roger, took place on 13 December 1152. It was burned by English troops in 1322, after which it was restored only to be again burned by Richard II in 1385, but it flourished in the fifteenth century. It was finally destroyed in 1544, briefly surviving until the Scottish Reformation, when it was given to the Earl of Mar by James VI of Scotland. It is now a designated scheduled monument and the surrounding landscape is included in the Inventory of Gardens and Designed Landscapes in Scotland. David Erskine, 11th Earl of Buchan bought the land in 1786. Sir Walter Scott and Douglas Haig are buried in its grounds. Their respective tomb and headst ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
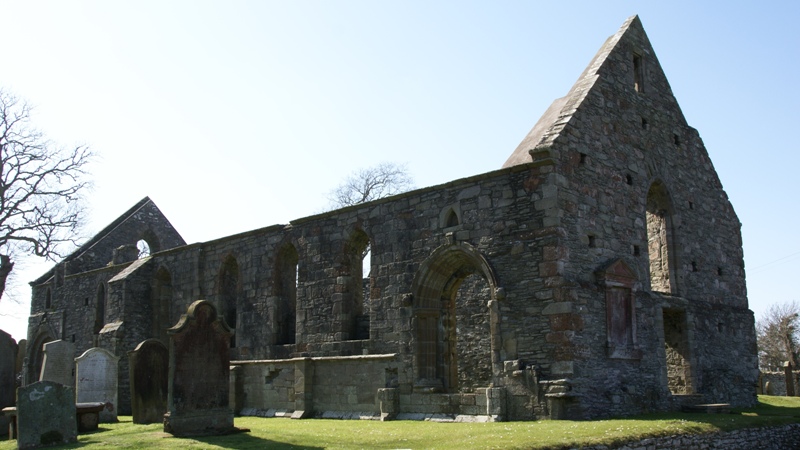
Whithorn Priory
Whithorn Priory was a medieval Scottish monastery that also served as a cathedral, located at 6 Bruce Street in Whithorn, Wigtownshire, Dumfries and Galloway (54.7357N, 4.415954W; OS grid reference NX445405). History The priory was founded about the middle of the 12th century by Fergus of Galloway, Fergus, the Lord of Galloway, during the reign of King David I of Scotland, initially for a community of Augustinian Canon regular, canons regular. Around 1175, the monks were replaced by Premonstratensians, Premonstratensian canons regular, referred to colloquially in Britain as the White Canons.Hunter-Blair, Oswald. "Whithorn Priory." The Catholic Encyclopedia Vol. 15. New York: Robert Appleton Company, 1912. 21 January 2019] Sometime before 1161, the Premonstratensians had been establi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
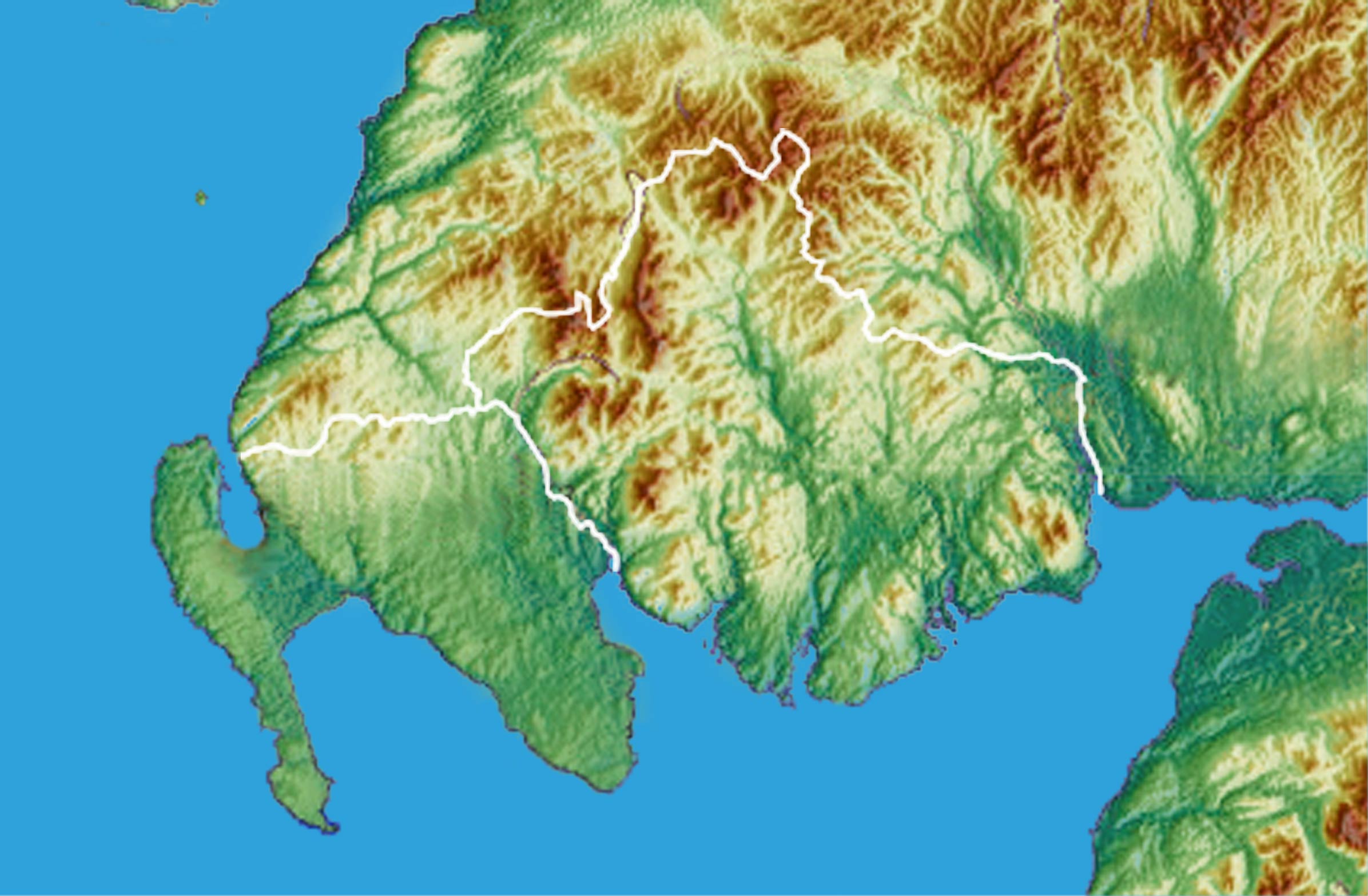
Galloway
Galloway ( ; ; ) is a region in southwestern Scotland comprising the counties of Scotland, historic counties of Wigtownshire and Kirkcudbrightshire. It is administered as part of the council areas of Scotland, council area of Dumfries and Galloway. Galloway is bounded by sea to the west and south, the Galloway Hills to the north, and the River Nith to the east; the border between Kirkcudbrightshire and Wigtownshire is marked by the River Cree. The definition has, however, fluctuated greatly in size over history. A native or inhabitant of Galloway is called a Gallovidian. The region takes its name from the ''Gall-Gàidheil'', or "stranger Gaels", Norse–Gaels, a people of mixed Gaelic and Norse descent who seem to have settled here in the 10th century. Galloway remained a Gàidhealtachd area for much longer than other regions of the Scottish Lowlands and a Galwegian Gaelic, distinct local dialect of the Scottish Gaelic language survived into at least the 18th century. A hardy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Veitch (poet)
John Veitch (24 October 1829 – 3 September 1894), Scotland, Scottish philosopher, poet and historian. He was born in Peebles, the only son of Peninsular War veteran James Veitch and his wife Nancy Ritchie, a woman steeped in the folk traditions of the Borders. He was educated at the University of Edinburgh.John Veitch University of Glasgow He was assistant lecturer successively to Sir William Hamilton, Bart, Sir William Hamilton and Alexander Campbell Fraser (1856–60). In 1860 he was appointed to the chair of logic, metaphysics and rhetoric at the University of St Andrews, and in 1864 to the Professor of Logic and Rhetoric, corresponding chair at the University of Glasgow. In St. Andrews, he lived at 8 Playfair Terrace. In Glasgow, he lectured to working men and women and between 1877 and 1883 put on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |