|
Intel Turbo Boost
Intel Turbo Boost is Intel's trade name for central processing units' (CPUs') dynamic frequency scaling feature that automatically raises certain versions of its operating frequency when demanding tasks are running, thus enabling a higher resulting performance. The frequency is accelerated when the operating system requests the highest performance state of the processor. Processor performance states are defined by the Advanced Configuration and Power Interface (ACPI) specification, an open standard supported by all major operating systems; no additional software or drivers are required to support the technology. The design concept behind Turbo Boost is commonly referred to as "dynamic overclocking". When the workload on the processor calls for faster performance, the processor's clock will try to increase the operating frequency in regular increments as required to meet demand. The increased clock rate is limited by the processor's power, current, and thermal limits, the numbe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intel
Intel Corporation is an American multinational corporation and technology company headquartered in Santa Clara, California, and Delaware General Corporation Law, incorporated in Delaware. Intel designs, manufactures, and sells computer components such as central processing units (CPUs) and related products for business and consumer markets. It is one of the world's List of largest semiconductor chip manufacturers, largest semiconductor chip manufacturers by revenue, and ranked in the Fortune 500, ''Fortune'' 500 list of the List of largest companies in the United States by revenue, largest United States corporations by revenue for nearly a decade, from 2007 to 2016 Fiscal year, fiscal years, until it was removed from the ranking in 2018. In 2020, it was reinstated and ranked 45th, being the List of Fortune 500 computer software and information companies, 7th-largest technology company in the ranking. It was one of the first companies listed on Nasdaq. Intel supplies List of I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Xeon
Xeon (; ) is a brand of x86 microprocessors designed, manufactured, and marketed by Intel, targeted at the non-consumer workstation, server, and embedded markets. It was introduced in June 1998. Xeon processors are based on the same architecture as regular desktop-grade CPUs, but have advanced features such as support for error correction code (ECC) memory, higher core counts, more PCI Express lanes, support for larger amounts of RAM, larger cache memory and extra provision for enterprise-grade reliability, availability and serviceability (RAS) features responsible for handling hardware exceptions through the Machine Check Architecture (MCA). They are often capable of safely continuing execution where a normal processor cannot due to these extra RAS features, depending on the type and severity of the machine-check exception (MCE). Some also support multi-socket systems with two, four, or eight sockets through use of the Ultra Path Interconnect (UPI) bus, which replaced ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
PowerNow!
__NOTOC__ AMD PowerNow! is AMD's dynamic frequency scaling and power saving technology for laptop processors. The CPU's clock speed and VCore are automatically decreased when the computer is under low load or idle, to save battery power, reduce heat and noise. The lifetime of the CPU is also extended because of reduced electromigration, which varies exponentially with temperature. AMD.com – TechDocs The technology is a concept similar to Intel's SpeedStep technology. The adaptation of PowerNow! for AMD's desktop CPUs is called Cool'n'Quiet. Newer Opterons also use an adaptation of PowerNow! called ''Optimized Power Management.'' AMD has supplied and supported drivers for its PowerNow! technology that work on Windows 98, ME, NT, and 2000. Processors supporting PowerNow! * K6-2+ * K6-III+ * Athlon XP-M - some models. * Mobile Athlon 64 * Mobile Sempron * Turion 64 and X2 * Athlon II * AMD Accelerated Processing Unit See also * Dynamic frequency scaling Dynamic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dynamic Frequency Scaling
Dynamic frequency scaling (also known as CPU throttling) is a power management technique in computer architecture whereby the frequency of a microprocessor can be automatically adjusted "on the fly" depending on the actual needs, to conserve power and reduce the amount of heat generated by the chip. Dynamic frequency scaling helps preserve battery on mobile devices and decrease cooling cost and noise on quiet computing settings, or can be useful as a security measure for overheated systems (e.g. after poor overclocking). Dynamic frequency scaling almost always appear in conjunction with dynamic voltage scaling, since higher frequencies require higher supply voltages for the digital circuit to yield correct results. The combined topic is known as dynamic voltage and frequency scaling (DVFS). Operation The dynamic power ('' switching power'') dissipated by a chip is ''C·V2·A·f'', where C is the capacitance being switched per clock cycle, V is voltage, A is the ''acti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cool'n'Quiet
AMD Cool'n'Quiet is a CPU dynamic frequency scaling and power saving technology introduced by AMD with its Athlon XP processor line. It works by reducing the processor's clock rate and voltage when the processor is idle. The aim of this technology is to reduce overall power consumption and lower heat generation, allowing for slower (thus quieter) cooling fan operation. The objectives of cooler and quieter result in the name Cool'n'Quiet. The technology is similar to Intel's SpeedStep and AMD's own PowerNow!, which were developed with the aim of increasing laptop battery life by reducing power consumption. Due to their different usage, ''Cool'n'Quiet'' refers to desktop and server chips, while ''PowerNow!'' is used for mobile chips; the technologies are similar but not identical. This technology was also introduced on "e-stepping" Opterons, however it is called ''Optimized Power Management'', which is essentially a re-tooled Cool'n'Quiet scheme designed to work with reg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
AMD Turbo Core
AMD Turbo Core a.k.a. AMD Core Performance Boost (CPB) is a dynamic frequency scaling technology implemented by AMD that allows the processor to dynamically adjust and control the processor operating frequency in certain versions of its processors which allows for increased performance when needed while maintaining lower power and thermal parameters during normal operation. AMD Turbo Core technology has been implemented beginning with the Phenom II X6 microprocessors based on the AMD K10 microarchitecture. AMD Turbo Core is available with some AMD A-Series accelerated processing units. AMD Turbo Core is similar to Intel Turbo Boost, which is another dynamic processor frequency adjustment technology used to increase performance, as well as AMD PowerNow!, which is used to dynamically adjust laptop processor's operating frequencies in order to decrease power consumption (saving battery life), reduce heat, and lower noise. AMD PowerNow! is used to ''decrease'' processor frequenc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
AMD PowerTune
AMD PowerTune is a series of dynamic frequency scaling technologies built into some AMD GPUs and APUs that allow the clock speed of the processor to be dynamically changed (to different ''P-states'') by software. This allows the processor to meet the instantaneous performance needs of the operation being performed, while minimizing power draw, heat generation and noise avoidance. AMD PowerTune aims to solve thermal design power and performance constraints. Besides the reduced energy consumption, AMD PowerTune helps to lower the noise levels created by the cooling in desktop computers, and extends battery life in mobile devices. AMD PowerTune is the successor to AMD PowerPlay. Support for "PowerPlay" was added to the Linux kernel driver "amdgpu" on November 11, 2015. As a lecture from CCC in 2014 shows, AMD's x86-64 SMU firmware is executed on some LatticeMico32 and PowerTune was modeled using Matlab. This is similar to Nvidia's PDAEMON, the RTOS responsible for power on the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Centrino
Centrino was a brand name of Intel Corporation which represented its Wi-Fi and WiMAX wireless computer networking adapters. The brand name was first used by the company as a platform-marketing initiative. The change of the meaning of the brand name occurred on January 7, 2010. The Centrino name for laptops was replaced by the Ultrabook. The old platform-marketing brand name covered a particular combination of mainboard chipset, mobile CPU and wireless network interface in the design of a laptop. Intel claimed that systems equipped with these technologies delivered better performance, longer battery life and broader wireless network interoperability than non-Centrino systems. The product line name for Intel wireless products became Intel Centrino Wireless in 2010. The Centrino brand was ultimately discontinued in 2013. Intel Centrino Notebook implementations Carmel platform (2003) Intel used " Carmel" as the codename for the first-generation Centrino platform, introduced ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intel Dynamic Acceleration
Intel Dynamic Acceleration (IDA) sometimes called Dynamic Acceleration Technology (DAT) is a technology created by Intel Corp. in certain multi-core Intel microprocessors. It increases the clock rate of a single core for every two cores above its base operating frequency if the other cores are idle. It is designed for single threaded programs to run faster on multi-core Intel microprocessors. Intel later released a version of IDA called enhanced Dynamic Acceleration Technology (eDAT) for its quad core processors that boosts the performance of 2 cores when only 2 cores are being utilized. History Intel Dynamic Acceleration was first released with the Core 2 Duo mobile processor line, as new microprocessor lines were released, Intel changed the technology and naming scheme slightly. Dual Dynamic Acceleration With the introduction of quad core processors, Intel modified IDA and released ''Dual Dynamic Acceleration'' (''DDA''). Intel Turbo Boost The later released Nehalem microa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Linux Kernel
The Linux kernel is a Free and open-source software, free and open source Unix-like kernel (operating system), kernel that is used in many computer systems worldwide. The kernel was created by Linus Torvalds in 1991 and was soon adopted as the kernel for the GNU operating system (OS) which was created to be a free software, free replacement for Unix. Since the late 1990s, it has been included in many Linux distributions, operating system distributions, many of which are called Linux. One such Linux kernel operating system is Android (operating system), Android which is used in many mobile and embedded devices. Most of the kernel code is written in C (programming language), C as supported by the GNU compiler collection (GCC) which has extensions beyond standard C. The code also contains assembly language, assembly code for architecture-specific logic such as optimizing memory use and task execution. The kernel has a Modular programming, modular design such that modules can be inte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Windows 10
Windows 10 is a major release of Microsoft's Windows NT operating system. The successor to Windows 8.1, it was Software release cycle#Release to manufacturing (RTM), released to manufacturing on July 15, 2015, and later to retail on July 29, 2015. Windows 10 was made available for download via MSDN and Microsoft Technet, TechNet, as a free upgrade for retail copies of Windows 8 and Windows 8.1 users via the Microsoft Store, and to Windows 7 users via Windows Update. Unlike previous Windows NT releases, Windows 10 receives new software build, builds on an ongoing basis, which are available at no additional cost to users; devices in enterprise environments can alternatively use long-term support milestones that only receive critical updates, such as security patch (computing), patches. It was succeeded by Windows 11, which was released on October 5, 2021. In contrast to the Tablet computer, tablet-oriented approach of Windows 8, Microsoft provided the desktop environment, de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
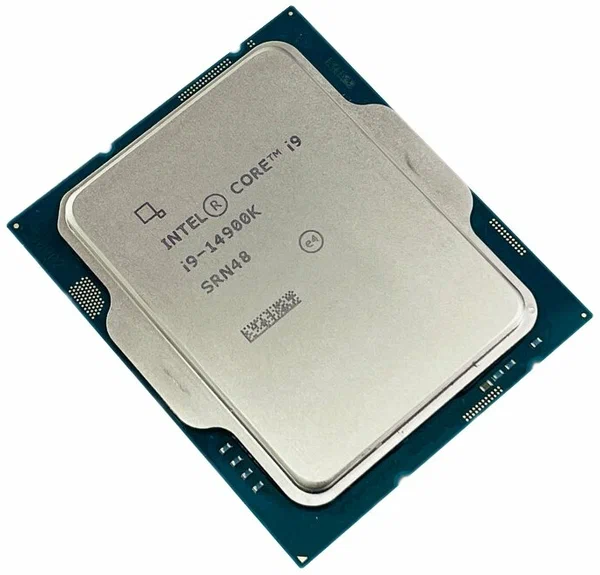
Core I7
Intel Core is a line of multi-core (with the exception of Core Solo and Core 2 Solo) central processing units (CPUs) for midrange, embedded, workstation, high-end and enthusiast computer markets marketed by Intel Corporation. These processors displaced the existing mid- to high-end Pentium processors at the time of their introduction, moving the Pentium to the entry level. Identical or more capable versions of Core processors are also sold as Xeon processors for the server and workstation markets. Core was launched in January 2006 as a mobile-only series, consisting of single- and dual-core models. It was then succeeded later in July by the Core 2 series, which included both desktop and mobile processors with up to four cores, and introduced 64-bit support. Since 2008, Intel began introducing the Core i3, Core i5, Core i7 and Core i9 lineup of processors, succeeding Core 2. A new naming scheme debuted in 2023, consisting of Core 3, Core 5, and Core 7 for mainstream processors ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |