|
Iota Ursae Majoris
Iota Ursae Majoris (ι Ursae Majoris, abbreviated Iota UMa, ι UMa), also named Talitha , is a star system in the northern circumpolar constellation of Ursa Major. It has an apparent visual magnitude of 3.14, making it visible to the naked eye and placing it among the brighter members of this constellation. Based upon parallax measurements, it is located at a distance of from the Sun. Nomenclature ''ι Ursae Majoris'' ( Latinised to ''Iota Ursae Majoris'') is the star's Bayer designation. The traditional name ''Talitha'', (which was shared with Kappa Ursae Majoris) comes from the Arabic phrase ( ar, الفقرة الثالثة), a mis-transcription of ( ar, القفزة الثالثة), which means "the third spring, or leap, of the ghazal". The term ''Borealis'' meaning "the north side" in Latin. In 2016, the International Astronomical Union organized a Working Group on Star Names (WGSN) to catalog and standardize proper names for stars. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ursa Major
Ursa Major (; also known as the Great Bear) is a constellation in the northern sky, whose associated mythology likely dates back into prehistory. Its Latin name means "greater (or larger) bear," referring to and contrasting it with nearby Ursa Minor, the lesser bear. In antiquity, it was one of the original 48 constellations listed by Ptolemy in the 2nd century AD, drawing on earlier works by Greek, Egyptian, Babylonian, and Assyrian astronomers. Today it is the third largest of the 88 modern constellations. Ursa Major is primarily known from the asterism of its main seven stars, which has been called the " Big Dipper," "the Wagon," "Charles's Wain," or "the Plough," among other names. In particular, the Big Dipper's stellar configuration mimics the shape of the " Little Dipper." Two of its stars, named Dubhe and Merak ( α Ursae Majoris and β Ursae Majoris), can be used as the navigational pointer towards the place of the current northern pole star, Polaris in Ursa Mino ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kappa Ursae Majoris
Kappa Ursae Majoris (κ Ursae Majoris, abbreviated Kappa UMa, κ UMa) is a binary star in the constellation of Ursa Major. With a combined apparent magnitude of +3.60, the system is approximately 358 light-years from Earth. The two components are designated Kappa Ursae Majoris A (officially named Alkaphrah , a traditional name of the system) and B. Nomenclature ''κ Ursae Majoris'' ( Latinised to ''Kappa Ursae Majoris'') is the system's Bayer designation. The designations of the two components as ''Kappa Ursae Majoris A'' and ''B'' derives from the convention used by the Washington Multiplicity Catalog (WMC) for multiple star systems, and adopted by the International Astronomical Union (IAU). The traditional name of the system is Alkafzah (corrupted to ''Alkaphrah'' or ''El Koprah''), from the Arabic القفزة ''al-qafzah'' "the leap". (Cf. Alula Borealis and Alula Australis.) In 2016, the IAU organized a Working Group on Star Names (WG ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Apollo 1
Apollo 1, initially designated AS-204, was intended to be the first crewed mission of the Apollo program, the American undertaking to land the first man on the Moon. It was planned to launch on February 21, 1967, as the first low Earth orbital test of the Apollo command and service module. The mission never flew; a cabin fire during a launch rehearsal test at Cape Kennedy Air Force Station Launch Complex 34 on January 27 killed all three crew members—Command Pilot Gus Grissom, Senior Pilot Ed White, and Pilot Roger B. Chaffee—and destroyed the command module (CM). The name Apollo 1, chosen by the crew, was made official by NASA in their honor after the fire. Immediately after the fire, NASA convened an Accident Review Board to determine the cause of the fire, and both chambers of the United States Congress conducted their own committee inquiries to oversee NASA's investigation. The ignition source of the fire was determined to be electrical, and the fire spread rapidly ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ed White (astronaut)
Edward Higgins White II (November 14, 1930 – January 27, 1967) was an American aeronautical engineer, United States Air Force officer, test pilot, and NASA astronaut. He was a member of the crews of Gemini 4 and Apollo 1. After graduating from West Point in 1952 with a Bachelor of Science degree, White was sent to flight training, and assigned to the 22nd Fighter Day Squadron at Bitburg Air Base, West Germany, where he flew the F-86 Sabre and F-100 Super Sabre fighters. In 1958, he enrolled in the University of Michigan to study aeronautical engineering, receiving his Master of Science degree in 1959. White then received test pilot training at Edwards Air Force Base, California, before being assigned as a test pilot for the Aeronautical Systems Division at Wright-Patterson Air Force Base, Ohio. White was selected as one of the second group of astronauts, the so-called "Next Nine", who were chosen to take part in the Gemini and Apollo missions. He was assigned as pilot o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chinese Star Names
Chinese star names ( Chinese: , ''xīng míng'') are named according to ancient Chinese astronomy and astrology. The sky is divided into star mansions (, ''xīng xiù'', also translated as "lodges") and asterisms (, ''xīng guān''). The system of 283 asterisms under Three Enclosures and Twenty-eight Mansions was established by Chen Zhuo of the Three Kingdoms period, who synthesized ancient constellations and the asterisms created by early astronomers Shi Shen, Gan De and Wuxian. Since the Han and Jin Dynasties, stars have been given reference numbers within their asterisms in a system similar to the Bayer or Flamsteed designations, so that individual stars can be identified. For example, Deneb (α Cyg) is referred to as (''Tiān Jīn Sì'', the Fourth Star of Celestial Ford). In the Qing Dynasty, Chinese knowledge of the sky was improved by the arrival of European star charts. ''Yixiang Kaocheng'', compiled in mid-18th century by then deputy Minister of Rites Ignaz K� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
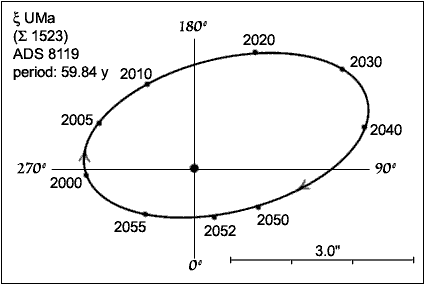
Xi Ursae Majoris
Xi Ursae Majoris is a star system in the constellation of Ursa Major. It has the traditional name Alula Australis; ''Xi Ursae Majoris'' is the Bayer designation, which is Latinised from ξ Ursae Majoris and abbreviated Xi UMa or ξ UMa. It was the first visual double star for which an orbit was calculated, when it was computed by Félix Savary in 1828. It is also a variable star with a small amplitude. Xi Ursae Majoris is found in the left hind paw of the Great Bear. Stellar system The two components are yellow main-sequence stars. The brighter component (designated Xi Ursae Majoris A), has a mean apparent magnitude of +4.41. The companion star (Xi Ursae Majoris B) has an apparent magnitude of +4.87. The orbital period of the two stars is 59.84 years. They are currently (2022) separated by 2.3 arcseconds, and will widen to a maximum 3.0 arcseconds in 2035. Each component of this double star is itself a single-lined spectroscopic binary. The orbit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nu Ursae Majoris
Nu Ursae Majoris (ν Ursae Majoris, abbreviated Nu UMa, ν UMa), formally named Alula Borealis , is a double star in the northern circumpolar constellation of Ursa Major. At an apparent visual magnitude of +3.490, it is bright enough to be seen with the naked eye. Based upon parallax measurements, the distance to ν Ursae Majoris is about . This is a giant star with a stellar classification of K3 III. It has expanded to about 57 times the radius of the Sun and is radiating 775 times the Sun's luminosity. The effective temperature of the outer envelope is 4,070 K; cool enough to give it an orange hue typical of a K-type star. It has a 10th-magnitude optical companion at an angular separation of 7.1 arcseconds. Nomenclature ''ν Ursae Majoris'' ( Latinised to ''Nu Ursae Majoris'') is the star's Bayer designation. It also bore the traditional name of ''Alula Borealis''. ''Alula'' (shared with Xi Ursae Majoris) comes from the Arabic phra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mu Ursae Majoris
Mu Ursae Majoris (μ Ursae Majoris, abbreviated Mu UMa, μ UMa), formally named Tania Australis , is a binary star in the constellation of Ursa Major. An apparent visual magnitude of +3.06 places it among the brighter members of the constellation. Parallax measurements give an estimated distance of roughly from the Sun, with a margin of error of 4%. Stellar system Mu Ursae Majoris is an evolved star that is currently in the red giant stage with a stellar classification of M0 IIIab. It has expanded to 75 times the radius of the Sun whilst the outer atmosphere has cooled to an effective temperature of 3,899 K, giving it the orange-red hued glow of an M-type star. Estimates of the luminosity range from 977–1,200 times that of the Sun. It is classified as a suspected variable star with a brightness variation from magnitude 2.99m to 3.33m. This is a spectroscopic binary star system with a companion a mere 0.2 AU from the primary, assuming ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lambda Ursae Majoris
Lambda Ursae Majoris (λ Ursae Majoris, abbreviated Lambda UMa, λ UMa), formally named Tania Borealis , is a star in the northern circumpolar constellation of Ursa Major. Properties This star has an apparent visual magnitude of +3.45, making it one of the brighter members of the constellation. The distance to this star has been measured directly using the parallax technique, which yields a value of roughly with a 4% margin of error. The stellar classification of Lambda Ursae Majoris is A2 IV, with the luminosity class of 'IV' indicating that, after 410 million years on the main sequence, this star is in the process of evolving into a giant star as the supply of hydrogen at its core becomes exhausted. Compared to the Sun it has 240% of the mass and 230% of the Sun's radius, but is radiating 37 times as much luminosity. This energy is being emitted from the star's outer atmosphere at an effective temperature of 9,280 K, giving it the ch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Purple Forbidden Enclosure
The Purple Forbidden enclosure ( Zǐ wēi yuán) is one of the San Yuan ( Sān yuán) or Three Enclosures. Stars and constellations of this group lie near the north celestial pole and are visible all year from temperate latitudes in the Northern Hemisphere. Asterisms The asterisms are : See also * Twenty-eight mansions References Chinese constellations Chinese astrology {{china-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chinese Astronomy
Astronomy in China has a long history stretching from the Shang dynasty, being refined over a period of more than 3,000 years. The ancient Chinese people have identified stars from 1300 BCE, as Chinese star names later categorized in the twenty-eight mansions have been found on oracle bones unearthed at Anyang, dating back to the mid-Shang dynasty. The core of the "mansion" (宿 ''xiù'') system also took shape around this period, by the time of King Wu Ding (1250–1192 BCE). Detailed records of astronomical observations began during the Warring States period (fourth century BCE) and flourished from the Han period onward. Chinese astronomy was equatorial, centered on close observation of circumpolar stars, and was based on different principles from those in traditional Western astronomy, where heliacal risings and settings of zodiac constellations formed the basic ecliptic framework. Joseph Needham has described the ancient Chinese as the most persistent and accurate ob ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
IAU Working Group On Star Names
The International Astronomical Union (IAU) established a Working Group on Star Names (WGSN) in May 2016 to catalog and standardize proper names for stars for the international astronomical community. It operates under Division C – Education, Outreach and Heritage. The IAU states that it is keen to make a distinction between the terms ''name'' and ''designation''. To the IAU, ''name'' refers to the (usually colloquial) term used for a star in everyday conversation, while ''designation'' is solely alphanumerical, and used almost exclusively in official catalogues and for professional astronomy. (The WGSN notes that transliterated Bayer designations (e.g., Tau Ceti) are considered a special historical case and are treated as designations.) Terms of reference The terms of reference for the WGSN for the period 2016–2018 were approved by the IAU Executive Committee at its meeting on 6 May 2016. In summary, these are to: * establish IAU guidelines for the proposal and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |