|
IBM IntelliStation
The IntelliStation was originally a workstation-class personal computer announced in March 1997 developed by IBM as the follow-on to the PC Series 360 and 365. Certain IntelliStation M Pro Series were near hardware identical to low end IBM Netfinity 1000 Series network servers (with variants in included video cards and SCSI options). In February 2002, POWER processor-based workstations, previously sold directly under the eServer pSeries brand, were also placed under the IntelliStation umbrella. The last IntelliStation models were discontinued in January 2009, ending the product line.Official IBM Hardware Withdrawal Announcement of IntelliStation POWER 185 and 285. IntelliStation Pro Intel or AMD processor based workstations, discontinued in March 2008. |
Workstation
A workstation is a special computer designed for technical or scientific applications. Intended primarily to be used by a single user, they are commonly connected to a local area network and run multi-user operating systems. The term ''workstation'' has been used loosely to refer to everything from a mainframe computer terminal to a PC connected to a network, but the most common form refers to the class of hardware offered by several current and defunct companies such as Sun Microsystems, Silicon Graphics, Apollo Computer, DEC, HP, NeXT, and IBM which powered the 3D computer graphics revolution of the late 1990s. Workstations offer higher performance than mainstream personal computers, especially in CPU, graphics, memory, and multitasking. Workstations are optimized for the visualization and manipulation of different types of complex data such as 3D mechanical design, engineering simulations like computational fluid dynamics, animation, medical imaging, image render ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
AT Attachment
Parallel ATA (PATA), originally , also known as IDE, is a standard interface designed for IBM PC-compatible computers. It was first developed by Western Digital and Compaq in 1986 for compatible hard drives and CD or DVD drives. The connection is used for storage devices such as hard disk drives, floppy disk drives, and optical disc drives in computers. The standard is maintained by the X3/ INCITS committee. It uses the underlying (ATA) and Packet Interface (ATAPI) standards. The Parallel ATA standard is the result of a long history of incremental technical development, which began with the original AT Attachment interface, developed for use in early PC AT equipment. The ATA interface itself evolved in several stages from Western Digital's original Integrated Drive Electronics (IDE) interface. As a result, many near-synonyms for ATA/ATAPI and its previous incarnations are still in common informal use, in particular Extended IDE (EIDE) and Ultra ATA (UATA). After the i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
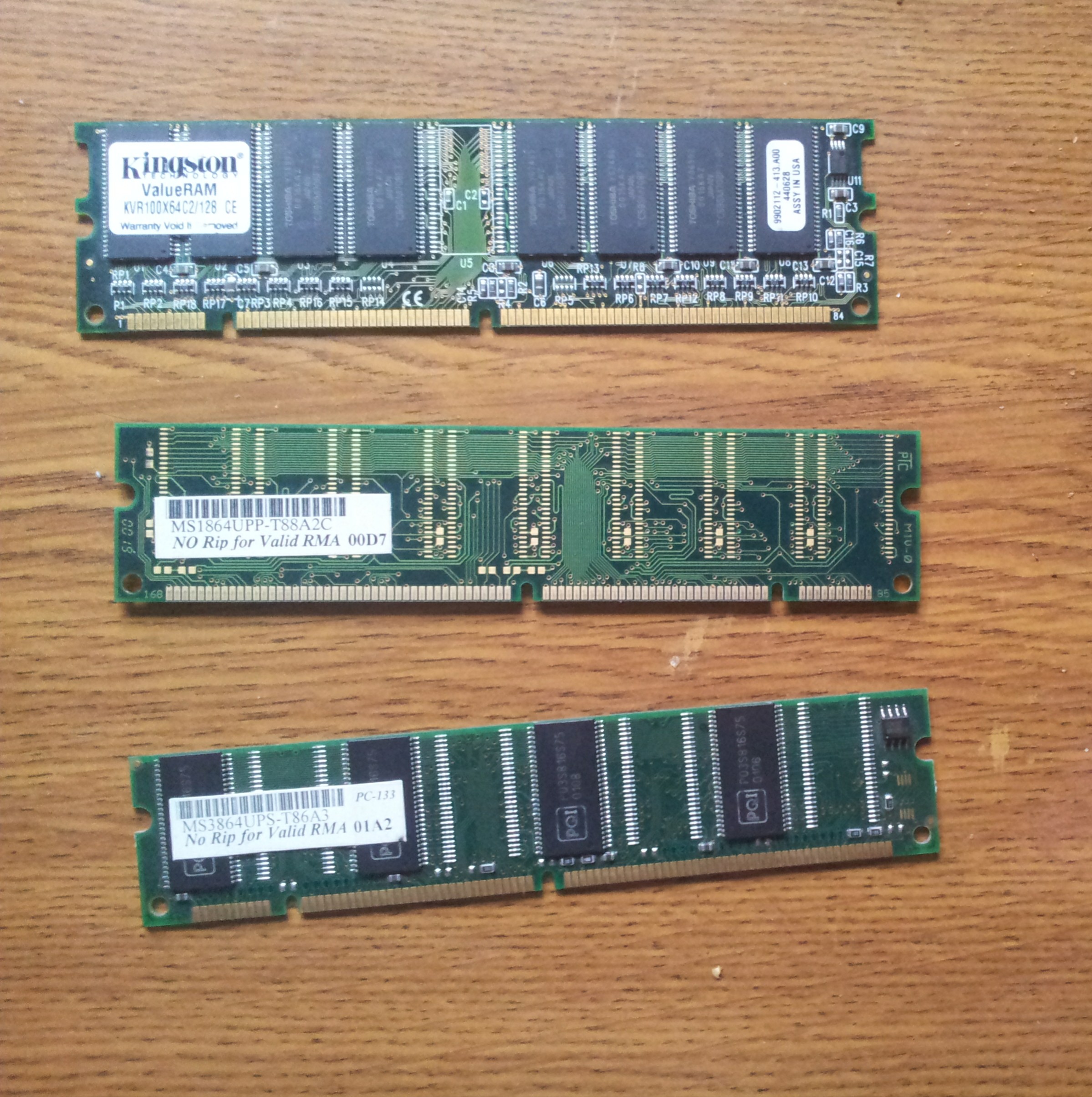
PC2100
Double Data Rate Synchronous Dynamic Random-Access Memory (DDR SDRAM) is a double data rate (DDR) synchronous dynamic random-access memory (SDRAM) class of memory integrated circuits used in computers. DDR SDRAM, also retroactively called DDR1 SDRAM, has been superseded by DDR2 SDRAM, DDR3 SDRAM, DDR4 SDRAM and DDR5 SDRAM. None of its successors are forward or backward compatible with DDR1 SDRAM, meaning DDR2, DDR3, DDR4 and DDR5 memory modules will not work in DDR1-equipped motherboards, and vice versa. Compared to single data rate ( SDR) SDRAM, the DDR SDRAM interface makes higher transfer rates possible by more strict control of the timing of the electrical data and clock signals. Implementations often have to use schemes such as phase-locked loops and self-calibration to reach the required timing accuracy. The interface uses double pumping (transferring data on both the rising and falling edges of the clock signal) to double data bus bandwidth without a correspon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ATI FireGL
AMD FirePro was AMD's brand of graphics cards designed for use in workstations and servers running professional Computer-aided design (CAD), Computer-generated imagery (CGI), Digital content creation (DCC), and High-performance computing/GPGPU applications. The GPU chips on FirePro-branded graphics cards are identical to the ones used on Radeon-branded graphics cards. The end products (i.e. the graphics card) differentiate substantially by the provided graphics device drivers and through the available professional support for the software. The product line is split into two categories: "W" workstation series focusing on workstation and primarily focusing on graphics and display, and "S" server series focused on virtualization and GPGPU/High-performance computing. The release of the Radeon Pro Duo in April 2016 and the announcement of the Radeon Pro WX Series in July 2016 marked the succession of Radeon Pro as AMD's professional workstation graphics card solution. Radeon Ins ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nvidia Quadro
Quadro was Nvidia's brand for graphics cards intended for use in workstations running professional computer-aided design (CAD), computer-generated imagery (CGI), digital content creation (DCC) applications, scientific calculations and machine learning. Differences between the professional Quadro and mainstream GeForce lines include the use of ECC memory and enhanced floating point precision. These are desirable properties when the cards are used for calculations which, in contrast to graphics rendering, require reliability and precision. The Nvidia Quadro product line directly competed with AMD's Radeon Pro (formerly FirePro/FireGL) line of professional workstation cards. Nvidia has moved away from the Quadro branding for new products, starting with the launch of the Ampere architecture-based RTX A6000 on October 5, 2020. To indicate the upgrade to the Nvidia Ampere architecture for their graphics cards technology, Nvidia RTX is the product line being produced and develope ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Matrox Millennium G450
The G400 is a video card made by Matrox, released in September 1999. The graphics processor contains a 2D GUI, video, and Direct3D 6.0 3D accelerator. Codenamed "Toucan", it was a more powerful and refined version of its predecessor, the G200. Overview The Matrox G200 graphics processor had been a successful product, competing with the various 2D & 3D combination cards available in 1998. Matrox took the technology developed from the G200 project, refined it, and basically doubled it up to form the G400 processor. The new chip featured several new and innovative additions, such as multiple monitor output support, an all-around 32-bit rendering pipeline with high performance, further improved 2D and video acceleration, and a new 3D feature known as Environment Mapped Bump Mapping. Internally the G400 is a 256-bit processor, using what Matrox calls a "DualBus" architecture. This is an evolution of G200's "DualBus", which had been 128-bit. A Matrox "DualBus" chip consists of twin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intel Pentium 4
Pentium 4 is a series of single-core CPUs for desktops, laptops and entry-level servers manufactured by Intel. The processors were shipped from November 20, 2000 until August 8, 2008. The production of Netburst processors was active from 2000 until May 21, 2010. All Pentium 4 CPUs are based on the NetBurst microarchitecture. The Pentium 4 '' Willamette'' (180 nm) introduced SSE2, while the '' Prescott'' (90 nm) introduced SSE3. Later versions introduced Hyper-Threading Technology (HTT). The first Pentium 4-branded processor to implement 64-bit was the ''Prescott'' (90 nm) (February 2004), but this feature was not enabled. Intel subsequently began selling 64-bit Pentium 4s using the ''"E0" revision'' of the Prescotts, being sold on the OEM market as the Pentium 4, model F. The E0 revision also adds eXecute Disable (XD) (Intel's name for the NX bit) to Intel 64. Intel's official launch of Intel 64 (under the name EM64T at that time) in mainstream desktop ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
PC133
Synchronous dynamic random-access memory (synchronous dynamic RAM or SDRAM) is any DRAM where the operation of its external pin interface is coordinated by an externally supplied clock signal. DRAM integrated circuits (ICs) produced from the early 1970s to early 1990s used an ''asynchronous'' interface, in which input control signals have a direct effect on internal functions only delayed by the trip across its semiconductor pathways. SDRAM has a ''synchronous'' interface, whereby changes on control inputs are recognised after a rising edge of its clock input. In SDRAM families standardized by JEDEC, the clock signal controls the stepping of an internal finite-state machine that responds to incoming commands. These commands can be pipelined to improve performance, with previously started operations completing while new commands are received. The memory is divided into several equally sized but independent sections called ''banks'', allowing the device to operate on a memory acce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ELSA Technology, Inc
Elsa may refer to: ELSA (acronym) * ELSA Technology, a manufacturer of computer hardware * English Language Skills Assessment *English Longitudinal Study of Ageing * Ethical, Legal and Social Aspects research * European Law Students' Association * European League of Stuttering Associations *Evangelical Lutheran Synod of Australia, a group in the history of the Lutheran Church of Australia *Experimental light-sport aircraft (E-LSA) People * Elsa (given name), a female given name * Pedro Elsa (1901–unknown), Argentine Olympic athlete Characters * Elsa of Brabant, a character in the 1850 Richard Wagner opera ''Lohengrin'' * Elsa (''Frozen''), fictional character from the Disney animated franchise, ''Frozen'' Places * Elsa, California, a place in California, U.S. * Elsa, Texas, U.S. * Elsa, Yukon, Canada Other * 182 Elsa, an asteroid * ''Elsa'' (album), debut album of Elsa Lunghini * Elsa (river), Tuscany, Italy * Elsa the lioness Elsa the lioness ( 28 January 195624 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
RDRAM
Rambus DRAM (RDRAM), and its successors Concurrent Rambus DRAM (CRDRAM) and Direct Rambus DRAM (DRDRAM), are types of synchronous dynamic random-access memory (SDRAM) developed by Rambus from the 1990s through to the early 2000s. The third-generation of Rambus DRAM, DRDRAM was replaced by XDR DRAM. Rambus DRAM was developed for high-bandwidth applications and was positioned by Rambus as replacement for various types of contemporary memories, such as SDRAM. DRDRAM was initially expected to become the standard in PC memory, especially after Intel agreed to license the Rambus technology for use with its future chipsets. Further, DRDRAM was expected to become a standard for graphics memory. However, RDRAM got embroiled in a standards war with an alternative technology—DDR SDRAM—and quickly lost out on grounds of price and, later, performance. By around 2003, DRDRAM was no longer supported in new personal computers. PC main memory The first PC motherboards with suppor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)