|
Icerya Littoralis Mimosae
''Icerya'' is a genus of scale insects in the family Monophlebidae. It is named after physician-naturalist Dr. Edmond Icery of British Mauritius. Hermaphroditism Hermaphroditism is extremely rare in the insect world despite the comparatively common nature of this condition in the crustaceans. Several species of ''Icerya'', including the pestiferous cottony-cushion scale, ''I. purchasi'', are known to be hermaphrodites that reproduce by self-fertilising. Occasionally males are produced from unfertilised eggs, but generally individuals are monoecious with a female-like nature but possessing an ovotestis (a part-testis, part-ovary organ) and sperm is transmitted ovarially from the female to her young. This hermaphroditic sexual self-sufficiency, where a single individual can populate new territory, has contributed to the invasive spread of the cottony-cushion scale insect away from its native Australia.The Insects An outline of Entomology, Gullan & Cranston, Wiley-Blackwell 2001 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Icerya Purchasi
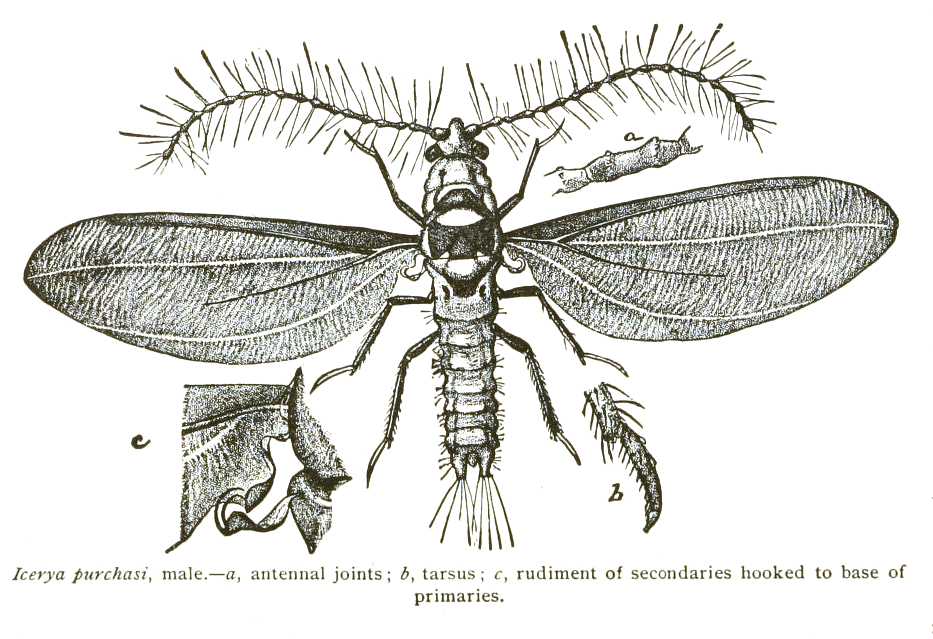
''Icerya purchasi'' ( common name: cottony cushion scale) is a scale insect that feeds on more than 80 families of woody plants, most notably on ''Citrus'' and ''Pittosporum''. Originally described in 1878 from specimens collected in New Zealand as pests of kangaroo acacia and named by W.M. Maskell "after the Rev. Dr. Purchas who, ebelieve first found it". It is now found worldwide where citrus crops are grown. The cottony cushion scale originates from Australia. Life cycle This scale infests twigs and branches. The mature hermaphrodite is oval in shape, reddish-brown with black hairs, 5 mm long. When mature, the insect remains stationary, attaches itself to the plant by waxy secretions, and produces a white egg sac in grooves, by extrusion, in the body which encases hundreds of red eggs. The egg sac will grow to be two to three times as long as the body. Newly hatched nymphs are the primary dispersal stage, with dispersion known to occur by wind and by crawling. Earl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |