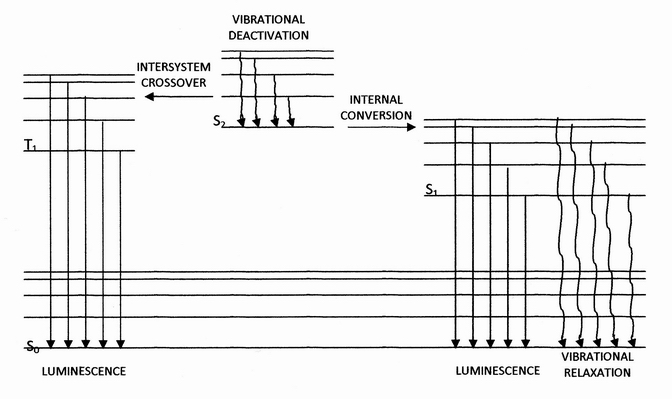
|
Jablonski Diagram
In molecular spectroscopy, a Jablonski diagram is a diagram that illustrates the electronic states and often the vibrational levels of a molecule, and also the transitions between them. The states are arranged vertically by energy and grouped horizontally by spin multiplicity. Nonradiative transitions are indicated by squiggly arrows and radiative transitions by straight arrows. The vibrational ground states of each electronic state are indicated with thick lines, the higher vibrational states with thinner lines. The diagram is named after the Polish physicist Aleksander Jabłoński who first proposed it in 1933. Transitions When a molecule absorbs a photon, the photon energy is converted and increases the molecule's internal energy level. Likewise, when an excited molecule releases energy, it can do so in the form of a photon. Depending on the energy of the photon, this could correspond to a change in vibrational, electronic, or rotational energy levels. The changes between ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Excited State
In quantum mechanics Quantum mechanics is the fundamental physical Scientific theory, theory that describes the behavior of matter and of light; its unusual characteristics typically occur at and below the scale of atoms. Reprinted, Addison-Wesley, 1989, It is ..., an excited state of a system (such as an atom, molecule or Atomic nucleus, nucleus) is any quantum state of the system that has a higher energy than the ground state (that is, more energy than the absolute minimum). Excitation refers to an increase in energy level above a chosen starting point, usually the ground state, but sometimes an already excited state. The temperature of a group of particles is indicative of the level of excitation (with the notable exception of systems that exhibit negative temperature). The lifetime of a system in an excited state is usually short: Spontaneous emission, spontaneous or stimulated emission, induced emission of a quantum of energy (such as a photon or a phonon) usually ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Molecular Physics
Molecular physics is the study of the physical properties of molecules and molecular dynamics. The field overlaps significantly with physical chemistry, chemical physics, and quantum chemistry. It is often considered as a sub-field of atomic, molecular, and optical physics. Research groups studying molecular physics are typically designated as one of these other fields. Molecular physics addresses phenomena due to both molecular structure and individual atomic processes within molecules. Like atomic physics, it relies on a combination of classical and quantum mechanics to describe interactions between electromagnetic radiation and matter. Experiments in the field often rely heavily on techniques borrowed from atomic physics, such as spectroscopy and scattering. Molecular structure In a molecule, both the electrons and nuclei experience similar-scale forces from the Coulomb interaction. However, the nuclei remain at nearly fixed locations in the molecule while the electrons ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diagrams
A diagram is a symbolic representation of information using visualization techniques. Diagrams have been used since prehistoric times on walls of caves, but became more prevalent during the Enlightenment. Sometimes, the technique uses a three-dimensional visualization which is then projected onto a two-dimensional surface. The word '' graph'' is sometimes used as a synonym for diagram. Overview The term "diagram" in its commonly used sense can have a general or specific meaning: * ''visual information device'' : Like the term "illustration", "diagram" is used as a collective term standing for the whole class of technical genres, including graphs, technical drawings and tables. * ''specific kind of visual display'' : This is the genre that shows qualitative data with shapes that are connected by lines, arrows, or other visual links. In science the term is used in both ways. For example, Anderson (1997) stated more generally: "diagrams are pictorial, yet abstract, represen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grotrian Diagram
A Grotrian diagram, or term diagram, shows the allowed electronic transitions between the energy levels of atoms. They can be used for one-electron and multi-electron atoms. They take into account the specific selection rules related to changes in angular momentum of the electron. The diagrams are named after Walter Grotrian, who introduced them in his 1928 book ''Graphische Darstellung der Spektren von Atomen und Ionen mit ein, zwei und drei Valenzelektronen'' ("Graphical representation of the spectra of atoms and ions with one, two and three valence electrons"). See also *Jablonski diagram In molecular spectroscopy, a Jablonski diagram is a diagram that illustrates the electronic states and often the vibrational levels of a molecule, and also the transitions between them. The states are arranged vertically by energy and grouped hor ... (for molecules) References External links Hyperphysics: Atomic Energy Level Diagrams Volumes with Grotrian diagrams of most elements ''At ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Franck–Condon Principle
The Franck–Condon principle describes the intensities of vibronic transitions, or the absorption or emission of a photon. It states that when a molecule is undergoing an electronic transition, such as ionization, the nuclear configuration of the molecule experiences no significant change. Overview The Franck–Condon principle has a well-established semiclassical interpretation based on the original contributions of James Franck. Electronic transitions are relatively instantaneous compared with the time scale of nuclear motions, therefore if the molecule is to move to a new vibrational level during the electronic transition, this new vibrational level must be instantaneously compatible with the nuclear positions and momenta of the vibrational level of the molecule in the originating electronic state. In the semiclassical picture of vibrations (oscillations) of a simple harmonic oscillator, the necessary conditions can occur at the turning points, where the momentum is zer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phosphorescence
Phosphorescence is a type of photoluminescence related to fluorescence. When exposed to light (radiation) of a shorter wavelength, a phosphorescent substance will glow, absorbing the light and reemitting it at a longer wavelength. Unlike fluorescence, a phosphorescent material does not immediately reemit the radiation it absorbs. Instead, a phosphorescent material absorbs some of the radiation energy and reemits it for a much longer time after the radiation source is removed. In a general sense, there is no distinct boundary between the emission times of fluorescence and phosphorescence (i.e.: if a substance glows under a black light it is generally considered fluorescent, and if it glows in the dark it is often simply called phosphorescent). In a modern, scientific sense, the phenomena can usually be classified by the three different mechanisms that produce the light, and the typical timescales during which those mechanisms emit light. Whereas fluorescent materials stop emitti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intersystem Crossing
Intersystem crossing (ISC) is an isoenergetic radiationless process involving a transition between the two electronic states with different spin multiplicity. Excited singlet and triplet states When an electron in a molecule with a singlet ground state is excited (''via'' absorption of radiation) to a higher energy level, either an excited singlet state or an excited triplet state will form. Singlet state is a molecular electronic state such that all electron spins are paired. That is, the spin of the excited electron is still paired with the ground state electron (a pair of electrons in the same energy level must have opposite spins, per the Pauli exclusion principle). In a triplet state the excited electron is no longer paired with the ground state electron; that is, they are parallel (same spin). Since excitation to a triplet state involves an additional "forbidden" spin transition, it is less probable that a triplet state will form when the molecule absorbs radiation. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Internal Conversion (chemistry)
Internal conversion is a transition from a higher to a lower electronic state in a molecule or atom.A general and quantitative discussion of intramolecular radiationless transitions is the subject of an article by M. Bixon and J. Jortner (''J. Chem. Phys.'', 48 (2) 715-726 (1968)). It is sometimes called "radiationless de-excitation", because no photons are emitted. It differs from intersystem crossing in that, while both are radiationless methods of de-excitation, the molecular spin state for internal conversion remains the same, whereas it changes for intersystem crossing. The energy of the electronically excited state is given off to vibrational modes of the molecule. The excitation energy is transformed into heat. Examples A classic example of this process is the quinine sulfate fluorescence, which can be quenched by the use of various halide salts. The excited molecule can de-excite by increasing the thermal energy of the surrounding solvated ions. Several natural molecules ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vibrational Energy Relaxation
Vibrational energy relaxation, or vibrational population relaxation, is a process in which the population distribution of molecules in quantum states of high energy level caused by an external perturbation returns to the Maxwell–Boltzmann distribution. In solution, the process proceeds with intra- and intermolecular energy transfer. The excess energy of the excited vibrational mode is transferred to the kinetic modes in the same molecule or to the surrounding molecules. Through this process, the initially excited vibrational mode moves to a vibrational state of a lower energy. The relaxation is called the longitudinal relaxation, and the time constant of the relaxation is called the longitudinal relaxation time, or ''T''1. Vibrational energy relaxation has been studied with time-resolved spectroscopy. By the excitation of the pump pulse, the population distribution of the vibrationally excited state is made by infrared absorption or a Raman process when the molecule is in th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |