|
Ipchains
Linux IP Firewalling Chains, normally called ipchains, is free software to control the packet filter or firewall capabilities in the 2.2 series of Linux kernels. It superseded ipfirewall (managed by ipfwadm command), but was replaced by iptables in the 2.4 series. Unlike iptables, ipchains is stateless. It is a rewrite of Linux's previous IPv4 firewall, ipfirewall. This newer ipchains was required to manage the packet filter in Linux kernels starting with version 2.1.102 (which was a 2.2 development release). Patches are also available to add ipchains to 2.0 and earlier 2.1 series kernels. Improvements include larger maxima for packet counting, filtering for fragmented packets and a wider range of protocols, and the ability to match packets based on the inverse of a rule. The ipchains suite also included some shell scripts for easier maintenance and to emulate the behavior of the old ipfwadm command. The ipchains software was superseded by the iptables system in Linux kerne ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ipfirewall
ipfirewall or ipfw is a FreeBSD Internet Protocol, IP, stateful firewall, packet filter and traffic accounting facility. Its ruleset logic is similar to many other packet filters except IPFilter. ipfw is authored and maintained by FreeBSD volunteer staff members. Its syntax enables use of sophisticated filtering capabilities and thus enables users to satisfy advanced requirements. It can either be used as a loadable kernel module or incorporated into the Kernel (computer science), kernel; use as a loadable kernel module where possible is highly recommended. ipfw was the built-in firewall of Mac OS X until Mac OS X 10.7 Lion in 2011 when it was replaced with the OpenBSD project's PF_(firewall), PF. Like FreeBSD, ipfw is Open-source license, open source. It is used in many FreeBSD-based firewall products, including m0n0wall and FreeNAS. A port of an early version of ipfw was used since Linux kernel, Linux 1.1 as the first implementation of firewall available for Linux, until it w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
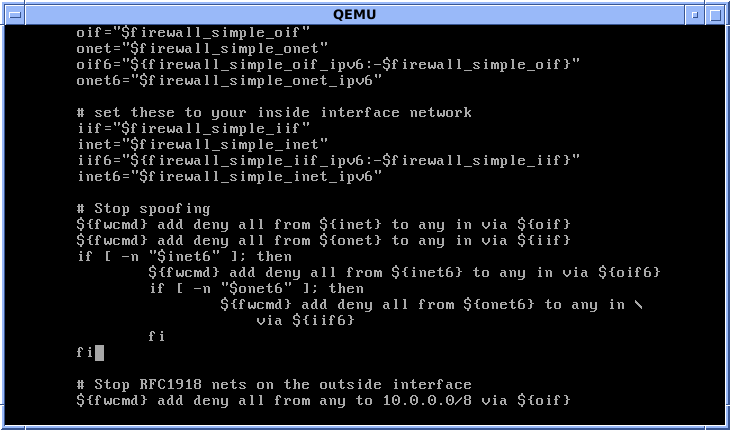
Iptables
iptables is a user-space utility program that allows a system administrator to configure the IP packet filter rules of the Linux kernel firewall, implemented as different Netfilter modules. The filters are organized in different tables, which contain chains of rules for how to treat network traffic packets. Different kernel modules and programs are currently used for different protocols; ''iptables'' applies to IPv4, ''ip6tables'' to IPv6, ''arptables'' to ARP, and ' to Ethernet frames. iptables requires elevated privileges to operate and must be executed by user root, otherwise it fails to function. On most Linux systems, iptables is installed as and documented in its man pages, which can be opened using man iptables when installed. It may also be found in /sbin/iptables, but since iptables is more like a service rather than an "essential binary", the preferred location remains . The term ''iptables'' is also commonly used to inclusively refer to the kernel-level componen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rusty Russell
Rusty Russell is an Australian free software programmer and advocate, known for his work on the Linux kernel's networking subsystem and the Filesystem Hierarchy Standard. Software development Russell wrote the packet filtering systems ipchains and netfilter/iptables in the Linux operating system kernel. Linus Torvalds referred to him as one of his "top deputies" in 2003. In 2002, Russell announced the creation of the Trivial Patch Monkey, an email address for kernel hackers to submit trivial patches such as spelling errors, one-liners, documentation tweaks and other minor amendments to the code base. Adrian Bunk took over the role in 2005. In 2006 Russell started work as the major developer of the " lguest" virtualisation system in the Linux Kernel. In October 2009, he was officially given a SAMBA Team T-shirt welcoming him to the Samba Team. In 2014 he started pettycoin, a cryptocurrency project. Rusty Russell authored the majority part of Bitcoin's Lightning Network ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Counting
Counting is the process of determining the number of elements of a finite set of objects, i.e., determining the size of a set. The traditional way of counting consists of continually increasing a (mental or spoken) counter by a unit for every element of the set, in some order, while marking (or displacing) those elements to avoid visiting the same element more than once, until no unmarked elements are left; if the counter was set to one after the first object, the value after visiting the final object gives the desired number of elements. The related term '' enumeration'' refers to uniquely identifying the elements of a finite (combinatorial) set or infinite set by assigning a number to each element. Counting sometimes involves numbers other than one; for example, when counting money, counting out change, "counting by twos" (2, 4, 6, 8, 10, 12, ...), or "counting by fives" (5, 10, 15, 20, 25, ...). There is archaeological evidence suggesting that humans have been count ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Free Software Programmed In C
Free may refer to: Concept * Freedom, having the ability to do something, without having to obey anyone/anything * Freethought, a position that beliefs should be formed only on the basis of logic, reason, and empiricism * Emancipate, to procure political rights, as for a disenfranchised group * Free will, control exercised by rational agents over their actions and decisions * Free of charge, also known as gratis. See Gratis vs libre. Computing * Free (programming), a function that releases dynamically allocated memory for reuse * Free format, a file format which can be used without restrictions * Free software, software usable and distributable with few restrictions and no payment * Freeware, a broader class of software available at no cost Mathematics * Free object ** Free abelian group ** Free algebra ** Free group ** Free module ** Free semigroup * Free variable People * Free (surname) * Free (rapper) (born 1968), or Free Marie, American rapper and media pers ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Firewall Software
In computing, a firewall is a network security system that monitors and controls incoming and outgoing network traffic based on predetermined security rules. A firewall typically establishes a barrier between a trusted network and an untrusted network, such as the Internet. History The term ''firewall'' originally referred to a wall intended to confine a fire within a line of adjacent buildings. Later uses refer to similar structures, such as the metal sheet separating the engine compartment of a vehicle or aircraft from the passenger compartment. The term was applied in the late 1980s to network technology that emerged when the Internet was fairly new in terms of its global use and connectivity. The predecessors to firewalls for network security were routers used in the late 1980s. Because they already segregated networks, routers could apply filtering to packets crossing them. Before it was used in real-life computing, the term appeared in the 1983 computer-hacking movie ' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Discontinued Software
Abandonware is a product, typically software, ignored by its owner and manufacturer, and for which no official support is available. Within an intellectual rights contextual background, abandonware is a software (or hardware) sub-case of the general concept of '' orphan works''. Museums and various organizations dedicated to preserving this software continue to provide legal access. The term "abandonware" is broad, and encompasses many types of old software. Definitions of "abandoned" vary, but in general it is like any item that is abandoned – it is ignored by the owner, and as such product support and possibly copyright enforcement are also "abandoned". Types ;Commercial software unsupported but still owned by a viable company: The availability of the software depends on the company's attitude toward the software. In many cases, the company which owns the software rights may not be that which originated it, or may not recognize their ownership. Some companies, such as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protocol (computing)
A communication protocol is a system of rules that allows two or more entities of a communications system to transmit information via any kind of variation of a physical quantity. The protocol defines the rules, syntax, semantics and synchronization of communication and possible error recovery methods. Protocols may be implemented by hardware, software, or a combination of both. Communicating systems use well-defined formats for exchanging various messages. Each message has an exact meaning intended to elicit a response from a range of possible responses pre-determined for that particular situation. The specified behavior is typically independent of how it is to be implemented. Communication protocols have to be agreed upon by the parties involved. To reach an agreement, a protocol may be developed into a technical standard. A programming language describes the same for computations, so there is a close analogy between protocols and programming languages: ''protocols are to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
IP Fragmentation
400px, An example of the fragmentation of a protocol data unit in a given layer into smaller fragments. IP fragmentation is an Internet Protocol (IP) process that breaks packets into smaller pieces (fragments), so that the resulting pieces can pass through a link with a smaller maximum transmission unit (MTU) than the original packet size. The fragments are reassembled by the receiving host. The details of the fragmentation mechanism, as well as the overall architectural approach to fragmentation, are different between IPv4 and IPv6. Process describes the procedure for IP fragmentation, and transmission and reassembly of IP packets. RFC 815 describes a simplified reassembly algorithm. The ''Identification'' field along with the ''foreign'' and ''local internet address'' and the ''protocol ID'', and ''Fragment'' offset field along with ''Don't Fragment'' and ''More Fragments'' flags in the IP header are used for fragmentation and reassembly of IP packets. If a receiving h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stateful Firewall
In computing, a stateful firewall is a network-based firewall that individually tracks sessions of network connections traversing it. Stateful packet inspection, also referred to as dynamic packet filtering, is a security feature often used in non-commercial and business networks. Description A stateful firewall keeps track of the state of network connections, such as TCP streams, UDP datagrams, and ICMP messages, and can apply labels such as ''LISTEN'', ''ESTABLISHED'', or ''CLOSING''. State table entries are created for TCP streams or UDP datagrams that are allowed to communicate through the firewall in accordance with the configured security policy. Once in the table, all ''RELATED'' packets of a stored session are streamlined allowed, taking fewer CPU cycles than standard inspection. Related packets are also permitted to return through the firewall even if no rule is configured to allow communications from that host. If no traffic is seen for a specified time (implementa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |