|
Iverni
The Iverni (, ') were a people of early Ireland first mentioned in Ptolemy's 2nd century ''Geography'' as living in the extreme south-west of the island. He also locates a "city" called Ivernis (, ') in their territory, and observes that this settlement has the same name as the island as a whole, Ivernia (, '). These Iverni can be identified linguistically with the Érainn (Éraind, Érnai, Érna), a people attested in Munster and elsewhere in the early Middle Ages. The prehistoric Érainn royal dynasties are sometimes referred to as the Dáirine. Etymology The name Iverni has been derived from Archaic Irish ''*Īwernī'' meaning "folk of ''*Īweriū'' " (the island of Ireland). This is in turn derived from Proto-Celtic *''Φīwerjon-'' and further from Proto-Indo-European *''piHwerjon-'' (the fertile land), which is cognate with the Ancient Greek '' píeira'' and Sanskrit ''pīvara'', which refer to fertile land. John T. Koch claims it was probably once the name given to all ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Osraige
Osraige (Old Irish) or Osraighe (Classical Irish), Osraí (Modern Irish), anglicized as Ossory, was a medieval Irish kingdom comprising what is now County Kilkenny and western County Laois, corresponding to the Diocese of Ossory. The home of the Osraige people, it existed from around the first century until the Norman invasion of Ireland in the 12th century. It was ruled by the Dál Birn dynasty, whose medieval descendants assumed the surname Mac Giolla Phádraig. According to tradition, Osraige was founded by Óengus Osrithe in the 1st century and was originally within the province of Leinster. In the 5th century, the Corcu Loígde of Munster displaced the Dál Birn and brought Osraige under Munster's direct control. The Dál Birn returned to power in the 7th century, though Osraige remained nominally part of Munster until 859, when it achieved formal independence under the powerful king Cerball mac Dúnlainge. Osraige's rulers remained major players in Irish politics ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
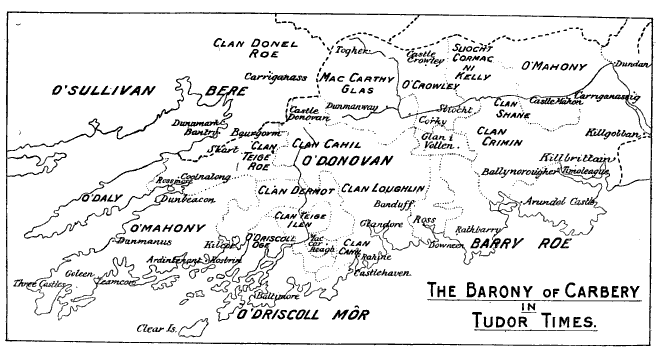
Corcu Loígde
The Corcu Loígde (Corcu Lóegde, Corco Luigde, Corca Laoighdhe, Laidhe), meaning Gens of the Calf Goddess, also called the Síl Lugdach meic Itha, were a kingdom centred in West County Cork who descended from the proto-historical rulers of Munster, the Dáirine, of whom they were the central royal sept. They took their name from Lugaid Loígde "Lugaid of the Calf Goddess", a King of Tara and High King of Ireland, son of the great Dáire Doimthech (a quo Dáirine). A descendant of Lugaid Loígde, and their most famous ancestor, is the legendary Lugaid Mac Con, who is listed in the Old Irish '' Baile Chuinn Chétchathaig''. Closest kin to the Corcu Loígde were the Dál Fiatach princes of the Ulaid. Overview The Corcu Loígde were the rulers of Munster, and likely of territories beyond the province, until the early 7th century AD, when their ancient alliance with the Kingdom of Osraige fell apart as the Eóganachta rose to power. Many peoples formerly subject to the Co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kingdom Of Munster
The Kingdom of Munster () was a kingdom of Gaelic Ireland which existed in the south-west of the island from at least the 1st century BC until 1118. According to traditional Irish history found in the ''Annals of the Four Masters'', the kingdom originated as the territory of the ''Clanna Dedad'' (sometimes known as the Dáirine), an Érainn tribe of Irish Gaels. Some of the early kings were prominent in the Red Branch Cycle such as Cú Roí and Conaire Mór. For a few centuries they were competitors for the List of High Kings of Ireland, High Kingship of Ireland, but ultimately lost out to the Connachta, descendants of Conn Cétchathach. The kingdom had different borders and internal divisions at different times during its history. Major changes reshaped Munster in the 6th century, as the Corcu Loígde (ancestors of the ''Ó hEidirsceoil'') fell from power. Osraige which had been brought under the control of Munster for two centuries was retaken by the Dál Birn (ancestors of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dáirine
The Dáirine (Dárine, Dáirfine, Dáirfhine, Dárfine, Dárinne, Dairinne), later known dynastically as the Corcu Loígde and associated, were the proto-historical rulers of Munster before the rise of the Eóganachta in the 7th century AD. They were derived from or closely associated with the Darini of Ptolemy and were also related to the Ulaid and Dál Riata of Ulster and Scotland.O'Rahilly 1946 Their ancestors appear frequently in the Ulster Cycle. In historical times the Dáirine were represented, as stated, by the Corcu Loígde, the Uí Fidgenti and Uí Liatháin, as well as a few other early historical kindreds of both Munster and Ulster. In ancient genealogical schemes, the historical Dál Fiatach of Ulaid also belong to the Dáirine. History Dáirine can sometimes refer to the Érainn dynasties as a whole instead of the distinct royal septs mentioned above. The Dáirine of Munster were said to descend from a certain Dáire (''*Dārios''), both Dáire Doimthech (Sírchrecht ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ulaid
(Old Irish, ) or (Irish language, Modern Irish, ) was a Gaelic Ireland, Gaelic Provinces of Ireland, over-kingdom in north-eastern Ireland during the Middle Ages made up of a confederation of dynastic groups. Alternative names include , which is the Latin form of , and , Irish for 'the Fifth'. The king of Ulaid was called the or . Ulaid also refers to a people of early Ireland, and it is from them that the province of Ulster derives its name. Some of the dynasties in the over-kingdom claimed descent from the Ulaid, but others are cited as being of Cruithin descent. In historical documents, the term Ulaid was used to refer to the population group of which the was the ruling dynasty. As such, the title held two meanings: over-king of the Kingdom of Ulaid and king of the Ulaid people, as in the . The Ulaid feature prominently in the Ulster Cycle of Irish mythology. According to legend, the ancient territory of Ulaid spanned the whole of the modern province of Ulster, excludin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dál Fiatach
Dál Fiatach was a Gaelic Ireland, Gaelic dynastic-grouping and the name of their territory in the north-east of Ireland, which lasted throughout the Middle Ages until their demise in the 13th century at the hands of Normans in Ireland, Normans. It was part of the over-kingdom of Ulaid, and they were its main ruling dynasty for most of Ulaid's history. Their territory lay in eastern County Down. Their capital was Dún Lethglaise (Downpatrick) and from the 9th century their main religious site was Bangor Abbey. Description The Dál Fiatach are claimed as being descended from Fiatach Finn, Fiatach Finn mac Dáire, a legendary King of Ulaid and High King of Ireland, and are thought to be related to both the Voluntii and Darini of Ptolemy's ''Geographia (Ptolemy), Geographia''. They are also perhaps more directly related to the pre-historic Dáirine, and the later Corcu Loígde of Munster. Kinship with the Osraige is also supported, and more distantly with the Dál Riata. The Ulaid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dál Riata
Dál Riata or Dál Riada (also Dalriada) () was a Gaels, Gaelic Monarchy, kingdom that encompassed the Inner Hebrides, western seaboard of Scotland and north-eastern Ireland, on each side of the North Channel (Great Britain and Ireland), North Channel. At its height in the 6th and 7th centuries, it covered what is now Argyll ("Coast of the Gaels") in Scotland and part of County Antrim in Northern Ireland.Clancy, Thomas Owen, "Philosopher King: Nechtan mac Der Ilei," SHR 83 (2004): 135–149 After a period of expansion, Dál Riata eventually became associated with the Gaelic Kingdom of Alba.''Oxford Companion to Scottish History'' pp. 161–162, edited by Michael Lynch, Oxford University Press. . In Argyll, it consisted of four main clan, kindreds or tribes, each with their own chief: the Cenél nGabráin (based in Kintyre), the Cenél nÓengusa (based on Islay), the Loarn mac Eirc, Cenél Loairn (who gave their name to the district of Lorne, Scotland, Lorn) and the Cenél Comgai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Múscraige
The Múscraighe (older spelling: Músgraige) were an important Érainn people of Munster, descending from Cairpre Músc, son of Conaire Cóem, a High King of Ireland. Closely related were the Corcu Duibne, Corcu Baiscind, both of Munster, and also the Dál Riata of Ulster and Scotland, all being referred to as the Síl Conairi in Irish and Scottish legends. A more distant ancestor was the legendary monarch Conaire Mór, son of Eterscél, son of Íar, son of Dedu mac Sin. While the Múscraige petty kingdoms were scattered throughout the province of Munster, the largest were centred on the present baronies of Muskerry (West and East) in central Cork. The tribes or septs were pre-Eóganachta, that is before the 6th century. At this time, the territory of ''Múscraige Mittaine'' did not extend south of the River Lee (although the river bisects the current baronies). A pedigree of the chieftains of the tribe may be found in the Book of Leinster.Book of Leinster, Dublin, TCD, M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Uí Liatháin
The Uí Liatháin () were an early kingdom of Munster in southern Ireland. They belonged the same kindred as the Uí Fidgenti, and the two are considered together in the earliest sources, for example '' The Expulsion of the Déisi'' (incidentally). The two have been given various origins among both the early or proto-Eóganachta and among the Érainn or Dáirine by different scholars working in a number of traditions, with no agreement ever reached or appearing reachable. It is entirely possible that they were the product of a combination of lineages from both these royal kindreds, or alternatively of another origin entirely. Eochu Liathán ("Eochu the Grey"), son of Dáire Cerbba, is the ancestor after which the Uí Liatháin is named. The small village of Castlelyons (Caisleán Ó Liatháin) in East County Cork preserves the name of one of their last royal seats in the High Middle Ages, as does the name of Killaliathan Church, County Limerick. The two most powerful septs o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eóganachta
The Eóganachta (Modern , ) were an Irish dynasty centred on Rock of Cashel, Cashel which dominated southern Ireland (namely the Kingdom of Munster) from the 6/7th to the 10th centuries, and following that, in a restricted form, the Kingdom of Desmond, and its offshoot Carbery (barony), Carbery, to the late 16th century. By tradition the dynasty was founded by Conall Corc but named after his ancestor Éogan Mór, Éogan, the firstborn son of the semi-mythological 3rd-century king Ailill Aulom. This dynastic clan-name, for it was never in any sense a 'surname,' should more accurately be restricted to those branches of the royal house which descended from Conall Corc, who established Cashel as his royal seat in the late 5th century. High Kingship issue Although the Eóganachta were powerful in Munster, they never provided Ireland with a List of High Kings of Ireland, High King. Serious challenges to the Uí Néill were however presented by Cathal mac Finguine and Feidlimid mac Cremt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ulster
Ulster (; or ; or ''Ulster'') is one of the four traditional or historic provinces of Ireland, Irish provinces. It is made up of nine Counties of Ireland, counties: six of these constitute Northern Ireland (a part of the United Kingdom); the remaining three are in the Republic of Ireland. It is the second-largest (after Munster) and second-most populous (after Leinster) of Ireland's four traditional provinces, with Belfast being its biggest city. Unlike the other provinces, Ulster has a high percentage of Protestantism in Ireland, Protestants, making up almost half of its population. English is the main language and Ulster English the main dialect. A minority also speak Irish, and there are (Irish-speaking regions) in County Donegal which is home to a quarter of the total Gaeltacht population of the Republic of Ireland. There are also large Irish-speaking networks in southern County Londonderry and in the Gaeltacht Quarter, Belfast. Ulster Scots dialect, Ulster-Scots is al ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
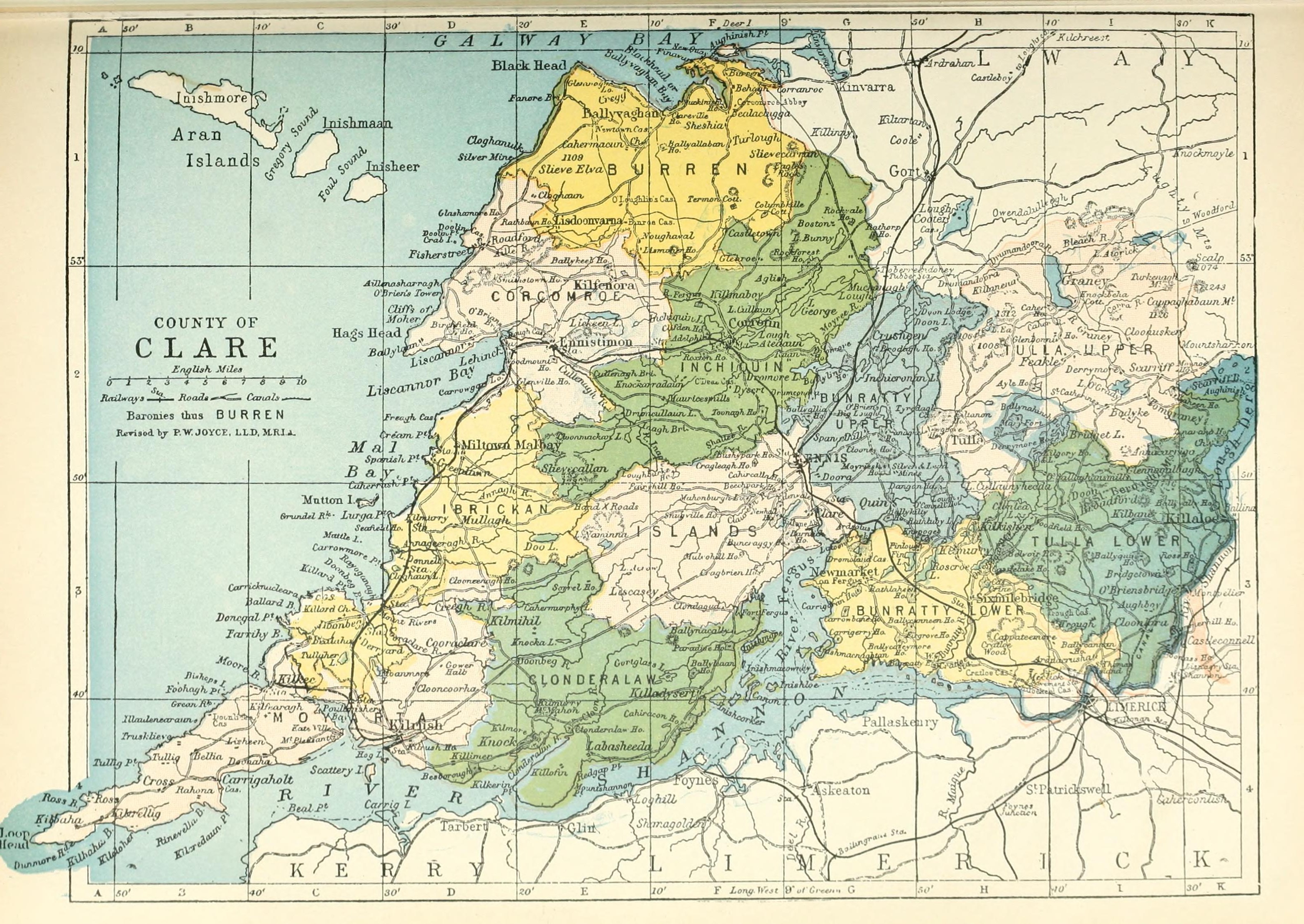
County Clare
County Clare () is a Counties of Ireland, county in the Provinces of Ireland, province of Munster in the Southern Region, Ireland, Southern part of Republic of Ireland, Ireland, bordered on the west by the Atlantic Ocean. Clare County Council is the Local government in the Republic of Ireland, local authority. The county had a population of 127,938 at the 2022 census of Ireland, 2022 census. The county seat and largest settlement is Ennis. Etymology There are two main hypotheses for the origins of the county name "Clare". One is that the name is derived from Thomas de Clare, Lord of Thomond, Thomas de Clare an Anglo-Norman peer and soldier from the de Clare family, who was deeply embroiled in local politics and fighting in the 1270s and 1280 and had had acquired land in Kilkenny and Thomond that included the Castle of Clare. In 1590 County Clare was named after the castle, which is in a strategic location. An alternative hypothesis is that the county name ''Clare'' comes from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |