|
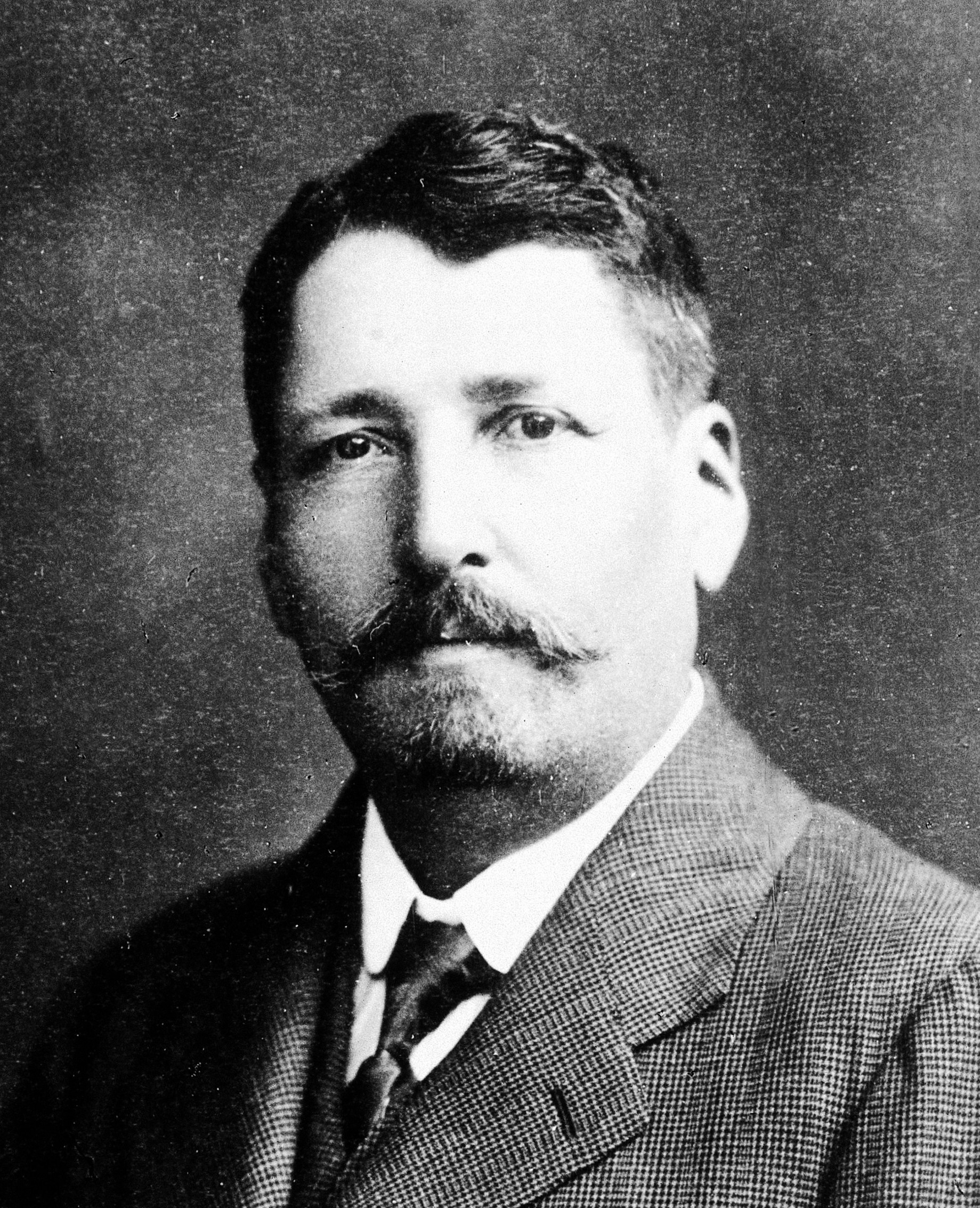
Ivan Honl
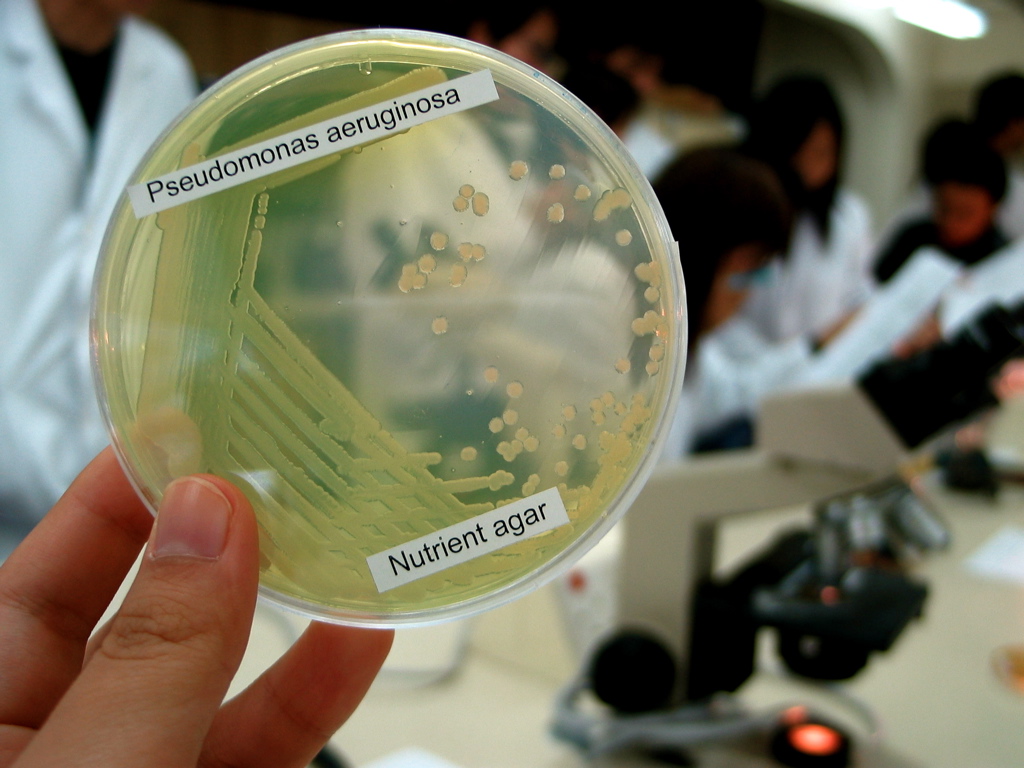
Ivan Honl (23 April 1866 in Zbýšov, Moravia – 7 June 1936 in , Náchod, Czechoslovakia) was a Czech bacteriologist, serologist and activist in the struggle against tuberculosis. Honl became one of founders of Czech microbiology. Under the guidance of Jaroslav Hlava Honl gained his habilitation in bacteriology at Charles University in Prague in 1898. In 1919 he was named head to the new Czech Bacteriological Institute (''Ústav pro bakteriologii a sérologii Lékařské fakulty Univerzity Karlovy''). . Honl was one of the early researchers of antibiotics. At the end of the 1890s he isolated a product of ''Bacterium pyocyaneum'' (today called ''Pseudomonas aeruginosa''), which was used as medicine (Anginol) from the start of WWI until it was replaced by penicillin after WWII. In 1899 he co-founded an institute to treat tuberculosis in Czechoslovakia , rue, Чеськословеньско, , yi, טשעכאסלאוואקיי, , common_name = Czec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ivan Honl
Ivan Honl (23 April 1866 in Zbýšov, Moravia – 7 June 1936 in , Náchod, Czechoslovakia) was a Czech bacteriologist, serologist and activist in the struggle against tuberculosis. Honl became one of founders of Czech microbiology. Under the guidance of Jaroslav Hlava Honl gained his habilitation in bacteriology at Charles University in Prague in 1898. In 1919 he was named head to the new Czech Bacteriological Institute (''Ústav pro bakteriologii a sérologii Lékařské fakulty Univerzity Karlovy''). . Honl was one of the early researchers of antibiotics. At the end of the 1890s he isolated a product of ''Bacterium pyocyaneum'' (today called ''Pseudomonas aeruginosa''), which was used as medicine (Anginol) from the start of WWI until it was replaced by penicillin after WWII. In 1899 he co-founded an institute to treat tuberculosis in Czechoslovakia , rue, Чеськословеньско, , yi, טשעכאסלאוואקיי, , common_name = Czec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charles University In Prague
) , image_name = Carolinum_Logo.svg , image_size = 200px , established = , type = Public, Ancient , budget = 8.9 billion CZK , rector = Milena Králíčková , faculty = 4,057 , administrative_staff = 4,026 , students = 51,438 , undergrad = 32,520 , postgrad = 9,288 , doctoral = 7,428 , city = Prague , country = Czech Republic , campus = Urban , colors = , affiliations = Coimbra Group EUA Europaeum , website = Charles University ( cs, Univerzita Karlova, UK; la, Universitas Carolina; german: Karls-Universität), also known as Charles University in Prague or historically as the University of Prague ( la, Universitas Pragensis, links=no), is the oldest and largest university in the Czech Republic. It is one of the oldest universities in Europe in continuous operation. Today, the university consists of 17 faculties located in Prague, Hradec Králové, and Plzeň. Charles University belongs among the top three universities in Central and Eastern Europe. It is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
People From Zbýšov
A person ( : people) is a being that has certain capacities or attributes such as reason, morality, consciousness or self-consciousness, and being a part of a culturally established form of social relations such as kinship, ownership of property, or legal responsibility. The defining features of personhood and, consequently, what makes a person count as a person, differ widely among cultures and contexts. In addition to the question of personhood, of what makes a being count as a person to begin with, there are further questions about personal identity and self: both about what makes any particular person that particular person instead of another, and about what makes a person at one time the same person as they were or will be at another time despite any intervening changes. The plural form "people" is often used to refer to an entire nation or ethnic group (as in "a people"), and this was the original meaning of the word; it subsequently acquired its use as a plural form of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1936 Deaths
Events January–February * January 20 – George V of the United Kingdom and the British Dominions and Emperor of India, dies at his Sandringham Estate. The Prince of Wales succeeds to the throne of the United Kingdom as King Edward VIII. * January 28 – Britain's King George V state funeral takes place in London and Windsor. He is buried at St George's Chapel, Windsor Castle * February 4 – Radium E (bismuth-210) becomes the first radioactive element to be made synthetically. * February 6 – The IV Olympic Winter Games open in Garmisch-Partenkirchen, Germany. * February 10– 19 – Second Italo-Ethiopian War: Battle of Amba Aradam – Italian forces gain a decisive tactical victory, effectively neutralizing the army of the Ethiopian Empire. * February 16 – 1936 Spanish general election: The left-wing Popular Front coalition takes a majority. * February 26 – February 26 Incident (二・二六事件, ''Niniroku Jiken''): The Impe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1866 Births
Events January–March * January 1 ** Fisk University, a historically black university, is established in Nashville, Tennessee. ** The last issue of the abolitionist magazine '' The Liberator'' is published. * January 6 – Ottoman troops clash with supporters of Maronite leader Youssef Bey Karam, at St. Doumit in Lebanon; the Ottomans are defeated. * January 12 ** The '' Royal Aeronautical Society'' is formed as ''The Aeronautical Society of Great Britain'' in London, the world's oldest such society. ** British auxiliary steamer sinks in a storm in the Bay of Biscay, on passage from the Thames to Australia, with the loss of 244 people, and only 19 survivors. * January 18 – Wesley College, Melbourne, is established. * January 26 – Volcanic eruption in the Santorini caldera begins. * February 7 – Battle of Abtao: A Spanish naval squadron fights a combined Peruvian-Chilean fleet, at the island of Abtao, in the Chiloé Archipelago of southern Chile. * Februar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposing military alliances: the Allies and the Axis powers. World War II was a total war that directly involved more than 100 million personnel from more than 30 countries. The major participants in the war threw their entire economic, industrial, and scientific capabilities behind the war effort, blurring the distinction between civilian and military resources. Aircraft played a major role in the conflict, enabling the strategic bombing of population centres and deploying the only two nuclear weapons ever used in war. World War II was by far the deadliest conflict in human history; it resulted in 70 to 85 million fatalities, mostly among civilians. Tens of millions died due to genocides (including the Holocaust), starvation, massa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Penicillin
Penicillins (P, PCN or PEN) are a group of β-lactam antibiotics originally obtained from '' Penicillium'' moulds, principally '' P. chrysogenum'' and '' P. rubens''. Most penicillins in clinical use are synthesised by P. chrysogenum using deep tank fermentation and then purified. A number of natural penicillins have been discovered, but only two purified compounds are in clinical use: penicillin G (intramuscular or intravenous use) and penicillin V (given by mouth). Penicillins were among the first medications to be effective against many bacterial infections caused by staphylococci and streptococci. They are still widely used today for different bacterial infections, though many types of bacteria have developed resistance following extensive use. 10% of the population claims penicillin allergies but because the frequency of positive skin test results decreases by 10% with each year of avoidance, 90% of these patients can tolerate penicillin. Additionally, those wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
World War I
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, the United States, and the Ottoman Empire, with fighting occurring throughout Europe, the Middle East, Africa, the Pacific, and parts of Asia. An estimated 9 million soldiers were killed in combat, plus another 23 million wounded, while 5 million civilians died as a result of military action, hunger, and disease. Millions more died in genocides within the Ottoman Empire and in the 1918 influenza pandemic, which was exacerbated by the movement of combatants during the war. Prior to 1914, the European great powers were divided between the Triple Entente (comprising France, Russia, and Britain) and the Triple Alliance (containing Germany, Austria-Hungary, and Italy). Tensions in the Balkans came to a head on 28 June 1914, following the assassination of Archduke Franz Ferdi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pseudomonas Aeruginosa
''Pseudomonas aeruginosa'' is a common encapsulated, gram-negative, aerobic–facultatively anaerobic, rod-shaped bacterium that can cause disease in plants and animals, including humans. A species of considerable medical importance, ''P. aeruginosa'' is a multidrug resistant pathogen recognized for its ubiquity, its intrinsically advanced antibiotic resistance mechanisms, and its association with serious illnesses – hospital-acquired infections such as ventilator-associated pneumonia and various sepsis syndromes. The organism is considered opportunistic insofar as serious infection often occurs during existing diseases or conditions – most notably cystic fibrosis and traumatic burns. It generally affects the immunocompromised but can also infect the immunocompetent as in hot tub folliculitis. Treatment of ''P. aeruginosa'' infections can be difficult due to its natural resistance to antibiotics. When more advanced antibiotic drug regimens are needed adverse effects ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antibiotics
An antibiotic is a type of antimicrobial substance active against bacteria. It is the most important type of antibacterial agent for fighting bacterial infections, and antibiotic medications are widely used in the treatment and prevention of such infections. They may either kill or inhibit the growth of bacteria. A limited number of antibiotics also possess antiprotozoal activity. Antibiotics are not effective against viruses such as the common cold or influenza; drugs which inhibit viruses are termed antiviral drugs or antivirals rather than antibiotics. Sometimes, the term ''antibiotic''—literally "opposing life", from the Greek roots ἀντι ''anti'', "against" and βίος ''bios'', "life"—is broadly used to refer to any substance used against microbes, but in the usual medical usage, antibiotics (such as penicillin) are those produced naturally (by one microorganism fighting another), whereas non-antibiotic antibacterials (such as sulfonamides and antisep ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jaroslav Hlava
Jaroslav Hlava (7 May 1855 – 31 October 1924) was an anatomical pathologist. In 1879, he graduated from the Medical Faculty of Charles University in Prague. In 1887, he became a full professor of pathological anatomy. He was rector of Prague's General Hospital and director of the Czech Institute of Pathological Anatomy. He was a pioneer in bacteriology and studied the etiology of infectious diseases and oncology. In 1887, Hlava authored a widely cited article entitled ''About Dysentery''. Due to a translation error, the article was attributed to O. Uplavici in English publications until 1938. The name of author was written in small characters, and the translator mistook ''O ÚPLAVICI'' (''About dysentery'' in Czech) for the name of the author and ''PŘEDBĚŽNÁ ZPRÁVA'' (preliminary report) for ''About Dysentery''. The mistake was corrected in 1939 by English biologist Clifford Dobell Cecil Clifford Dobell FRS (22 February 1886, Birkenhead – 23 December 1949, Lo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zbýšov
Zbýšov is a town in Brno-Country District in the South Moravian Region of the Czech Republic. It has about 3,700 inhabitants. Geography Zbýšov is located about west of Brno. It lies on the border between the Křižanov Highlands and Boskovice Furrow. The highest point is at above sea level. History The first written mention of Zbýšov is from 1280, when the settlement of Zbýšov was given to the Oslavany monastery by Bohuš of Drahotuše, the supreme marshal. The village belonged to the Oslavany estate and shared its owners. In 1790, Zbýšov had 53 houses and 313 inhabitants. Until the end of the 18th century, Zbýšov was an insignificant settlement, which changed with the discovery of bituminous coal. In 1820, a mining company called Láska Boží (i.e. "God's blessing") was founded. Since then, the importance of Zbýšov and the entire area has grown. The Simson mine was established in 1848 and coal was mined there from 1853 to 1925. In the mid-19th century, the v ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


_1938.jpg)