|
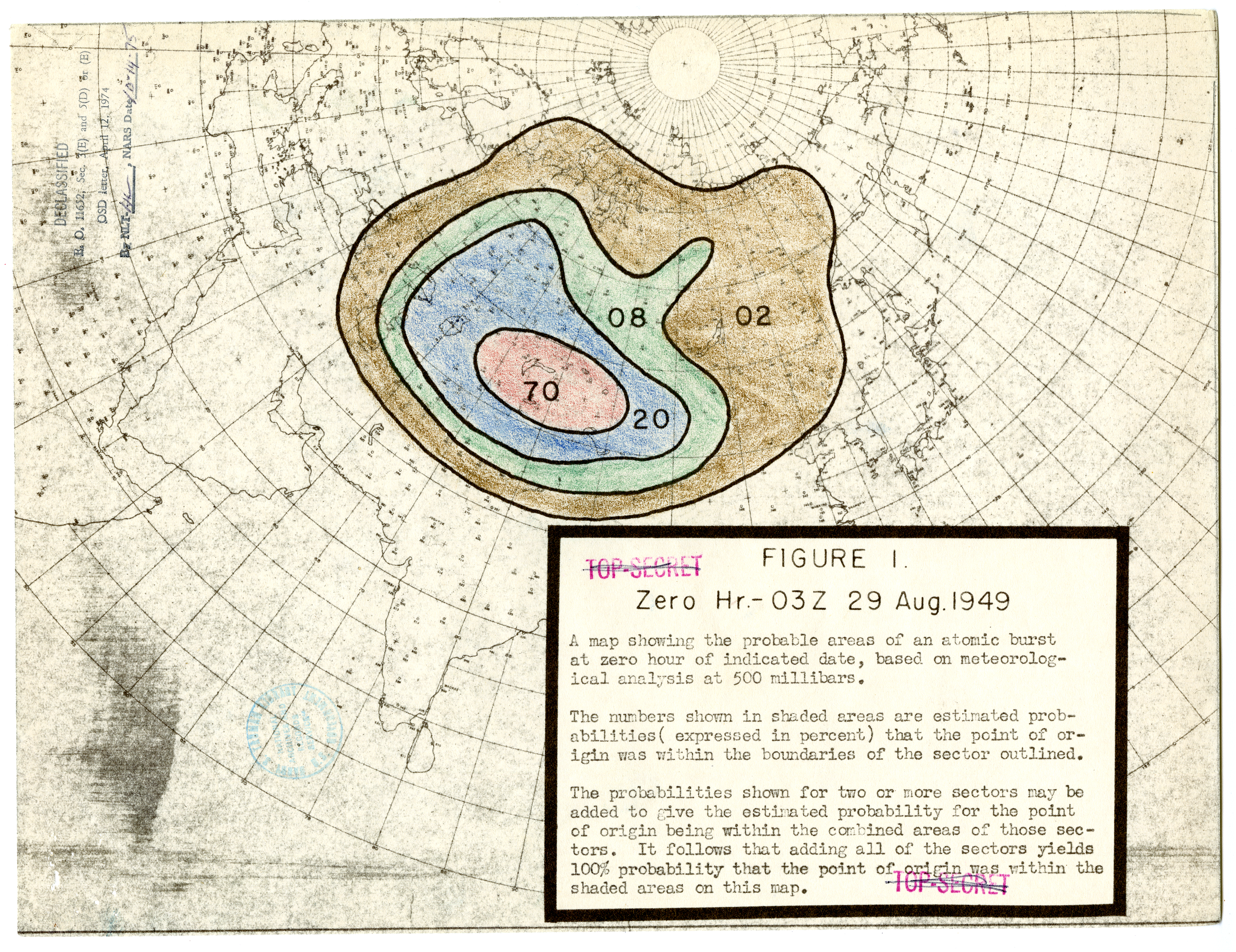
Joe-1 Location Prediction 1949
The RDS-1 (), also known as Izdeliye 501 (device 501) and First Lightning (), was the nuclear bomb used in the Soviet Union's first nuclear weapon test. The United States assigned it the code-name Joe-1, in reference to Joseph Stalin. It was detonated on 29 August 1949 at 7:00 a.m., at the Semipalatinsk Test Site, Kazakh Soviet Socialist Republic, Kazakh SSR, after top-secret research and development as part of the Soviet atomic bomb project. Etymology There are several explanations for the Soviet code-name of RDS-1, usually an arbitrary designation: a backronym "Special Jet Engine" (, ''Reaktivnyi Dvigatel Spetsialnyi''), or "Stalin's Jet Engine" (, ''Reaktivnyi Dvigatel Stalina''), or "Russia does it herself" (, ''Rossiya Delayet Sama''). Later weapons were also designated RDS but with different model numbers. Description The weapon was designed at the Kurchatov Institute, then at the time officially known as "Laboratory № 2" but designated as the "office" or "b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Casing For The First Soviet Atomic Bomb, RDS-1
Casing may refer to an enclosing shell, tube, or surrounding material. It may also refer to: * Cartridge (firearms), shell enclosing the explosive propellant in ammunition * Casing (borehole), metal tube used during the drilling of a well * Casing (molding), decorative molding surrounding door or window openings * Casing (sausage), thin covering holding the food contents of sausage * Casing (submarine), platform attached to the upper side of a submersible vehicle * Computer case, the enclosure that contains most of the components of a computer * Letter case, the distinction between upper and lowercase letters in typography * Surreptitious reconnaissance, especially to aid a robbery See also * * * Cas (other), French for "case" * Case (other) * Casting (other) * Cover (other) Cover or covers may refer to: Packaging * Another name for a lid * Cover (philately), generic term for envelope or package * Album cover, the front of the packagi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trinity (nuclear Test)
Trinity was the first detonation of a nuclear weapon, conducted by the United States Army at 5:29 a.m. MWT (11:29:21 GMT) on July 16, 1945, as part of the Manhattan Project. The test was of an implosion-design plutonium bomb, or "gadget", of the same design as the Fat Man bomb later detonated over Nagasaki, Japan, on August 9, 1945. Concerns about whether the complex Fat Man design would work led to a decision to conduct the first nuclear test. The code name "Trinity" was assigned by J. Robert Oppenheimer, the director of the Los Alamos Laboratory, possibly inspired by the poetry of John Donne. The test, both planned and directed by Kenneth Bainbridge, was conducted in the Jornada del Muerto desert about southeast of Socorro, New Mexico, on what was the Alamogordo Bombing and Gunnery Range (renamed the White Sands Proving Ground just before the test). The only structures originally in the immediate vicinity were the McDonald Ranch House and its ancillary build ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Joe-1 Location Prediction 1949
The RDS-1 (), also known as Izdeliye 501 (device 501) and First Lightning (), was the nuclear bomb used in the Soviet Union's first nuclear weapon test. The United States assigned it the code-name Joe-1, in reference to Joseph Stalin. It was detonated on 29 August 1949 at 7:00 a.m., at the Semipalatinsk Test Site, Kazakh Soviet Socialist Republic, Kazakh SSR, after top-secret research and development as part of the Soviet atomic bomb project. Etymology There are several explanations for the Soviet code-name of RDS-1, usually an arbitrary designation: a backronym "Special Jet Engine" (, ''Reaktivnyi Dvigatel Spetsialnyi''), or "Stalin's Jet Engine" (, ''Reaktivnyi Dvigatel Stalina''), or "Russia does it herself" (, ''Rossiya Delayet Sama''). Later weapons were also designated RDS but with different model numbers. Description The weapon was designed at the Kurchatov Institute, then at the time officially known as "Laboratory № 2" but designated as the "office" or "b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mikhail Pervukhin
Mikhail Georgiyevich Pervukhin (; 14 October Old_Style_and_New_Style_dates.html" ;"title="nowiki/>O.S. 1 October1904 – 22 July 1978) was a Soviet people">Soviet politician and an engineer who served as people's commissar for various commissions under Council of Ministers from 1955 to 1957. Early life and career He was born on 14 October 1904 in the village of Yuryuzansky Zavod, Ufa Governorate, Russian Empire">Ufa_Governorate.html" ;"title="Yuryuzan, Chelyabinsk Oblast">Yuryuzansky Zavod, Yuryuzan, Chelyabinsk Oblast">Yuryuzansky Zavod, Ufa Governorate, Russian Empire to a Russian working class">working-class family. Pervukhin was a political activist for the communist cause and became a party member of the Communist Party of the Soviet Union">Russian Communist Party in 1919. In August to September 1919, Pervukhin was a member of the Zlatoust city commission on the nationalisation of property belonging to the Russian bourgeoisie. He began working for the Zlatoust newspap ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rapid Transit
Rapid transit or mass rapid transit (MRT) or heavy rail, commonly referred to as metro, is a type of high-capacity public transport that is generally built in urban areas. A grade separation, grade separated rapid transit line below ground surface through a tunnel can be regionally called a subway, tube, metro or underground. They are sometimes grade-separated on elevated railways, in which case some are referred to as el trains – short for "elevated" – or skytrains. Rapid transit systems are usually electric railway, electric railways, that unlike buses or trams operate on an exclusive right-of-way (transportation), right-of-way, which cannot be accessed by pedestrians or other vehicles. Modern services on rapid transit systems are provided on designated lines between metro station, stations typically using electric multiple units on railway tracks. Some systems use rubber-tyred metro, guided rubber tires, magnetic levitation (''maglev''), or monorail. The stations typica ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Security Agency
The National Security Agency (NSA) is an intelligence agency of the United States Department of Defense, under the authority of the director of national intelligence (DNI). The NSA is responsible for global monitoring, collection, and processing of information and data for global intelligence and counterintelligence purposes, specializing in a discipline known as signals intelligence (SIGINT). The NSA is also tasked with the protection of U.S. communications networks and information systems. The NSA relies on a variety of measures to accomplish its mission, the majority of which are clandestine. The NSA has roughly 32,000 employees. Originating as a unit to decipher coded communications in World War II, it was officially formed as the NSA by President Harry S. Truman in 1952. Between then and the end of the Cold War, it became the largest of the U.S. intelligence organizations in terms of personnel and budget. Still, information available as of 2013 indicates that the C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Venona Project
The Venona project was a United States counterintelligence program initiated during World War II by the United States Army's Signal Intelligence Service and later absorbed by the National Security Agency (NSA), that ran from February 1, 1943, until October 1, 1980. It was intended to decrypt messages transmitted by the intelligence agencies of the Soviet Union (e.g. the NKVD, the KGB, and the GRU). Initiated when the Soviet Union was an ally of the US, the program continued during the Cold War, when the Soviet Union was considered an enemy. During the 37-year duration of the Venona project, the Signal Intelligence Service decrypted and translated approximately 3,000 messages. The signals intelligence yield included discovery of the Cambridge Five espionage ring in the United Kingdom, and also of Soviet espionage of the Manhattan Project in the US, known as Project Enormous. Some of the espionage was undertaken to support the Soviet atomic bomb project. The Venona project remai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Julius And Ethel Rosenberg
Julius Rosenberg (May 12, 1918 – June 19, 1953) and Ethel Rosenberg (born Greenglass; September 28, 1915 – June 19, 1953) were an American married couple who were convicted of First Chief Directorate, spying for the Soviet Union, including providing top-secret information about American radar, sonar, jet propulsion engines, and nuclear weapon designs. Convicted of espionage in 1951, they were Capital punishment by the United States federal government, executed by the federal government of the United States in 1953 using New York's state execution chamber in Sing Sing in Ossining (village), New York, Ossining, New York, becoming the first American civilians to be executed for such charges and the first to be executed during peacetime. Other convicted co-conspirators were sentenced to prison, including Ethel's brother, David Greenglass (who had made a Plea bargain, plea agreement), Harry Gold, and Morton Sobell. Klaus Fuchs, a German scientist working at the Project Y, Los Alam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
World War II
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the world's countries participated, with many nations mobilising all resources in pursuit of total war. Tanks in World War II, Tanks and Air warfare of World War II, aircraft played major roles, enabling the strategic bombing of cities and delivery of the Atomic bombings of Hiroshima and Nagasaki, first and only nuclear weapons ever used in war. World War II is the List of wars by death toll, deadliest conflict in history, causing World War II casualties, the death of 70 to 85 million people, more than half of whom were civilians. Millions died in genocides, including the Holocaust, and by massacres, starvation, and disease. After the Allied victory, Allied-occupied Germany, Germany, Allied-occupied Austria, Austria, Occupation of Japan, Japan, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atomic Spies
Atomic spies or atom spies were people in the United States, the United Kingdom, and Canada who are known to have illicitly given information about nuclear weapons production or design to the Soviet Union during World War II and the early Cold War. Exactly what was given, and whether everyone on the list gave it, are still matters of some scholarly dispute. In some cases, some of the arrested suspects or government witnesses had given strong testimonies or confessions which they recanted later or said were fabricated. Their work constitutes the most publicly well-known and well-documented case of nuclear espionage in the history of nuclear weapons. At the same time, numerous nuclear scientists wanted to share the information with the world scientific community, but this proposal was firmly quashed by the United States government. Atomic spies were motivated by a range of factors. Some, such as ideology or a belief in communism, were committed to advancing the interests of the S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
RDS-2
The RDS-2 (Russian: РДС-2) was the second atomic bomb developed by the Soviet Union as an improved version of the RDS-1. It included new explosive lenses along with a new core design to decrease the probability of pre-detonation or 'fizzle'. The RDS-2 weighed approximately and had a diameter of 1.25 m. The RDS-2 was tested on September 24, 1951 and produced a 38.3 kiloton yield. It was detonated from the top of a tower thirty meters high. The detonation was initiated by a bomber flying over the testing site instead of the detonation being initiated by a ground control center. See also *Soviet atomic bomb project *RDS-1 *RDS-3 RDS-3 () was the third atomic bomb developed by the Soviet Union in 1951, after the RDS-1 and RDS-2. It was called ''Marya'' in the military. The bomb had a composite design with a plutonium core inside a uranium shell, providing an explosive powe ... Notes References Citations Bibliography * * * * * {{Soviet nuclear weapons 1951 in military hist ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plutonium
Plutonium is a chemical element; it has symbol Pu and atomic number 94. It is a silvery-gray actinide metal that tarnishes when exposed to air, and forms a dull coating when oxidized. The element normally exhibits six allotropes and four oxidation states. It reacts with carbon, halogens, nitrogen, silicon, and hydrogen. When exposed to moist air, it forms oxides and hydrides that can expand the sample up to 70% in volume, which in turn flake off as a powder that is pyrophoric. It is radioactive and can accumulate in bones, which makes the handling of plutonium dangerous. Plutonium was first synthesized and isolated in late 1940 and early 1941, by deuteron bombardment of uranium-238 in the cyclotron at the University of California, Berkeley. First, neptunium-238 (half-life 2.1 days) was synthesized, which then beta-decayed to form the new element with atomic number 94 and atomic weight 238 (half-life 88 years). Since uranium had been named after the planet Uranus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |