|
Inertial Supercharging Effect
The inertial supercharging effect is the increase of volumetric efficiency in the cylinder of an engine. Background The internal combustion engine is the most common engine found in mechanical devices across the world. The engine is powered by an air/gasoline mixture and the physics principles of heat and pressure. Overview Inertial supercharging effect is the result of incoming fuel/air charge developing momentum greater than intake stroke would generate alone. It is achieved by the careful design of the shape of the piston head, the valves and cam profile/valve timing which creates a vacuum that pulls more exhaust gases (and some of the intake gasses) out of the engine. This is immediately followed by a reflected pressure wave timed to force the extra intake gasses back into the cylinder, thus achieving a greater mass of air/fuel mix in the combustion chamber than possible with conventional methods. Expansion chambers only work well at a narrow engine speed range which is w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Internal Combustion Engine
An internal combustion engine (ICE or IC engine) is a heat engine in which the combustion of a fuel occurs with an oxidizer (usually air) in a combustion chamber that is an integral part of the working fluid flow circuit. In an internal combustion engine, the expansion of the high-temperature and high- pressure gases produced by combustion applies direct force to some component of the engine. The force is typically applied to pistons ( piston engine), turbine blades (gas turbine), a rotor (Wankel engine), or a nozzle ( jet engine). This force moves the component over a distance, transforming chemical energy into kinetic energy which is used to propel, move or power whatever the engine is attached to. This replaced the external combustion engine for applications where the weight or size of an engine was more important. The first commercially successful internal combustion engine was created by Étienne Lenoir around 1860, and the first modern internal combustion engi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intake Stroke
In the context of an internal combustion engine, the term stroke has the following related meanings: * A phase of the engine's cycle (e.g. compression stroke, exhaust stroke), during which the piston travels from top to bottom or vice versa. * The type of power cycle used by a piston engine (e.g. two-stroke engine, four-stroke engine). * "Stroke length", the distance travelled by the piston during each cycle. The stroke length––along with bore diameter––determines the engine's displacement. Phases in the power cycle Commonly used engine phases or strokes (i.e. those used in a four-stroke engine) are described below. Other types of engines can have very different phases. Induction-intake stroke The induction stroke is the first phase in a four-stroke (e.g. Otto cycle or Diesel cycle) engine. It involves the downward movement of the piston, creating a partial vacuum that draws a air-fuel mixture (or air alone, in the case of a direct injection engine) into the combust ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Valve Timing
In a piston engine, the valve timing is the precise timing of the opening and closing of the valves. In an internal combustion engine those are usually poppet valves and in a steam engine they are usually slide valves or piston valves. Internal combustion engines Camshaft In four-stroke cycle engines and some two-stroke cycle engines, the valve timing is controlled by the camshaft. It can be varied by modifying the camshaft, or it can be varied during engine operation by variable valve timing. It is also affected by the adjustment of the valve mechanism, and particularly by the tappet clearance. However, this variation is normally unwanted. Valve overlap With traditional fixed valve timing, an engine will have a period of "valve overlap" at the end of the exhaust stroke, when both the intake and exhaust valves are open. The intake valve is opened before the exhaust gases have completely left the cylinder, and their considerable velocity assists in drawing in the fresh cha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
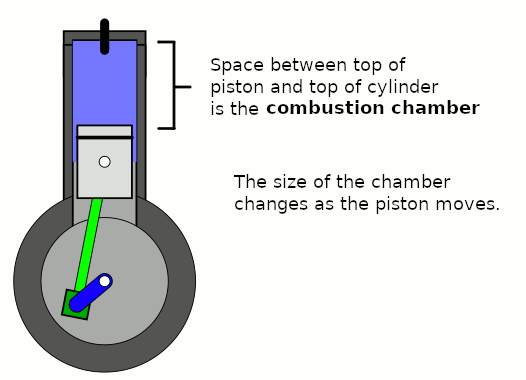
Combustion Chamber
A combustion chamber is part of an internal combustion engine in which the fuel/air mix is burned. For steam engines, the term has also been used for an extension of the firebox which is used to allow a more complete combustion process. Internal combustion engines In an internal combustion engine, the pressure caused by the burning air/fuel mixture applies direct force to part of the engine (e.g. for a piston engine, the force is applied to the top of the piston), which converts the gas pressure into mechanical energy (often in the form of a rotating output shaft). This contrasts an external combustion engine, where the combustion takes place in a separate part of the engine to where the gas pressure is converted into mechanical energy. Spark-ignition engines In spark ignition engines, such as petrol (gasoline) engines, the combustion chamber is usually located in the cylinder head. The engines are often designed such that the bottom of combustion chamber is roughly in l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Exhaust Pulse Pressure Charging
Exhaust pulse pressure charging (EPPC) is a system for supercharging two-stroke diesel engines of the loop-scavenge type. Loop-scavenge engines cannot be pressure-charged in the same way as uniflow engines or four-stroke engines because the inlet and exhaust ports are open at the same time. Overview The engine usually has a Roots blower to provide air for scavenging and this is arranged to deliver excess air so that air follows the exhaust gases into the exhaust manifold. Some of this air is then forced back into the cylinder by a rise in pressure in the exhaust manifold resulting from the exhaust pulse from another cylinder. For additional pressure charging a turbocharger may be fitted, in series with the Roots blower, but a turbocharger cannot be used alone because it would not provide enough air for scavenging at low speeds. Exhaust Pulse Pressure Charging Advantages and Disadvantages Pulse pressure charging is much more effective with a low load and at low speed than tr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kadenacy Effect
The Kadenacy effect is an effect of pressure-waves in gases. It is named after Michel Kadenacy who obtained a French patent for an engine utilizing the effect in 1933. There are also European and US patents. In simple terms, the momentum of the exhaust gas leaving the cylinder of an internal combustion engine creates a pressure-drop in the cylinder which assists the flow of a fresh charge of air, or fuel-air mixture, into the cylinder. The effect can be maximized by careful design of the inlet and exhaust passages. Uses The Kadenacy effect has been utilized in pulse jet engines and in two-stroke piston engines and is important in the design of high-performance motorcycle engines. Pulse jets Two-stroke engines In a two-stroke engine the pressure-drop resulting from the Kadenacy effect assists the flow of a fresh fuel-air mixture charge into the cylinder. However, the Kadenacy effect alone is not sufficient and must be boosted in some way. In small engines this is done by cra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pressure Wave Supercharger
A pressure wave supercharger (also known as a wave rotor) is a type of supercharger technology that harnesses the pressure waves produced by an internal combustion engine exhaust gas pulses to compress the intake air. Its automotive use is not widespread; the most widely used example is the ''Comprex'', developed by Brown Boveri.A Review of Wave Rotor Technology and its Applications including details of Comprex supercharger Valmet Tractors of Finland were one of the first to use the device when they fitted it to the 411CX engine which powered their 1203 model of 1980. Although it provided a useful increase in performance it was considered too expensive to be incorporated into later models. Ferrari tested such a device ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Supercharger
In an internal combustion engine, a supercharger compresses the intake gas, forcing more air into the engine in order to produce more power for a given displacement. The current categorisation is that a supercharger is a form of forced induction that is mechanically powered (usually by a belt from the engine's crankshaft), as opposed to a turbocharger, which is powered by the kinetic energy of the exhaust gasses. However, up until the mid-20th century, a turbocharger was called a "turbosupercharger" and was considered a type of supercharger. The first supercharged engine was built in 1878, with usage in aircraft engines beginning in the 1910s and usage in car engines beginning in the 1920s. In piston engines used by aircraft, supercharging was often used to compensate for the lower air density at high altitudes. Supercharging is less commonly used in the 21st century, as manufacturers have shifted to turbochargers to reduce fuel consumption and/or increase power outputs. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Two-stroke Engine Technology
A two-stroke (or two-stroke cycle) engine is a type of internal combustion engine that completes a power cycle with two strokes (up and down movements) of the piston during one power cycle, this power cycle being completed in one revolution of the crankshaft. A four-stroke engine requires four strokes of the piston to complete a power cycle during two crankshaft revolutions. In a two-stroke engine, the end of the combustion stroke and the beginning of the compression stroke happen simultaneously, with the intake and exhaust (or scavenging) functions occurring at the same time. Two-stroke engines often have a high power-to-weight ratio, power being available in a narrow range of rotational speeds called the power band. Two-stroke engines have fewer moving parts than four-stroke engines. History The first commercial two-stroke engine involving cylinder compression is attributed to Scottish engineer Dugald Clerk, who patented his design in 1881. However, unlike most later two- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |