|
Intercontinental Press
''Intercontinental Press'' (IP) was a weekly news magazine produced on behalf of the Fourth International (FI) between 1963 and 1986. The magazine was founded in Paris as ''World Outlook'' in 1963 under the editorial direction of Joseph Hansen, Pierre Frank and Reba Hansen as a "labor press service". A parallel edition in French was named ''Perspective mondiale''. World Outlook and Intercontinental Press produced a table of contents for the whole year in each year's last issue. Starting with volume 5 of 1967, World Outlook numbered the pages per year from the first to the last issue, with the year index referencing only the thru page number instead of issue and page within the issue. The publication was interrupted after the October 29, 1965 issue (Vol. 3 No 31) because of an illness of editor Joseph Hansen, after which weekly publication resumed in New York with the February 4, 1966 issue (Vol 4 No 1). In order to avoid costly litigation over the name with another maga ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Joseph Hansen (socialist)
Joseph Leroy Hansen (June 16, 1910 – January 18, 1979) was an American Trotskyist and leading figure in the Socialist Workers Party. Early life Joseph Hansen was born on June 16, 1910, in Richfield, Utah (162 miles south of Salt Lake City), the oldest of 15 children in a poor working-class family. He was the only one of the children who could attend college. His father, Conrad Johan Zahl Hansen, was a tailor, originally from the island Kvitvær, Lurøy, Nordland, in northern Norway. His parents had immigrated after they had converted to Mormonism. In school, he read a book on tariffs by Daniel De Leon. Socialism Hansen was the only member of his LDS family graduating from college. He became politically radicalized in the campus of the University of Utah by his professor of English literature Earle Birney, the follower of Trotsky, when Hansen edited University literary journal. Hansen became a convinced socialist and joined the American Trotskyist group strongly opposed to J ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fourth International (post-reunification)
The Fourth International (FI), founded in 1938, is a Trotskyist international. In 1963, following a ten-year schism, the majorities of the two public factions of the Fourth International, the International Secretariat and the International Committee, reunited, electing a United Secretariat of the Fourth International. In 2003, the United Secretariat was replaced by an Executive Bureau and an International Committee, although some other Trotskyists still refer to the organisation as the USFI or USec. Background The ISFI was the leadership body of the Fourth International, established in 1938. In 1953 many prominent members of the International, and supported by the majority of the Austrian, British, Chinese, French, New Zealand and Swiss sections together with the U.S. Socialist Workers Party organized against the views of Michel Pablo, a central leader of the ISFI who successfully argued for the FI to adapt to the growth of the social democratic and communist parties. This ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New International
''The New International'' is a magazine of Marxist theory published first by the Socialist Workers Party of the United States (SWP) from 1934 to 1940, then by the Workers Party from 1940 to 1958, and then revived by the SWP since 1983. Current format Since the magazine's resumption in 1983, ''The New International'' has included articles written by leaders of the ' Pathfinder tendency' which left the Fourth International in the 1980s. Content focuses on speeches and resolutions of the SWP's biannual conference, and archival documents by Bolshevik and Castroist communists. It is now published roughly once every two years. The magazine's last publication (online) was a 2008 issue with a covers story entitled "Revolution, Internationalism, and Socialism: The Last Year of Malcolm X" by Jack Barnes. Other articles were: "The Clintons’ Antilabor Legacy: Roots of the 2008 World Financial Crisis," "The Stewardship of Nature Also Falls to the Working Class," and "Setting the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Militant
''The Militant'' is an international socialist newsweekly connected to the Socialist Workers Party (SWP) and the Pathfinder Press. It is published in the United States and distributed in other countries such as Canada, the United Kingdom, Australia, France, Sweden, Iceland, and New Zealand. Publication history Forerunners An earlier publication called ''The Militant'was launched in November 1928 by James P. Cannon and other American Trotskyists gathered together in the Communist League of America (CLA). It declared its goal to be a fight "''in the interest of the working people''" against the capitalist system, imperialist wars, and the Stalinist regime in the Soviet Union, which according to the Trotskyists had betrayed and corrupted the October Revolution. The original ''Militant'' terminated in 1934 at the time of the merger of the Cannon-led CLA with the American Workers Party headed by A. J. Muste to form the Workers Party of the United States (WPUS). ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
International Viewpoint
''International Viewpoint'' is the English-language online magazine of the Trotskyist reunified Fourth International. It focuses on publishing articles on the political and social situation throughout the world, notably by translating articles into English written by socialists in other languages. Its ISSN is . The ''International'' also publishes a magazine in French ''Inprecor''. The German-speaking sections produce the Germa''Inprekorr'' The Spanish-languag''Punto de vista internacional''site is under the responsibility of the Spanish-speaking sections of the ''International''. The magazine was established in 1982 to replace ''Intercontinental Press'', which for a brief period had been the common English-language publication of the Fourth International having merged with the English-language ''Inprecor'' of the 1970s. In 1995, ''International Viewpoint'' absorbed ''International Marxist Review'', the Fourth International's theoretical magazine in English. The magazine has a n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inprecor
''Inprecor'' is a multilingual monthly Marxist magazine published by the reunified Fourth International. Its name is a contraction of International Press Correspondence and indicates that the magazine translates articles and letters from revolutionaries around the world.https://www.google.com/search?num=50&hl=en&safe=off&rlz=1B3GGGL_enUS219GB227&q=%22International+Press+Correspondence%22+inprecor&btnG=Search&meta= ''Inprecor'' was established by the Third International in the wake of the Russian Revolution The Russian Revolution was a period of Political revolution (Trotskyism), political and social revolution that took place in the former Russian Empire which began during the First World War. This period saw Russia abolish its monarchy and ad ... to allow communists to read the documents and thoughts of their comrades around the world. The Third International closed ''Inprecor'' in July 1938, replacing it with ''World News and Views''. After World War II, Ernest M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Socialist Workers Party (US)
The Socialist Workers Party (SWP) is a communist party in the United States. Originally a group in the Communist Party USA that supported Leon Trotsky against Soviet leader Joseph Stalin, it places a priority on "solidarity work" to aid Strike action, strikes and is strongly supportive of Cuban Revolution, Cuba. The SWP publishes ''The Militant'', a weekly newspaper that dates back to 1928. It also maintains Pathfinder Press. History Communist League of America The SWP traces its origins back to the former Communist League of America (CLA), founded in 1928 by members of the CPUSA expelled for supporting Russian communist leader Leon Trotsky against Joseph Stalin. Concentrated almost exclusively in New York City and Minneapolis, the CLA did not have more than 100 adherents in 1929. After five years of propaganda work, the CLA remained a tiny organization, with a membership of about 200 and very little influence. The rise of fascism in Nazi Germany and the failure of the c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Isaac Deutscher
Isaac; grc, Ἰσαάκ, Isaák; ar, إسحٰق/إسحاق, Isḥāq; am, ይስሐቅ is one of the three patriarchs of the Israelites and an important figure in the Abrahamic religions, including Judaism, Christianity, and Islam. He was the son of Abraham and Sarah, the father of Jacob and Esau, and the grandfather of the twelve tribes of Israel. Isaac's name means "he will laugh", reflecting the laughter, in disbelief, of Abraham and Sarah, when told by God that they would have a child., He is the only patriarch whose name was not changed, and the only one who did not move out of Canaan. According to the narrative, he died aged 180, the longest-lived of the three patriarchs. Etymology The anglicized name "Isaac" is a transliteration of the Hebrew name () which literally means "He laughs/will laugh." Ugaritic texts dating from the 13th century BCE refer to the benevolent smile of the Canaanite deity El. Genesis, however, ascribes the laughter to Isaac's parents, Abrah ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mimeograph
A mimeograph machine (often abbreviated to mimeo, sometimes called a stencil duplicator) is a low-cost duplicating machine that works by forcing ink through a stencil onto paper. The process is called mimeography, and a copy made by the process is a mimeograph. Mimeographs, along with spirit duplicators and hectographs, were common technologies for printing small quantities of a document, as in office work, classroom materials, and church bulletins. Early fanzines were printed by mimeograph because the machines and supplies were widely available and inexpensive. Beginning in the late 1960s and continuing into the 1970s, photocopying gradually displaced mimeographs, spirit duplicators, and hectographs. For even smaller quantities, up to about five, a typist would use carbon paper. Origins Use of stencils is an ancient art, butthrough chemistry, papers, and pressestechniques advanced rapidly in the late nineteenth century: Papyrograph A description of the Papyrograph m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gestetner
The Gestetner is a type of duplicating machine named after its inventor, David Gestetner (18541939). During the 20th century, the term ''Gestetner'' was used as a verb—as in ''Gestetnering''. The Gestetner company established its base in London, filing its first patent in 1879. The business grew, remaining within the control of the Gestetner family, and acquiring other businesses. In 1995, the Gestetner company was acquired by the Ricoh Corporation of Japan. History David Gestetner was born in Hungary in 1854, and after working in Vienna and New York, he moved to London, England, filing his first copying patent there in 1879. A later patent in 1881 was for the Cyclostyle, a stylus that was part of the Cyclograph copying device. That same year, he also established the Gestetner Cyclograph Company to produce duplicating machines, stencils, styli, ink rollers and related products. The Gestetner works opened in 1906 at Tottenham Hale, north London, and employed several thousand pe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stencil
Stencilling produces an image or pattern on a surface, by applying pigment to a surface through an intermediate object, with designed holes in the intermediate object, to create a pattern or image on a surface, by allowing the pigment to reach only some parts of the surface. The stencil is both the resulting image or pattern and the intermediate object; the context in which ''stencil'' is used makes clear which meaning is intended. In practice, the (object) stencil is usually a thin sheet of material, such as paper, plastic, wood or metal, with letters or a design cut from it, used to produce the letters or design on an underlying surface by applying pigment through the cut-out holes in the material. The key advantage of a stencil is that it can be reused to repeatedly and rapidly produce the same letters or design. Although aerosol or painting stencils can be made for one-time use, typically they are made with the intention of being reused. To be reusable, they must remain in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
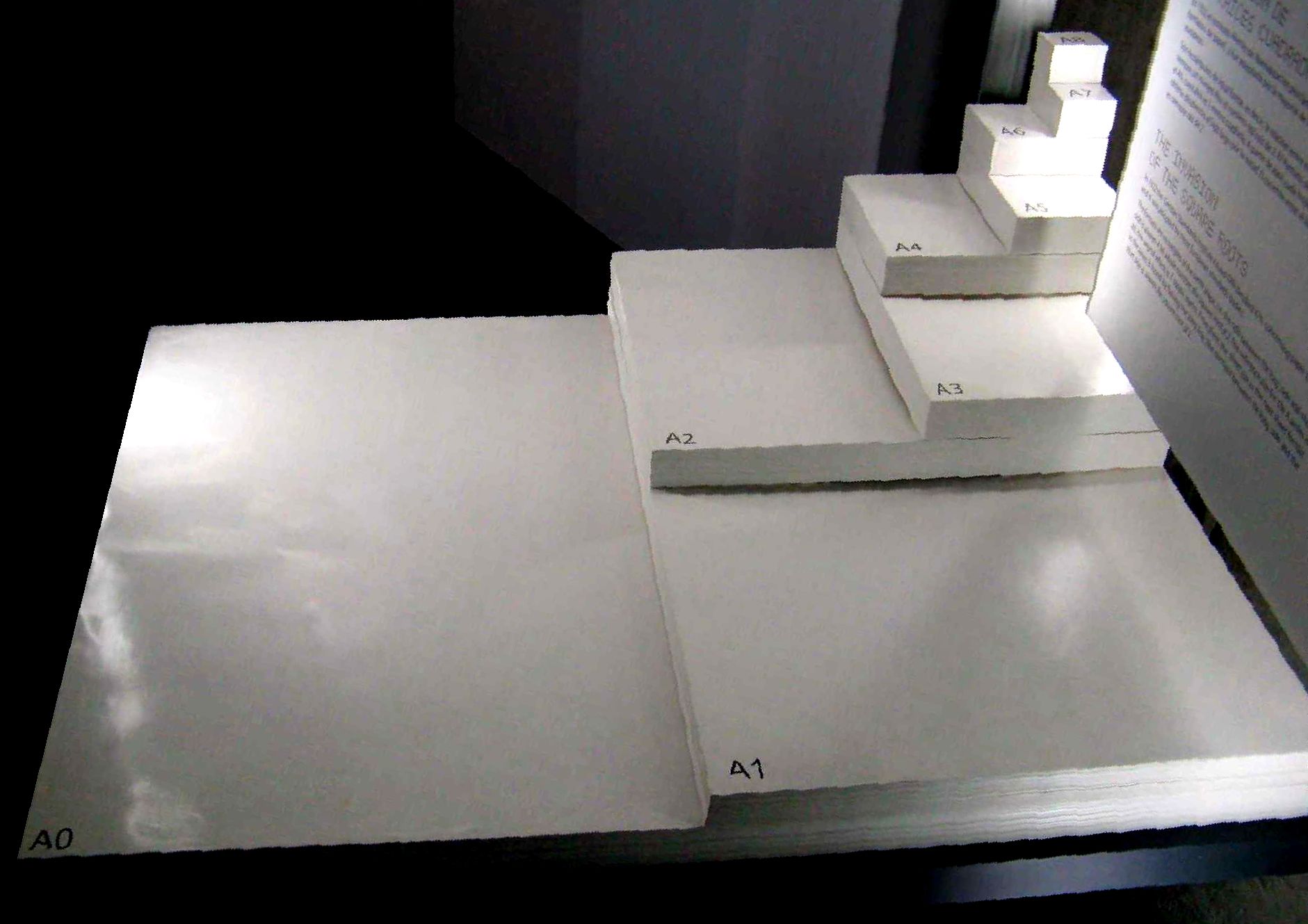
Paper Size
Paper size standards govern the size of sheets of paper used as writing paper, stationery, cards, and for some printed documents. The ISO 216 standard, which includes the commonly used A4 size, is the international standard for paper size. It is used across the world except in North America and parts of Central and South America, where North American paper sizes such as " Letter" and " Legal" are used. The international standard for envelopes is the C series of ISO 269. International paper sizes The international paper size standard is ISO 216. It is based on the German DIN 476 standard for paper sizes. ISO paper sizes are all based on a single aspect ratio of the square root of 2, or approximately 1:1.41421. There are different series, as well as several extensions. The following international paper sizes are included in Cascading Style Sheets (CSS): ''A3'', ''A4'', ''A5'', ''B4'', ''B5''. A series There are 11 sizes in the A series, designated A0–A10, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |