|
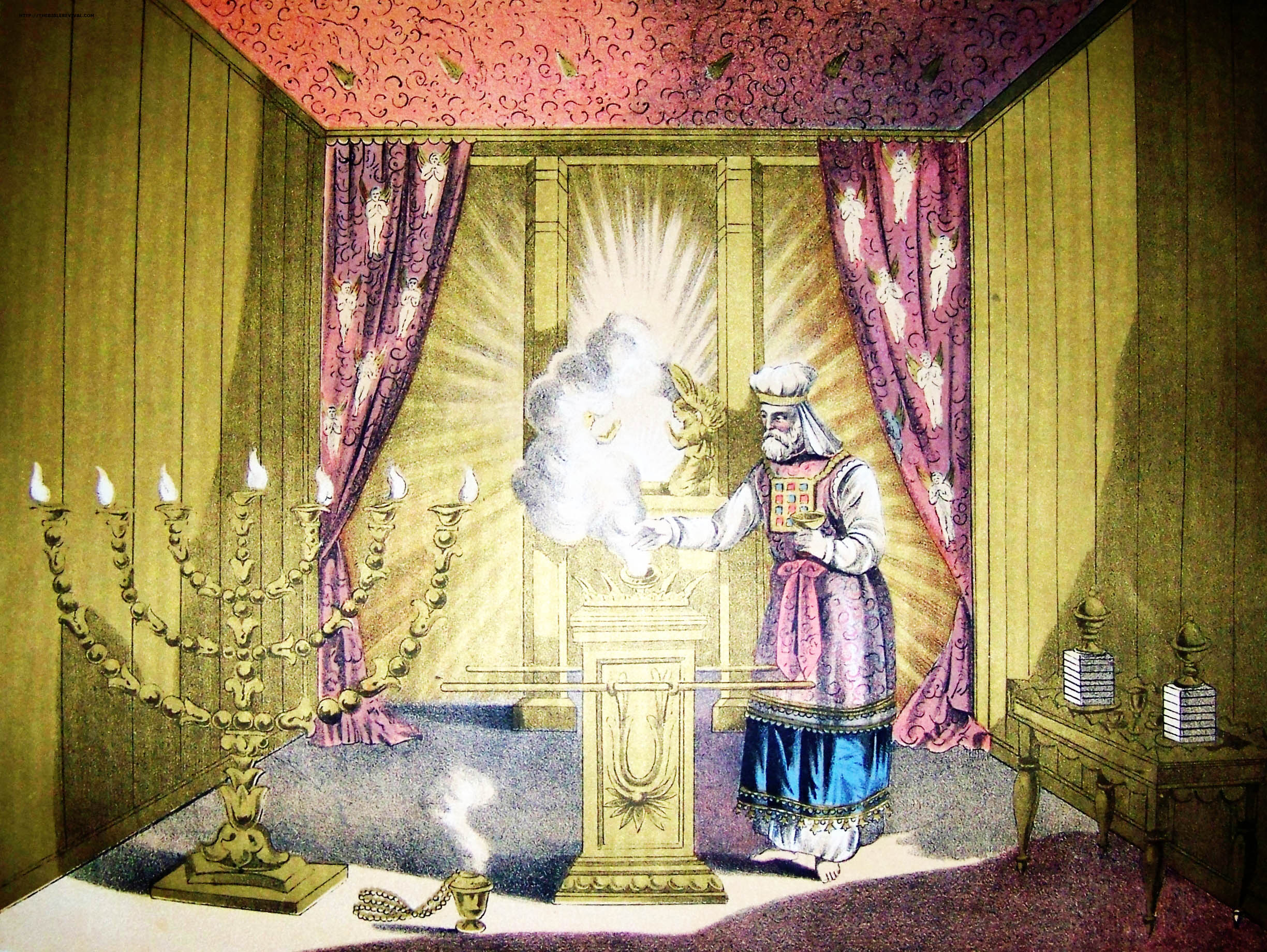
Jehoiada
Jehoiada ( ''Yəhōyāḏā‘'', "Yahweh knows") in the Hebrew Bible, was a prominent priest in the kingdom of Judah during the reigns of Ahaziah (reigned c. 842 - 841 BCE), Athaliah (reigned c. 841–835 BCE), and Joash (reigned c. 836–796 BC). Jehoiada became the brother-in-law of King Ahaziah as a result of his marriage with princess Jehosheba. Both Jehosheba and Ahaziah were children of King Jehoram of Judah (reigned c. 849 – 842 BCE). Ahaziah died a year after assuming the throne, which was then usurped by his mother Athaliah, who ordered the execution of all members of the royal family. Jehosheba and Jehoiada rescued Athaliah's one-year-old grandson, Joash, from Athaliah's slaughter. For six years, they hid the sole surviving heir to the throne within Solomon's Temple. Jehoiada was instrumental in the staging of a coup d'état which dethroned and killed Athaliah. The account in 2 Chronicles notes thresolveof Jehoiada (''Jehoiada strengthened himself'' in the King Jame ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zechariah Ben Jehoiada
Zechariah ben Jehoiada ''Zəḵaryā ben-Yǝhōyāḏāʿ''; ar, زكريّا بن يهوياداع ''Zakariya bin Yehuyada'') is a figure in the Hebrew Bible described as a priest who was stoned to death by Jehoash of Judah and may possibly have been alluded to in the New Testament. Lineage Zechariah was the son of Jehoiada, the High Priest in the times of Ahaziah and Jehoash of Judah. After the death of Jehoiada, Zechariah condemned both King Jehoash and the people for their rebellion against God (). This so stirred up their resentment against him that at the king's commandment they stoned him, and he died "in the court of the house of the Lord" (). In rabbinical literature In rabbinical literature, Zechariah was the son-in-law of the king, and, being also a priest, prophet, and judge, he dared censure the monarch. He was killed in the priests' courtyard of the Temple on a Sabbath which was likewise the Day of Atonement. Later, when Nebuzar-adan, the captain of Nebuchad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jehoash Of Judah
Jehoash (; el, Ιωας; la, Joas), also known as Joash (in King James Version), Joas (in Douay–Rheims) or Joás (), was the eighth king of Judah, and the sole surviving son of Ahaziah after the massacre of the royal family ordered by his grandmother, Athaliah. His mother was Zibiah of Beersheba. Jehoash was 7 years old when his reign began, and he reigned for 40 years. ( 2 Kings 12:1, 2 Chronicles 24:1) He was succeeded by his son, Amaziah of Judah. He is said to have been righteous "all the days of Jehoiada the priest" () but to have deviated from fidelity to Yahweh after Jehoiada's death (). William F. Albright has dated his reign to 837–800 BCE, while E. R. Thiele offers the dates 835–796 BCE. Early life According to the Hebrew Bible, following the death of his father, Ahaziah, Jehoash was spared from the rampages of Ahaziah's mother, Athaliah, by Jehoash's paternal aunt, Jehosheba, who was married to the high priest, Jehoiada. After hiding him in t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jehosheba
Jehosheba (alternately Jehoshabeath; he, יְהוֹשֶׁ֫בַע ''Yəhōšeḇa‘'', "Yahweh is an oath"), or Josaba, is a figure in the Hebrew Bible. She was the daughter of King Jehoram of Judah, sister to King Ahaziah of Judah and wife of Jehoiada the priest. She was a daughter of Jehoram, but not necessarily of Athaliah. After the death of Ahaziah, his mother, Athaliah, made herself Queen of Judah and ordered the execution of all members of the royal family that could claim the throne. However, according to , Jehosheba saved from the massacre her infant nephew Jehoash, Ahaziah's son and Athaliah's grandson: Jehoash, then one year old, was the only survivor of the massacre. Jehosheba and Jehoiada hid him in the Temple for six years. In the seventh year, Jehoiada and the other priests devised a plan to reestablish the Davidic line in Judah through the coronation of Jehoash (aged seven). When the plan was implemented, Athaliah overheard the noise of the people chantin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Benaiah
Benaiah ( he, בניה, "Yahweh builds up") is a common name in the Hebrew Bible. Etymology In the etymology of the name, the first part of Benaiah comes from the root-verb בנה (bana), which is a common Hebrew verb meaning "to build". The second part of Benaiah is יה (Yah), which is not a derivative of the Tetragrammaton, but a contraction of it (ie, the first and last consonants of יהוה are contracted as יה). Benaiah, son of Jehoiada The most famous Benaiah in the Bible is the son of Jehoiada, who came from the southern Judean town of Kabzeel. Benaiah was one of King David’s mighty men, commander of the 3rd rotational army division; (; ). He helped David's son Solomon become king, killed Solomon's enemies, and served as the chief of Solomon's army. On Solomon's instructions he was responsible for the deaths of Adonijah (), Joab () and Shimei (). He was in charge of the Cherethites and Pelethites. Several verses in make clear that Benaiah was closely ass ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Athaliah
Athaliah ( el, Γοθολία ''Gotholía''; la, Athalia) was the daughter of either king Omri, or of King Ahab and Queen Jezebel of Israel, the queen consort of Judah as the wife of King Jehoram, a descendant of King David, and later queen regnant c. 841–835 BCE. Biblical narrative Accounts of the life of Athaliah are to be found in 2 Kings 8:16–11:16 and 2 Chronicles 22:10–23:15 in the Hebrew Bible. The text states that she was the daughter of king Omri of Israel, however, she is usually considered to have been the daughter of King Ahab and his wife, Queen Jezebel. Some scholars are of the opinion that Athaliah was indeed the daughter of Omri, but that she grew up as an orphan in the court of Ahab. Athaliah was married to Jehoram of Judah to seal a treaty between the kingdoms of Israel and Judah, and to secure his position Jehoram killed his six brothers. Jehoram became king of Judah in the fifth year of Joram of Israel's reign (). Depending on her pater ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Book Of Chronicles
The Book of Chronicles ( he, דִּבְרֵי־הַיָּמִים ) is a book in the Hebrew Bible, found as two books (1–2 Chronicles) in the Christian Old Testament. Chronicles is the final book of the Hebrew Bible, concluding the third section of the Jewish Tanakh, the Ketuvim ("Writings"). It contains a genealogy starting with Adam and a history of ancient Judah and Israel up to the Edict of Cyrus in 539 BC. The book was divided into two books in the Septuagint and translated mid 3rd century BC. In Christian contexts Chronicles is referred to in the plural as the Books of Chronicles, after the Latin name given to the text by Jerome, but are also rarely referred to by their Greek name as the Books of Paralipomenon. In Christian Bibles, they usually follow the two Books of Kings and precede Ezra–Nehemiah, the last history-oriented book of the Protestant Old Testament. Summary The Chronicles narrative begins with Adam, Seth and Enosh, and the story is then carrie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kohen Gadol
High Priest ( he, כהן גדול, translit=Kohen Gadol or ; ) was the title of the chief religious official of Judaism from the early post-Exilic times until the destruction of the Second Temple in Jerusalem by the Romans in 70 CE. Previously, in the Israelite religion, including during the time of the kingdoms of Israel and Judah, other terms were used to designate the leading priests; however, as long as a king was in place, the supreme ecclesiastical authority lay with him. The official introduction of the term "high priest" went hand-in-hand with a greatly enhanced ritual and political significance bestowed upon the chief priest of the Israelites in the post-Exilic period, especially from 411 BCE onward due to the religious transformations brought about during the time of the Babylonian captivity and due to the lack of a Jewish king and kingdom. The high priests belonged to the Jewish priestly families that trace their paternal line back to Aaron—the first high prie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antiquities Of The Jews
''Antiquities of the Jews'' ( la, Antiquitates Iudaicae; el, Ἰουδαϊκὴ ἀρχαιολογία, ''Ioudaikē archaiologia'') is a 20-volume historiographical work, written in Greek, by historian Flavius Josephus in the 13th year of the reign of Roman emperor Flavius Domitian which was around AD 93 or 94.Freedman, David Noel, ed., ''The Anchor Bible Dictionary'', (New York: Doubleday, 1997, 1992). ''Antiquities of the Jews'' contains an account of the history of the Jewish people for Josephus' gentile patrons. In the first ten volumes, Josephus follows the events of the Hebrew Bible beginning with the creation of Adam and Eve. The second ten volumes continues the history of the Jewish people beyond the biblical text and up to the Jewish War, or the First Jewish–Roman War, 66 to 73 CE. This work, along with Josephus's other major work, ''The Jewish War'' (''De Bello Iudaico''), provides valuable background material for historians wishing to understand 1st-century AD Ju ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seder Olam Zutta
Seder Olam Zutta (Hebrew: ) is an anonymous chronicle from 803 CE, called "Zuta" (= "smaller," or "younger") to distinguish it from the older ''Seder Olam Rabbah.'' This work is based upon, and to a certain extent completes and continues, the older aforementioned chronicle. It consists of two main parts: the first, comprising about three-fifths of the whole, deals with the chronology of the 50 generations from Adam to Jehoiakim (who, according to this chronicle, was the first of the Babylonian exilarch), the second deals with 39 generations of exilarchs, beginning with Jehoiachin and going until the 9th century CE. Contents The authorial intention of this work was to demonstrate that the Babylonian exilarchs were direct descendants of David, King of Israel, through a cascading genealogy. From Genesis to the Exile After a short introduction, taken from the ''Seder Olam Rabbah'', giving the general chronology from Adam to the destruction of the Second Temple (a period of 3,828 ye ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jacob
Jacob (; ; ar, يَعْقُوب, Yaʿqūb; gr, Ἰακώβ, Iakṓb), later given the name Israel, is regarded as a patriarch of the Israelites and is an important figure in Abrahamic religions, such as Judaism, Christianity, and Islam. Jacob first appears in the Book of Genesis, where he is described as the son of Isaac and Rebecca, and the grandson of Abraham, Sarah, and Bethuel. According to the biblical account, he was the second-born of Isaac's children, the elder being Jacob's fraternal twin brother, Esau. Jacob is said to have bought Esau's birthright and, with his mother's help, deceived his aging father to bless him instead of Esau. Later in the narrative, following a severe drought in his homeland of Canaan, Jacob and his descendants, with the help of his son Joseph (who had become a confidant of the pharaoh), moved to Egypt where Jacob died at the age of 147. He is supposed to have been buried in the Cave of Machpelah. Jacob had twelve sons through fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abraham
Abraham, ; ar, , , name=, group= (originally Abram) is the common Hebrews, Hebrew patriarch of the Abrahamic religions, including Judaism, Christianity, and Islam. In Judaism, he is the founding father of the Covenant (biblical), special relationship between the Jews and God in Judaism, God; in Christianity, he is the spiritual progenitor of all believers, whether Jewish or gentile, non-Jewish; and Abraham in Islam, in Islam, he is a link in the Prophets and messengers in Islam, chain of Islamic prophets that begins with Adam (see Adam in Islam) and culminates in Muhammad. His life, told in the narrative of the Book of Genesis, revolves around the themes of posterity and land. Abraham is called by God to leave the house of his father Terah and settle in the land of Canaan, which God now promises to Abraham and his progeny. This promise is subsequently inherited by Isaac, Abraham's son by his wife Sarah, while Isaac's half-brother Ishmael is also promised that he will be th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |





.jpg)