|
International Sanitary Regulations
The International Sanitary Conferences were a series of 14 conferences, the first of them organized by the French Government in 1851 to standardize international quarantine regulations against the spread of cholera, plague, and yellow fever. In total 14 conferences took place from 1851 to 1938; the conferences played a major role in the formation of the Office international d'hygiène publique before world war II, and the World Health Organization in 1948. Background The outbreak of the Second cholera pandemic in 1829 prompted European Governments to appoint medical missions to investigate the causes of the epidemic. Among others, the Royal Academy of Medicine of Paris in June 1831 sent Auguste Gérardin and Paul Gaimard on medical mission to Russia, Prussia, and Austria. Later the Minister of Commerce of France appointed the Secretary of the Conseil supérieur de la santé, P. de. Ségur-Dupeyron, with the task of creating a report on the sanitary regulations of the Mediterra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
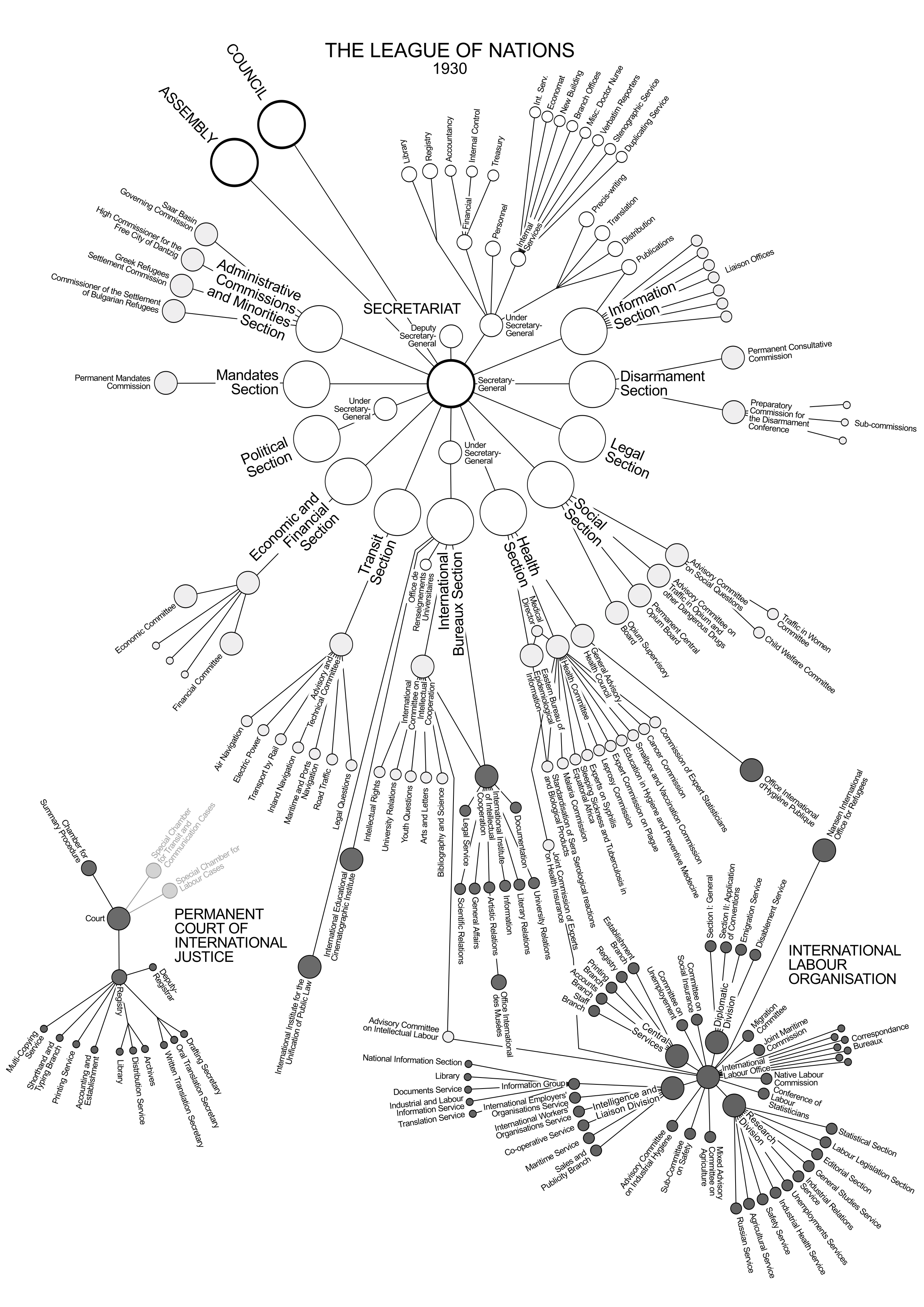
Office International D'hygiène Publique
The International Office of Public Hygiene, also known by its French name as the Office International d'Hygiène Publique and abbreviated as OIHP, was an international organization founded 9 December 1907 and based in Paris, France. It merged onto the World Health Organization after World War II. History It was created to oversee international rules regarding the quarantining of ships and ports to prevent the spread of plague and cholera, and to administer other public health conventions, leading to engage on other epidemics, and the collection of broader epidemiological data on various diseases, as well as issues such as the control of medicinal opium, cannabis, and other drugs, the traumas created by World War I, etc. The OIHP was part of the complex structure known as the Health Organization () of the League of Nations, in an often-competing, and sometimes collaborative relation with the League of Nations' Health Committee. The OIHP was dissolved by protocols signed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Washington, D
Washington commonly refers to: * Washington (state), United States * Washington, D.C., the capital of the United States ** A metonym for the federal government of the United States ** Washington metropolitan area, the metropolitan area centered on Washington, D.C. * George Washington (1732–1799), the first president of the United States Washington may also refer to: Places England * Washington, Tyne and Wear, a town in the City of Sunderland metropolitan borough ** Washington Old Hall, ancestral home of the family of George Washington * Washington, West Sussex, a village and civil parish Greenland * Cape Washington, Greenland * Washington Land Philippines *New Washington, Aklan, a municipality *Washington, a barangay in Catarman, Northern Samar *Washington, a barangay in Escalante, Negros Occidental *Washington, a barangay in San Jacinto, Masbate *Washington, a barangay in Surigao City United States * Washington, Wisconsin (other) * Fort Washington (disambiguati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
France
France (), officially the French Republic ( ), is a country primarily located in Western Europe. It also comprises of overseas regions and territories in the Americas and the Atlantic, Pacific and Indian Oceans. Its metropolitan area extends from the Rhine to the Atlantic Ocean and from the Mediterranean Sea to the English Channel and the North Sea; overseas territories include French Guiana in South America, Saint Pierre and Miquelon in the North Atlantic, the French West Indies, and many islands in Oceania and the Indian Ocean. Due to its several coastal territories, France has the largest exclusive economic zone in the world. France borders Belgium, Luxembourg, Germany, Switzerland, Monaco, Italy, Andorra, and Spain in continental Europe, as well as the Netherlands, Suriname, and Brazil in the Americas via its overseas territories in French Guiana and Saint Martin. Its eighteen integral regions (five of which are overseas) span a combined area of and contain clos ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spain
, image_flag = Bandera de España.svg , image_coat = Escudo de España (mazonado).svg , national_motto = ''Plus ultra'' (Latin)(English: "Further Beyond") , national_anthem = (English: "Royal March") , image_map = , map_caption = , image_map2 = , capital = Madrid , coordinates = , largest_city = Madrid , languages_type = Official language , languages = Spanish , ethnic_groups = , ethnic_groups_year = , ethnic_groups_ref = , religion = , religion_ref = , religion_year = 2020 , demonym = , government_type = Unitary parliamentary constitutional monarchy , leader_title1 = Monarch , leader_name1 = Felipe VI , leader_title2 = Prime Minister , leader_name2 = Pedro Sánchez , legislature = C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Portugal
Portugal, officially the Portuguese Republic ( pt, República Portuguesa, links=yes ), is a country whose mainland is located on the Iberian Peninsula of Southwestern Europe, and whose territory also includes the Atlantic archipelagos of the Azores and Madeira. It features the westernmost point in continental Europe, and its Iberian portion is bordered to the west and south by the Atlantic Ocean and to the north and east by Spain, the sole country to have a land border with Portugal. Its two archipelagos form two autonomous regions with their own regional governments. Lisbon is the capital and largest city by population. Portugal is the oldest continuously existing nation state on the Iberian Peninsula and one of the oldest in Europe, its territory having been continuously settled, invaded and fought over since prehistoric times. It was inhabited by pre-Celtic and Celtic peoples who had contact with Phoenicians and Ancient Greek traders, it was ruled by the Ro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Greece
Greece,, or , romanized: ', officially the Hellenic Republic, is a country in Southeast Europe. It is situated on the southern tip of the Balkans, and is located at the crossroads of Europe, Asia, and Africa. Greece shares land borders with Albania to the northwest, North Macedonia and Bulgaria to the north, and Turkey to the northeast. The Aegean Sea lies to the east of the mainland, the Ionian Sea to the west, and the Sea of Crete and the Mediterranean Sea to the south. Greece has the longest coastline on the Mediterranean Basin, featuring thousands of islands. The country consists of nine traditional geographic regions, and has a population of approximately 10.4 million. Athens is the nation's capital and largest city, followed by Thessaloniki and Patras. Greece is considered the cradle of Western civilization, being the birthplace of democracy, Western philosophy, Western literature, historiography, political science, major scientific and mathematica ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Great Britain
Great Britain is an island in the North Atlantic Ocean off the northwest coast of continental Europe. With an area of , it is the largest of the British Isles, the largest European island and the ninth-largest island in the world. It is dominated by a maritime climate with narrow temperature differences between seasons. The 60% smaller island of Ireland is to the west—these islands, along with over 1,000 smaller surrounding islands and named substantial rocks, form the British Isles archipelago. Connected to mainland Europe until 9,000 years ago by a landbridge now known as Doggerland, Great Britain has been inhabited by modern humans for around 30,000 years. In 2011, it had a population of about , making it the world's third-most-populous island after Java in Indonesia and Honshu in Japan. The term "Great Britain" is often used to refer to England, Scotland and Wales, including their component adjoining islands. Great Britain and Northern Ireland now cons ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
International Health Regulations
The International Health Regulations (IHR), first adopted by the World Health Assembly in 1969 and last revised in 2005, are a legally binding rules that only apply to the WHO that is an instrument that aims for international collaboration "to prevent, protect against, control, and provide a public health response to the international spread of disease in ways that are commensurate with and restricted to public health risks and that avoid unnecessary interference with international traffic and trade". The IHR is the only international legal treaty with the responsibility of empowering the World Health Organization (WHO) to act as the main global surveillance system. In 2005, following the 2002–2004 SARS outbreak, several changes were made to the previous revised IHRs originating from 1969. The 2005 IHR came into force in June 2007, with 196 binding countries that recognised that certain public health incidents, extending beyond disease, ought to be designated as a Public Health ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carte Jaune
The International Certificate of Vaccination or Prophylaxis (ICVP), also known as the Carte Jaune or Yellow Card, is an official vaccination report created by the World Health Organization (WHO). As a travel document, it is a kind of ''medical passport'' that is recognised internationally and may be required for entry to certain countries where there are increased health risks for travellers. The ICVP is not an immunity passport; the primary difference is that vaccination certificates such as the ICVP incentivise individuals to obtain vaccination against a disease, while immunity passports incentivise individuals to get infected with and recover from a disease. Various schemes for health passports or vaccination certificates have been proposed for people who have been vaccinated against COVID-19. Name The ICVP's nickname ''Yellow Card'' or its French equivalent ''Carte Jaune'' derives from the yellow colour of the document. The fact that yellow fever is a commonly required v ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
International Sanitary Convention For Aerial Navigation (1933)
The International Sanitary Convention for Aerial Navigation (1933) was an international sanitary convention, drawn up in 1932 and signed at The Hague on 12 April 1933 (without a conference) and came into force on 1 August 1935 to protect communities against diseases liable to be imported by aircraft and to protect air crew against diseases due to flying. It contained a number of regulations consisting of measures to prevent the spread of plague, cholera, yellow fever, typhus and smallpox. It was formally ratified by around ten countries. Service aircraft were included in March 1939. Intelligence on infectious disease at ports was provided to health authorities by the health organisation at the League of Nations. It was amended in Washington on 15 December 1944, to form the International Sanitary Convention for Aerial Navigation (1944), which came into force on 15 January 1945. After the amendment of the Convention in 1944, in addition to Personal, Aircraft and Maritime Declarati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Camille Barrère
Camille Barrère (23 October 1851 – 7 October 1940) was a French diplomat, most notably the ambassador to Italy from 1897 to 1924. In 1902, Barrère negotiated a secret accord with Italian Minister of Foreign Affairs Giulio Prinetti that ended the two nation's historical rivalry for North Africa. The Prinetti-Barrère Accord stated that, in the event of a redistribution of Ottoman lands in northern Africa, France would not contest an Italian claim on the lands of the Tripolitania Vilayet, which makes up modern Libya. In return, Italy would not contest a French claim on the Ottoman territory of Morocco. This agreement allowed for the French Agadir Crisis in Morocco in 1911 and the Italo-Turkish War of 1911-1912 that resulted in the taking of those territories. Barrère also was a key figure in arranging the 1915 secret Treaty of London between Italy and the Triple Entente that resulted in Italy abandoning its Triple Alliance partners of Germany and Austro-Hungary durin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dresden
Dresden (, ; Upper Saxon: ''Dräsdn''; wen, label= Upper Sorbian, Drježdźany) is the capital city of the German state of Saxony and its second most populous city, after Leipzig. It is the 12th most populous city of Germany, the fourth largest by area (after Berlin, Hamburg and Cologne), and the third most populous city in the area of former East Germany, after Berlin and Leipzig. Dresden's urban area comprises the towns of Freital, Pirna, Radebeul, Meissen, Coswig, Radeberg and Heidenau and has around 790,000 inhabitants. The Dresden metropolitan area has approximately 1.34 million inhabitants. Dresden is the second largest city on the River Elbe after Hamburg. Most of the city's population lives in the Elbe Valley, but a large, albeit very sparsely populated area of the city east of the Elbe lies in the West Lusatian Hill Country and Uplands (the westernmost part of the Sudetes) and thus in Lusatia. Many boroughs west of the Elbe lie in the foreland of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |