|
Isocyanide
An isocyanide (also called isonitrile or carbylamine) is an organic compound with the functional group –. It is the isomer of the related nitrile (–C≡N), hence the prefix is ''isocyano''.IUPAC Goldboo''isocyanides''/ref> The organic fragment is connected to the isocyanide group through the nitrogen atom, not via the carbon. They are used as building blocks for the synthesis of other compounds. Properties Structure and bonding The C-N distance in isocyanides is 115.8 pm in methyl isocyanide. The C-N-C angles are near 180°. Akin to carbon monoxide, isocyanides are described by two resonance structures, one with a triple bond between the nitrogen and the carbon and one with a double bond between. The π lone pair of the nitrogen stabilizes the structure and is responsible of the linearity of isocyanides, although the reactivity of isocyanides reflects some carbene character, at least in a formal sense. Thus, both resonance structures are useful representations. They are s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Methyl Isocyanide
Methyl isocyanide or isocyanomethane is an organic compound and a member of the isocyanide family. This colorless liquid is isomeric to methyl cyanide (acetonitrile), but its reactivity is very different. In contrast to the faintly sweet, ethereal odor of acetonitrile, the smell of methyl isocyanide, like that of other simple volatile isocyanides, is distinctly penetrating and vile. Methyl isocyanide is mainly used for making 5-membered heterocyclic rings. The C-N distance in methyl isocyanide is very short, 1.158 Å as is characteristic of isocyanides. Preparation and uses Methyl isocyanide was first prepared by A. Gautier by reaction of silver cyanide with methyl iodide Iodomethane, also called methyl iodide, and commonly abbreviated "MeI", is the chemical compound with the formula CH3I. It is a dense, colorless, volatile liquid. In terms of chemical structure, it is related to methane by replacement of one .... The common method for preparing methyl isocyanides is the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
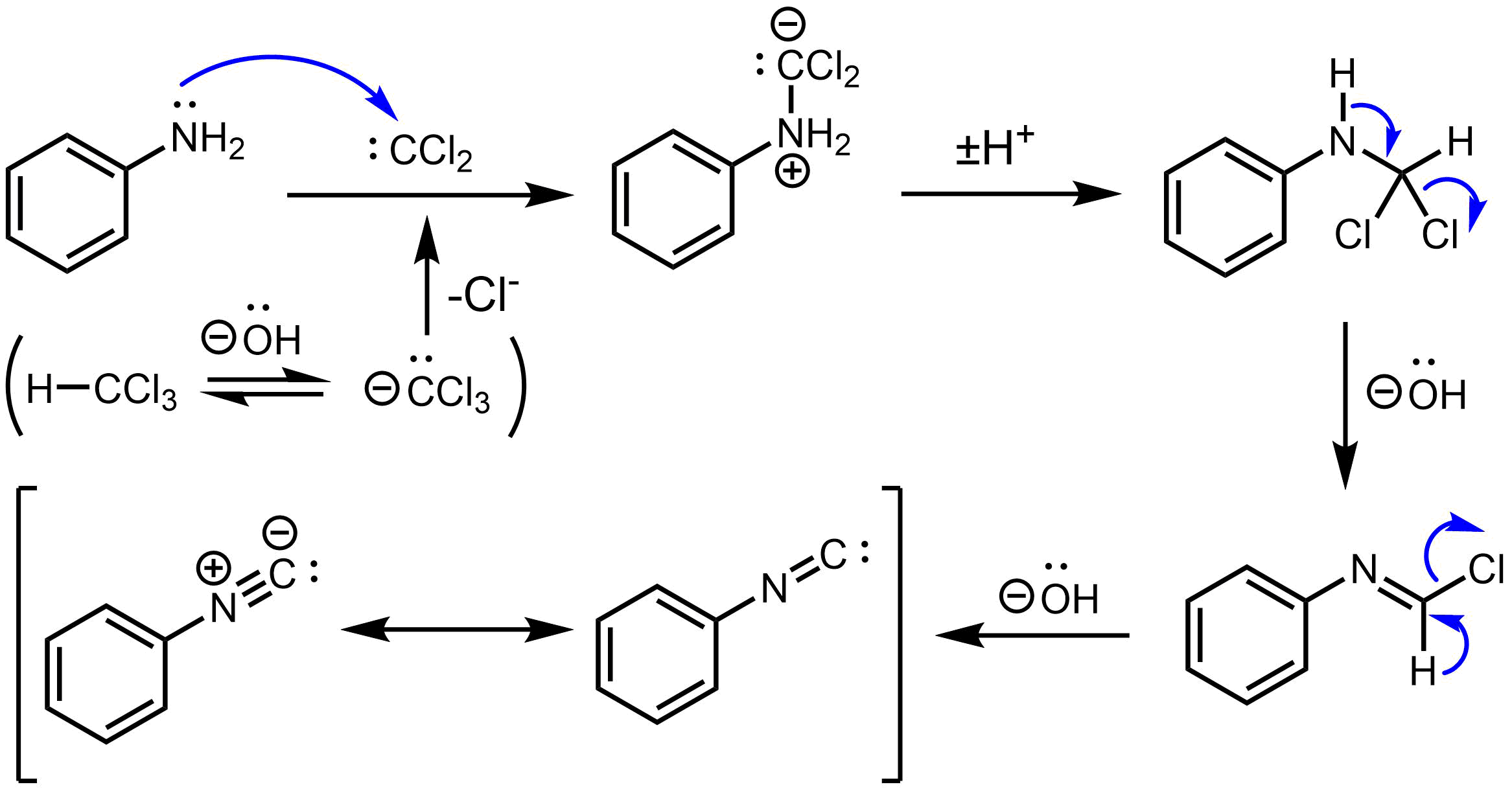
Carbylamine Reaction
The carbylamine reaction (also known as the Hoffmann isocyanide synthesis) is the synthesis of an isocyanide by the reaction of a primary amine, chloroform, and base. The conversion involves the intermediacy of dichlorocarbene. Illustrative is the synthesis of ''tert''-butyl isocyanide from ''tert''-butylamine in the presence of catalytic amount of the phase transfer catalyst benzyltriethylammonium chloride. :Me3CNH2 + CHCl3 + 3 NaOH → Me3CNC + 3 NaCl + 3 H2O Similar reactions have been reported for aniline. It is used to prepare secondary amines. Test for primary amines As it is only effective for primary amines, the carbylamine reaction can be used as a chemical test for their presence. In this context, the reaction is also known as Saytzeff's isocyanide test. In this reaction, the analyte is heated with alcoholic potassium hydroxide and chloroform. If a primary amine is present, the isocyanide (carbylamine) is formed, as indicated by a foul odour. The carbylamine test does ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tosylmethyl Isocyanide
TosMIC (toluenesulfonylmethyl isocyanide) is an organic compound with the formula CH3C6H4SO2CH2NC. The molecule contains both sulfonyl and isocyanide groups. It is a colourless solid that, unlike many isocyanides, is odorless. It is prepared by dehydration of the related formamide derivative. It is used in the Van Leusen reaction which is used to convert aldehydes to nitriles or in the preparation of oxazoles and imidazole Imidazole (ImH) is an organic compound with the formula C3N2H4. It is a white or colourless solid that is soluble in water, producing a mildly alkaline solution. In chemistry, it is an aromatic heterocycle, classified as a diazole, and has non-ad ...s. The versatility of TosMIC in organic synthesis has been documented. It is a fairly strong carbon acid, with an estimated p''K''a of 14 (compared to 29 for methyl tolyl sulfone), the isocyano group acting as an electron acceptor of strength comparable to an ester group. Further reading * References {{reflist ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dichlorocarbene
Dichlorocarbene is the reactive intermediate with chemical formula CCl2. Although this chemical species has not been isolated, it is a common intermediate in organic chemistry, being generated from chloroform. This bent diamagnetic molecule rapidly inserts into other bonds. Preparation Dichlorocarbene is most commonly generated by reaction of chloroform and a base such as potassium ''tert''-butoxide or aqueous sodium hydroxide. A phase transfer catalyst, for instance benzyltriethylammonium bromide, facilitates the migration of the hydroxide in the organic phase. :HCCl3 + NaOH → CCl2 + NaCl + H2O Other reagents and routes Another precursor to dichlorocarbene is ethyl trichloroacetate. Upon treatment with sodium methoxide it releases CCl2. Phenyl(trichloromethyl)mercury decomposes thermally to release CCl2. :PhHgCCl3 → CCl2 + PhHgCl Dichlorodiazirine, which is stable in the dark, decomposes into dichlorocarbene and nitrogen via photolysis. Dichlorocarbene can also be ob ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Functional Group
In organic chemistry, a functional group is a substituent or moiety in a molecule that causes the molecule's characteristic chemical reactions. The same functional group will undergo the same or similar chemical reactions regardless of the rest of the molecule's composition. This enables systematic prediction of chemical reactions and behavior of chemical compounds and the design of chemical synthesis. The reactivity of a functional group can be modified by other functional groups nearby. Functional group interconversion can be used in retrosynthetic analysis to plan organic synthesis. A functional group is a group of atoms in a molecule with distinctive chemical properties, regardless of the other atoms in the molecule. The atoms in a functional group are linked to each other and to the rest of the molecule by covalent bonds. For repeating units of polymers, functional groups attach to their nonpolar core of carbon atoms and thus add chemical character to carbon chai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Triple Bond
A triple bond in chemistry is a chemical bond between two atoms involving six bonding electrons instead of the usual two in a covalent single bond. Triple bonds are stronger than the equivalent single bonds or double bonds, with a bond order of three. The most common triple bond, that between two carbon atoms, can be found in alkynes. Other functional groups containing a triple bond are cyanides and isocyanides. Some diatomic molecules, such as dinitrogen and carbon monoxide, are also triple bonded. In skeletal formulae the triple bond is drawn as three parallel lines (≡) between the two connected atoms. Bonding The types of bonding can be explained in terms of orbital hybridization. In the case of acetylene each carbon atom has two sp-orbitals and two p-orbitals. The two sp-orbitals are linear with 180° angles and occupy the x-axis (cartesian coordinate system). The p-orbitals are perpendicular on the y-axis and the z-axis. When the carbon atoms approach each other, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ivar Karl Ugi
Ivar Karl Ugi (9 September 1930 in Saaremaa, Estonia – 29 September 2005 in Munich) was an Estonian-born German chemist who made major contributions to organic chemistry. He is known for the research on multicomponent reactions, yielding the Ugi reaction. Biography After he went to Germany from Estonia in 1941 he began his studies of chemistry in 1949 at the University of Tübingen until 1951. He became Dr. rer. nat. in 1954 at the Ludwig Maximilian University of Munich. He did his habilitation 1960 at the same university. After a short but very successful career in industry at Bayer from 1962 until 1968 when he joined the University of Southern California at Los Angeles. From 1971 he worked at the Technical University of Munich, and was an emeritus from 1999 until his death in 2005. Research and development The one pot reaction of a ketone or aldehyde, an amine, an isocyanide and a carboxylic acid to form a bis-amide is generally known as Ugi reaction The Ugi reaction is a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diphosgene
Diphosgene is an organic chemical compound with the formula ClCO2CCl3. This colorless liquid is a valuable reagent in the synthesis of organic compounds. Diphosgene is related to phosgene and has comparable toxicity, but is more conveniently handled because it is a liquid, whereas phosgene is a gas. Production and uses Diphosgene is prepared by radical chlorination of methyl chloroformate under UV light: :Cl-CO-OCH3 + 3 Cl2 —(hv)→ Cl-CO-OCCl3 + 3 HCl Another method is the radical chlorination of methyl formate: :H-CO-OCH3 + 4 Cl2 —(hv)→ Cl-CO-OCCl3 + 4 HCl Diphosgene converts to phosgene upon heating or upon catalysis with charcoal. It is thus useful for reactions traditionally relying on phosgene. For example, it convert amines into isocyanates, secondary amines into carbamoyl chlorides, carboxylic acids into acid chlorides, and formamides into isocyanides. Diphosgene serves as a source of two equivalents of phosgene: :2 RNH2 + ClCO2CCl3 → 2 RNCO + 4 HCl Wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phosphorus Oxychloride
Phosphoryl chloride (commonly called phosphorus oxychloride) is a colourless liquid with the formula . It hydrolyses in moist air releasing phosphoric acid and fumes of hydrogen chloride. It is manufactured industrially on a large scale from phosphorus trichloride and oxygen or phosphorus pentoxide. It is mainly used to make phosphate esters such as tricresyl phosphate. Structure Like phosphate, is tetrahedral in shape. It features three P−Cl bonds and one strong P=O double bond, with an estimated bond dissociation energy of 533.5 kJ/mol. On the basis of bond length and electronegativity, the Schomaker-Stevenson rule suggests that the double bond form is dominant, in contrast with the case of . The P=O bond involves the donation of the lone pair electrons on oxygen ''p''-orbitals to the antibonding combinations associated with phosphorus-chlorine bonds, thus constituting ''π'' bonding. Phosphoryl chloride exists as neutral molecules in the solid, liquid and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Toluenesulfonyl Chloride
4-Toluenesulfonyl chloride (''p''-toluenesulfonyl chloride, toluene-''p''-sulfonyl chloride) is an organic compound with the formula CH3C6H4SO2Cl. This white, malodorous solid is a reagent widely used in organic synthesis. Abbreviated TsCl or TosCl, it is a derivative of toluene and contains a sulfonyl chloride (−SO2Cl) functional group. Uses In characteristic manner, TsCl converts alcohols (abbreviated ROH) into the corresponding toluenesulfonate esters, or tosyl derivatives ("tosylates"): : CH3C6H4SO2Cl + ROH → CH3C6H4SO2OR + HCl Tosylates can be cleaved with lithium aluminium hydride: : 4 CH3C6H4SO2OR + LiAlH4 → LiAl(O3SC6H4CH3)4 + 4 RH Thus, tosylation followed by reduction allows for removal of a hydroxyl group. Likewise, TsCl is used to prepare sulfonamides from amines: :CH3C6H4SO2Cl + R2NH → CH3C6H4SO2NR2 + HCl The resulting sulfonamides are non-basic and, when derived from primary amines, are even acidic. TsCl reacts with hydrazine to give p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amine
In chemistry, amines (, ) are compounds and functional groups that contain a basic nitrogen atom with a lone pair. Amines are formally derivatives of ammonia (), wherein one or more hydrogen atoms have been replaced by a substituent such as an alkyl or aryl group (these may respectively be called alkylamines and arylamines; amines in which both types of substituent are attached to one nitrogen atom may be called alkylarylamines). Important amines include amino acids, biogenic amines, trimethylamine, and aniline; Inorganic derivatives of ammonia are also called amines, such as monochloramine (). The substituent is called an amino group. Compounds with a nitrogen atom attached to a carbonyl group, thus having the structure , are called amides and have different chemical properties from amines. Classification of amines Amines can be classified according to the nature and number of substituents on nitrogen. Aliphatic amines contain only H and alkyl substituen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Angewandte Chemie
''Angewandte Chemie'' (, meaning "Applied Chemistry") is a weekly peer-reviewed scientific journal that is published by Wiley-VCH on behalf of the German Chemical Society (Gesellschaft Deutscher Chemiker). Publishing formats include feature-length reviews, short highlights, research communications, minireviews, essays, book reviews, meeting reviews, correspondences, corrections, and obituaries. This journal contains review articles covering all aspects of chemistry. According to the ''Journal Citation Reports'', the journal had a 2021 impact factor of 16.823. Editions The journal appears in two editions with separate volume and page numbering: a German edition, ''Angewandte Chemie'' ( (print), (online)), and a fully English-language edition, ''Angewandte Chemie International Edition'' ( (print), (online)). The editions are identical in content with the exception of occasional reviews of German-language books or German translations of IUPAC recommendations. Business model ' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |