|
Ivan Nikitich Nikitin
Ivan Nikitich Nikitin (russian: link=no, Иван Никитич Никитин c. 1690–1741) was a Russian painter, an author of portraits and battle paintings. Biography Ivan Nikitin was born in Moscow to a family of an Orthodox priest. He received his first artistic lessons from a Dutch artist Schwonbek at the engraving shop of the Kremlin Armoury. In 1711 the Armory together with Ivan Nikitin was moved to Saint Petersburg. In 1716–1720 he and his brother Roman Nikitin were sent to Italy by Peter the Great. The brothers learnt the art of painting at Florence and Venice. After returning to Russia Nikitin became the favorite court painter of Peter the Great. He worked in Moscow and Saint Petersburg. After Peter's death in 1725 Nikitin continued to work at the court until 1732, when he and his brothers Roman and Rodion (the dean of the Cathedral of the Annunciation in Moscow Kremlin) were arrested for the distribution of pamphlets against vice-Procurator of Synod Feofan P ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nikitin Getman
Nikitin (russian: Никитин), or Nikitina (feminine; Никитина) is a common Russians, Russian surname that derives from the male given name Nikita (given name), Nikita and literally means ''Nikita's''. It may refer to: Artists, musicians, authors *Yevgeny Nikitin (bass-baritone), bass-baritone *Ivan Nikitich Nikitin (c. 1690–1742), Russian painter *Gury Nikitin (1620–1691), Russian icon painter *Ivan Savvich Nikitin (1824–1861), Russian poet *Basil Nikitin (1885–1960), Russian orientalist and diplomat *Sergey Nikitin (musician), contemporary Russian composer, singer and bard *Tatyana Nikitina, contemporary Russian singer and composer (wife of musician Sergey Nikitin) *Victor Ivanovich Nikitin, Soviet soloist with the Alexandrov Ensemble *Yuri Nikitin (author), contemporary Russian sci-fi writer * (b. 1950), Russian sculptor Athletes *Andriy Nikitin, Ukrainian football player and manager *Larisa Nikitina, contemporary Russian heptathlete *Vera Nikitina, co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Catherine I Of Russia
Catherine I ( rus, Екатери́на I Алексе́евна Миха́йлова, Yekaterína I Alekséyevna Mikháylova; born , ; – ) was the second wife and empress consort of Peter the Great, and Empress Regnant of Russia from 1725 until her death in 1727. Life as a servant The life of Catherine I was said by Voltaire to be nearly as extraordinary as that of Peter the Great himself. Said to have been born on 15 April 1684 ( o.s. 5 April), she was originally named Marta Helena Skowrońska. Marta was the daughter of Samuel Skowroński (later spelt ''Samuil Skavronsky''), a Roman Catholic farmer from the eastern parts of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, born to Minsker parents. In 1680 he married Dorothea Hahn at Jakobstadt. Her mother is named in at least one source as Elizabeth Moritz, the daughter of a Baltic German woman and there is debate as to whether Moritz's father was a Swedish officer. It is likely that two stories were conflated, and Swedish sources sug ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Natalya Alexeyevna Of Russia
Tsarevna Natalya Alexeyevna of Russia (russian: Наталья Алексеевна Романова; 22 August 167318 June 1716) was a Russian playwright. She was the elder daughter of Tsar Alexis and his second wife, Natalia Naryshkina, and the sister of Peter the Great. Life Natalia shared the difficulties of her mother and brother during the regency of her half-sister, Tsarevna Sophia. She was very close to her brother Peter. She shared Peter's wish to reform Russia to a Western country, it was said that "she loved everything that her brother liked", and she supported his ideas from their childhood. During his reign, Peter thought it was important to inform his sister about his achievements and the affairs of the state, and every time he won a victory, he either informed her personally or had Golovin and Menshikov do so. She was young when Peter instituted his Western reforms, and in contrast to her half-sisters, it was not hard for her to adjust to the new ideals. Her ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anna Petrovna
Grand Duchess Anna Petrovna of Russia (russian: А́нна Петро́вна; 27 January 1708 – 4 March 1728) was the eldest daughter of Emperor Peter I of Russia and his wife Empress Catherine I. Her younger sister, Empress Elizabeth, ruled between 1741 and 1762. While a potential heir in the reign of her nephew Peter II, she never acceded to the throne due to political reasons. However, her son Peter III became Emperor in 1762, succeeding Elizabeth. She was the Duchess Consort of Holstein-Gottorp by marriage. She was born in Moscow and died in Kiel in her youth, at the age of 20. Early life Anna and Elizabeth were born out of wedlock, although their parents were married in 1712 and they were later legitimized. Their earlier illegitimacy would pose great challenges for their marriages. Anna grew up in the houses of Peter's younger sister Natalia and Prince Alexander Menshikov. Although born illegitimate, she and her younger sister Elizabeth were awarded the tit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tsarevna Praskovya Ivanovna Of Russia
Praskovya Ivanovna (24 September 1694 – 8 October 1731) was a Russian tsarevna, being the daughter of Tsar Ivan V of Russia and his wife Praskovia Saltykova. She was the niece of Tsar Peter the Great and the sister of Empress Anna Ivanovna. Biography Praskovya Ivanovna’s father died in 1696, and she was raised with her sisters Catherine and Anna at the estate awarded to her mother by Tsar Peter, the Izmaylovo Estate in Moscow. Praskovya was tutored in literature and science by German teachers. Praskovya was described by the Spanish ambassador in comparison to her sisters as lacking in intelligence, in addition to being very sickly. The court official, Bergholtz, described her in his journal as a “pretty brunette”, and the noblewoman Rondo noted that despite her bad health, she was quite beautiful. In contrast to that of her sisters, Peter the Great did not arrange a dynastic marriage for Praskovya. By the consent of her mother, she was married to a Rurikid noble, ge ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Kulikovo
The Battle of Kulikovo (russian: Мамаево побоище, Донское побоище, Куликовская битва, битва на Куликовом поле) was fought between the armies of the Golden Horde, under the command of Mamai, and various Russian principalities, under the united command of Prince Dmitry of Moscow. The battle took place on 8 September 1380, at the Kulikovo Field near the Don River (now Tula Oblast, Russia) and was won by Dmitry, who became known as russian: script=Latn, Donskoy, label=none, lit=of the Don after the battle. Although the victory did not end Mongol domination over Rus, it is widely regarded by Russian historians as the turning point at which Mongol influence began to wane and Moscow's power began to rise. The process eventually led to Grand Duchy of Moscow independence and the formation of the modern Russian state. Background After the Mongol-Tatar conquest, the territories of the disintegrating Kievan Rus became pa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
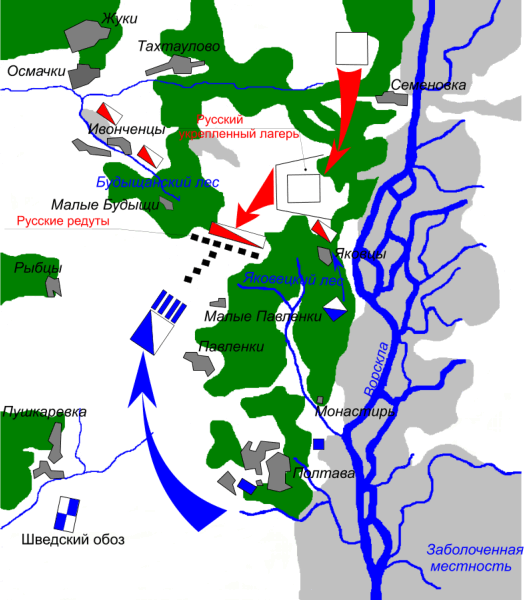
Battle Of Poltava
The Battle of Poltava; russian: Полта́вская би́тва; uk, Полта́вська би́тва (8 July 1709) was the decisive and largest battle of the Great Northern War. A Russian army under the command of Tsar Peter I defeated a Swedish army, under the command of Carl Gustaf Rehnskiöld. The battle put an end to the status of the Swedish Empire as a European great power, as well as its eastbound expansion, and marked the beginning of Russian hegemony in Northern Europe. During the course of six years in the initial stages of the war, King Charles XII and the Swedish Empire had defeated almost all participants in the anti-Swedish coalition, which initially consisted of the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth, Denmark-Norway and the Tsardom of Russia. The latter under Tsar Peter I's rule was the only one still undefeated. Charles XII therefore chose to invade Russia in the autumn of 1707 and march towards Moscow with a large Swedish army. However, the campaign ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pavlo Polubotok
Pavlo Polubotok ( uk, Павло Леонтійович Полуботок, russian: Павел Леонтьевич Полуботок, pl, Paweł Połubotok; born around 1660, died on 29 December 1724), was a Ukrainian Cossack political and military leader and Acting Hetman of Left-bank Ukraine between 1722 and 1724. Biography Pavlo Polubotok was born around 1660 in Borzna (according to another version, at his family's khutor-farm Polubotivka, today part of Shramkivka) into a rich Cossack family and as a young man served under his relative Hetman Ivan Samoylovych. In 1706 he became polkovnyk (colonel) of Chernigov Regiment and during the Great Northern War remained loyal to the Imperial Russians and fought against Ivan Mazepa. Pavel Polubotok was seen by many as a possible replacement for the disgraced Hetman, but the Russian Tsar Peter the Great distrusted Polubotok and supported Ivan Skoropadsky, who became the next Hetman. Nonetheless, Polubotok's loyalty was rewarde ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ivan Skoropadsky
Ivan Skoropadsky ( uk, Іван Скоропадський) (1646 – 3 July 1722) was a Cossack Hetman of the Zaporizhian Host (in office: 1708–1722), and the successor to the famous Hetman Ivan Mazepa. Biography Born into a noble Cossack family in Uman, Ukraine in 1646, Skoropadsky was educated in Kyiv-Mohyla Academy. In 1675 he joined Cossack military service under Hetman Ivan Samoylovych and distinguished himself in Russo-Turkish War of 1676–1681 and once again in the Crimean expedition against the Ottoman Empire and Crimean Khanate in 1688. Ivan Skoropadsky was briefly an ambassador representing Cossack Hetmanate in negotiations with the Russian Tsar Peter the Great. During the Great Northern War Skoropadsky was a Cossack colonel of the Ukrainian Starodub regiment and after Swedish army crossed into Ukraine in 1708, refused to join Ivan Mazepa who decided to switch sides and fight against Russia. Only about 3,000 Cossacks, mostly Zaporozhians, followed Mazepa, whi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ivan Mazepa
Ivan Stepanovych Mazepa (also spelled Mazeppa; uk, Іван Степанович Мазепа, pl, Jan Mazepa Kołodyński; ) was a Ukrainian military, political, and civic leader who served as the Hetman of Zaporizhian Host in 1687–1708. He was awarded a title of Prince of the Holy Roman Empire in 1707 for his efforts for the Holy League. The historical events of Mazepa's life have inspired many literary, artistic and musical works. He was famous as a patron of the arts. Mazepa played an important role in the Battle of Poltava (1709), where after learning that Tsar Peter I intended to relieve him as acting Hetman (military leader) of Zaporozhian Host (a Cossack state) and to replace him with Alexander Menshikov, he defected from his army and sided with King Charles XII of Sweden. The political consequences and interpretation of this defection have resonated in the national histories both of Russia and of Ukraine. The Russian Orthodox Church laid an anathema (e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |