|
Immorality Act, 1957
The Sexual Offences Act, 1957 (Act No. 23 of 1957, originally the Immorality Act, 1957) is an act of the Parliament of South Africa which, in its current form, prohibits prostitution, brothel-keeping and procuring, and other activities related to prostitution. Before the law relating to sex offences was consolidated and revised by the Criminal Law (Sexual Offences and Related Matters) Amendment Act, 2007, it also prohibited various other sex offences, including sex with children under the age of consent and sex with the mentally incompetent. As the Immorality Act it was infamous for prohibiting sex between a white person and a person of another race, until that prohibition was removed by a 1985 amendment. Provisions in force ;Brothel-keeping :Section 2 makes it a crime to keep a brothel, and section 3 defines various people who are deemed to be brothel-keepers, including anyone who lives in a brothel, manages or knowingly receives money from a brothel, knowingly permits a buil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parliament Of South Africa
The Parliament of the Republic of South Africa is South Africa's legislature; under the present Constitution of South Africa, the bicameral Parliament comprises a National Assembly and a National Council of Provinces. The current twenty-seventh Parliament was first convened on 22 May 2019. From 1910 to 1994, members of Parliament were elected chiefly by the South African white minority. The first elections with universal suffrage were held in 1994. Both chambers held their meetings in the Houses of Parliament, Cape Town that were built 1875–1884. A fire broke out within the buildings in early January 2022, destroying the session room of the National Assembly. The National Assembly will temporarily meet at the Good Hope Chamber. History Before 1910 The predecessor of the Parliament of South Africa, before the 1910 Union of South Africa, was the bicameral Parliament of the Cape of Good Hope. This was composed of the House of Assembly (the lower house) and the Legislat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
South African Pound
The pound (Afrikaans: ''pond''; symbol £, £SA for distinction) was the currency of the Union of South Africa from the formation of the country as a British Dominion in 1910. It was replaced by the rand in 1961 when South Africa decimalised. In 1825, an imperial order-in-council made sterling coinage legal tender in all the British colonies. At that time, the only British colony in Southern Africa was the Cape of Good Hope Colony. As time went on, sterling and its associated coinage became the currency of every British territory in Southern Africa. At that time sterling followed the Carolingian monetary system of a pound divided into 20 shillings, each of 12 pence. History The pound sterling became the standard currency of the Cape of Good Hope colony in 1825 following an imperial order-in-council that was issued for the purpose of introducing sterling coinage into all British colonies. British coins then replaced the Dutch currency. Before a unified South Africa, many au ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
South African Legislation
South is one of the cardinal directions or compass points. The direction is the opposite of north and is perpendicular to both east and west. Etymology The word ''south'' comes from Old English ''sūþ'', from earlier Proto-Germanic ''*sunþaz'' ("south"), possibly related to the same Proto-Indo-European root that the word ''sun'' derived from. Some languages describe south in the same way, from the fact that it is the direction of the sun at noon (in the Northern Hemisphere), like Latin meridies 'noon, south' (from medius 'middle' + dies 'day', cf English meridional), while others describe south as the right-hand side of the rising sun, like Biblical Hebrew תֵּימָן teiman 'south' from יָמִין yamin 'right', Aramaic תַּימנַא taymna from יָמִין yamin 'right' and Syriac ܬܰܝܡܢܳܐ taymna from ܝܰܡܝܺܢܳܐ yamina (hence the name of Yemen, the land to the south/right of the Levant). Navigation By convention, the ''bottom or down-facing side'' of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sex Laws In South Africa
Sex is the trait that determines whether a sexually reproducing animal or plant produces male or female gametes. Male plants and animals produce smaller mobile gametes (spermatozoa, sperm, pollen), while females produce larger ones (ova, often called egg cells). Organisms that produce both types of gametes are called hermaphrodites. During sexual reproduction, male and female gametes fuse to form zygotes, which develop into offspring that inherit traits from each parent. Males and females of a species may have physical similarities (sexual monomorphism) or differences (sexual dimorphism) that reflect various reproductive pressures on the respective sexes. Mate choice and sexual selection can accelerate the evolution of physical differences between the sexes. The terms ''male'' and ''female'' typically do not apply in sexually undifferentiated species in which the individuals are isomorphic (look the same) and the gametes are isogamous (indistinguishable in size and shape) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sex Crimes In South Africa
Sex is the trait that determines whether a sexually reproducing animal or plant produces male or female gametes. Male plants and animals produce smaller mobile gametes (spermatozoa, sperm, pollen), while females produce larger ones (ova, often called egg cells). Organisms that produce both types of gametes are called hermaphrodites. During sexual reproduction, male and female gametes fuse to form zygotes, which develop into offspring that inherit traits from each parent. Males and females of a species may have physical similarities (sexual monomorphism) or differences (sexual dimorphism) that reflect various reproductive pressures on the respective sexes. Mate choice and sexual selection can accelerate the evolution of physical differences between the sexes. The terms ''male'' and ''female'' typically do not apply in sexually undifferentiated species in which the individuals are isomorphic (look the same) and the gametes are isogamous (indistinguishable in size and shape) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Immorality Amendment Act, 1988
The Sexual Offences Act, 1957 (Act No. 23 of 1957, originally the Immorality Act, 1957) is an act of the Parliament of South Africa which, in its current form, prohibits prostitution, brothel-keeping and procuring, and other activities related to prostitution. Before the law relating to sex offences was consolidated and revised by the Criminal Law (Sexual Offences and Related Matters) Amendment Act, 2007, it also prohibited various other sex offences, including sex with children under the age of consent and sex with the mentally incompetent. As the Immorality Act it was infamous for prohibiting sex between a white person and a person of another race, until that prohibition was removed by a 1985 amendment. Provisions in force ;Brothel-keeping :Section 2 makes it a crime to keep a brothel, and section 3 defines various people who are deemed to be brothel-keepers, including anyone who lives in a brothel, manages or knowingly receives money from a brothel, knowingly permits a bu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Immorality Amendment Act, 1969
The Sexual Offences Act, 1957 (Act No. 23 of 1957, originally the Immorality Act, 1957) is an act of the Parliament of South Africa which, in its current form, prohibits prostitution, brothel-keeping and procuring, and other activities related to prostitution. Before the law relating to sex offences was consolidated and revised by the Criminal Law (Sexual Offences and Related Matters) Amendment Act, 2007, it also prohibited various other sex offences, including sex with children under the age of consent and sex with the mentally incompetent. As the Immorality Act it was infamous for prohibiting sex between a white person and a person of another race, until that prohibition was removed by a 1985 amendment. Provisions in force ;Brothel-keeping :Section 2 makes it a crime to keep a brothel, and section 3 defines various people who are deemed to be brothel-keepers, including anyone who lives in a brothel, manages or knowingly receives money from a brothel, knowingly permits a bu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Immorality Amendment Act, 1967
The Sexual Offences Act, 1957 (Act No. 23 of 1957, originally the Immorality Act, 1957) is an act of the Parliament of South Africa which, in its current form, prohibits prostitution, brothel-keeping and procuring, and other activities related to prostitution. Before the law relating to sex offences was consolidated and revised by the Criminal Law (Sexual Offences and Related Matters) Amendment Act, 2007, it also prohibited various other sex offences, including sex with children under the age of consent and sex with the mentally incompetent. As the Immorality Act it was infamous for prohibiting sex between a white person and a person of another race, until that prohibition was removed by a 1985 amendment. Provisions in force ;Brothel-keeping :Section 2 makes it a crime to keep a brothel, and section 3 defines various people who are deemed to be brothel-keepers, including anyone who lives in a brothel, manages or knowingly receives money from a brothel, knowingly permits a bu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Immorality Act, 1957
The Sexual Offences Act, 1957 (Act No. 23 of 1957, originally the Immorality Act, 1957) is an act of the Parliament of South Africa which, in its current form, prohibits prostitution, brothel-keeping and procuring, and other activities related to prostitution. Before the law relating to sex offences was consolidated and revised by the Criminal Law (Sexual Offences and Related Matters) Amendment Act, 2007, it also prohibited various other sex offences, including sex with children under the age of consent and sex with the mentally incompetent. As the Immorality Act it was infamous for prohibiting sex between a white person and a person of another race, until that prohibition was removed by a 1985 amendment. Provisions in force ;Brothel-keeping :Section 2 makes it a crime to keep a brothel, and section 3 defines various people who are deemed to be brothel-keepers, including anyone who lives in a brothel, manages or knowingly receives money from a brothel, knowingly permits a buil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sexual Offences Act, 1957
The Sexual Offences Act, 1957 (Act No. 23 of 1957, originally the Immorality Act, 1957) is an act of the Parliament of South Africa which, in its current form, prohibits prostitution, brothel-keeping and procuring, and other activities related to prostitution. Before the law relating to sex offences was consolidated and revised by the Criminal Law (Sexual Offences and Related Matters) Amendment Act, 2007, it also prohibited various other sex offences, including sex with children under the age of consent and sex with the mentally incompetent. As the Immorality Act it was infamous for prohibiting sex between a white person and a person of another race, until that prohibition was removed by a 1985 amendment. Provisions in force ;Brothel-keeping :Section 2 makes it a crime to keep a brothel, and section 3 defines various people who are deemed to be brothel-keepers, including anyone who lives in a brothel, manages or knowingly receives money from a brothel, knowingly permits a bu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
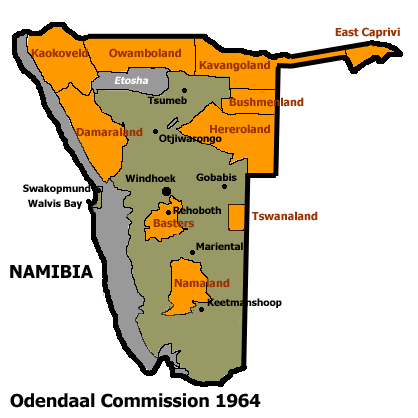
Namibia
Namibia (, ), officially the Republic of Namibia, is a country in Southern Africa. Its western border is the Atlantic Ocean. It shares land borders with Zambia and Angola to the north, Botswana to the east and South Africa to the south and east. Although Kazungula, it does not border Zimbabwe, less than 200 metres (660 feet) of the Botswanan right bank of the Zambezi, Zambezi River separates the two countries. Namibia gained independence from South Africa on 21 March 1990, following the Namibian War of Independence. Its capital and largest city is Windhoek. Namibia is a member state of the United Nations (UN), the Southern African Development Community (SADC), the African Union (AU) and the Commonwealth of Nations. The driest country in sub-Saharan Africa, Namibia has been inhabited since pre-historic times by the San people, San, Damara people, Damara and Nama people. Around the 14th century, immigration, immigrating Bantu peoples arrived as part of the Bantu expansion. Since ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
South West Africa
South West Africa ( af, Suidwes-Afrika; german: Südwestafrika; nl, Zuidwest-Afrika) was a territory under South African administration from 1915 to 1990, after which it became modern-day Namibia. It bordered Angola (Portuguese colony before 1975), Botswana ( Bechuanaland before 1966), South Africa, and Zambia (Northern Rhodesia before 1964). Previously the German colony of South West Africa from 1884–1915, it was made a League of Nations mandate of the Union of South Africa following Germany's defeat in the First World War. Although the mandate was abolished by the United Nations in 1966, South African control over the territory continued despite its illegality under international law. The territory was administered directly by the South African government from 1915 to 1978, when the Turnhalle Constitutional Conference laid the groundwork for semi-autonomous rule. During an interim period between 1978 and 1985, South Africa gradually granted South West Africa a limited f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |