|
Intel Socket G3
Socket G3, also known as rPGA 946B/947 or FCPGA 946, is a socket for Intel microprocessors that supports Haswell-based mobile CPUs. Compatible SKUs have an 'M' suffix in the model number. Socket G3 is designed as a replacement for the Socket G2, which is also known as rPGA 988B. Socket G3 has holes to make contact with 946 or 947 pins of the processor's pin grid array (PGA). Lynx Point is the Platform Controller Hub (PCH) associated with Socket G3. Socket rPGA 947 has one extra pin hole, other than that it is identical to socket G3. It is the last pin grid array socket for Intel's mobile processors - all mobile processors in microarchitectures succeeding Haswell are exclusively available in BGA packaging. AMD also adopted the same practice, starting with their Steamroller microarchitecture. See also * List of Intel microprocessors * Micro-FCPGA * Socket G2 * Socket G1 * Socket P * Socket M Socket M (mPGA478MT) is a CPU interface introduced by Intel in 2 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Pin Grid Array
A pin grid array (PGA) is a type of integrated circuit packaging. In a PGA, the package is square or rectangular, and the pins are arranged in a regular array on the underside of the package. The pins are commonly spaced 2.54 mm (0.1") apart, and may or may not cover the entire underside of the package. PGAs are often mounted on printed circuit boards using the Through-hole technology, through hole method or inserted into a CPU socket, socket. PGAs allow for more pins per integrated circuit than older packages, such as dual in-line package (DIP). Chip mounting The chip can be mounted either on the top or the bottom (the pinned side). Connections can be made either by wire bonding or through flip chip mounting. Typically, PGA packages use wire bonding when the chip is mounted on the pinned side, and flip chip construction when the chip is on the top side. Some PGA packages contain multiple dies, for example Zen 2 and Zen 3 Ryzen CPUs for the Socket AM4, AM4 socket. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Microprocessor
A microprocessor is a computer processor (computing), processor for which the data processing logic and control is included on a single integrated circuit (IC), or a small number of ICs. The microprocessor contains the arithmetic, logic, and control circuitry required to perform the functions of a computer's central processing unit (CPU). The IC is capable of interpreting and executing program instructions and performing arithmetic operations. The microprocessor is a multipurpose, Clock signal, clock-driven, Processor register, register-based, digital integrated circuit that accepts binary code, binary data as input, processes it according to instruction (computing), instructions stored in its computer memory, memory, and provides results (also in binary form) as output. Microprocessors contain both combinational logic and sequential logic, sequential digital logic, and operate on numbers and symbols represented in the binary number system. The integration of a whole CPU on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Socket P
The Intel Socket P (mPGA478MN) is the mobile processor socket replacement for Core microarchitecture chips such as Core 2 Duo. It launched on May 9, 2007, as part of the Santa Rosa platform with the Merom and Penryn processors. Technical specifications The front-side bus (FSB) of CPUs that install in Socket P can run at 400, 533, 667, 800, or 1066 MT/s. By adapting the multiplier the frequency of the CPU can throttle up or down to save power, given that all Socket P CPUs support EIST, except for Celeron that do not support EIST. Socket P has 478 pins, but is not electrically pin-compatible with Socket M or Socket 478. Socket P is also known as a 478-pin Micro FCPGA or μFCPGA-478. On the plastic grid is printed mPGA478MN. See also * List of Intel microprocessors This generational list of Intel processors attempts to present all of Intel's processors from the 4-bit 4004 (1971) to the present high-end offerings. Concise technical data is given for each product. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Socket G1
Socket G1, also known as rPGA 988A, is a CPU socket introduced by Intel in 2009 for the mobile variants of the first-generation Intel Core processors. It is the successor to Socket P, and the mobile counterpart to LGA 1156 and LGA 1366. History The first CPUs for the Socket G1 platform were released on September 23, 2009, in the form of the i7-720QM, 820QM, and 920XM. These CPUs use the Clarksfield core, which maintained the same 45 nm manufacturing process as the desktop Nehalem architecture. On January 4, 2010, the range was expanded with Core i3, i5, and i7 processors using the 32 nm Arrandale core and based on the Westmere architecture. On March 28, 2010, low-end Arrandale-based CPUs were released as the Pentium P6x00 series and Celeron P4x00 series. Further Clarksfield-based processors were released as the i7-740QM, 840QM, and 940XM on June 21, 2010. All Socket G1 processors, except for the quad-core i7 CPUs have the Intel HD Graphics Ironlake core packaged onto the CPU ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
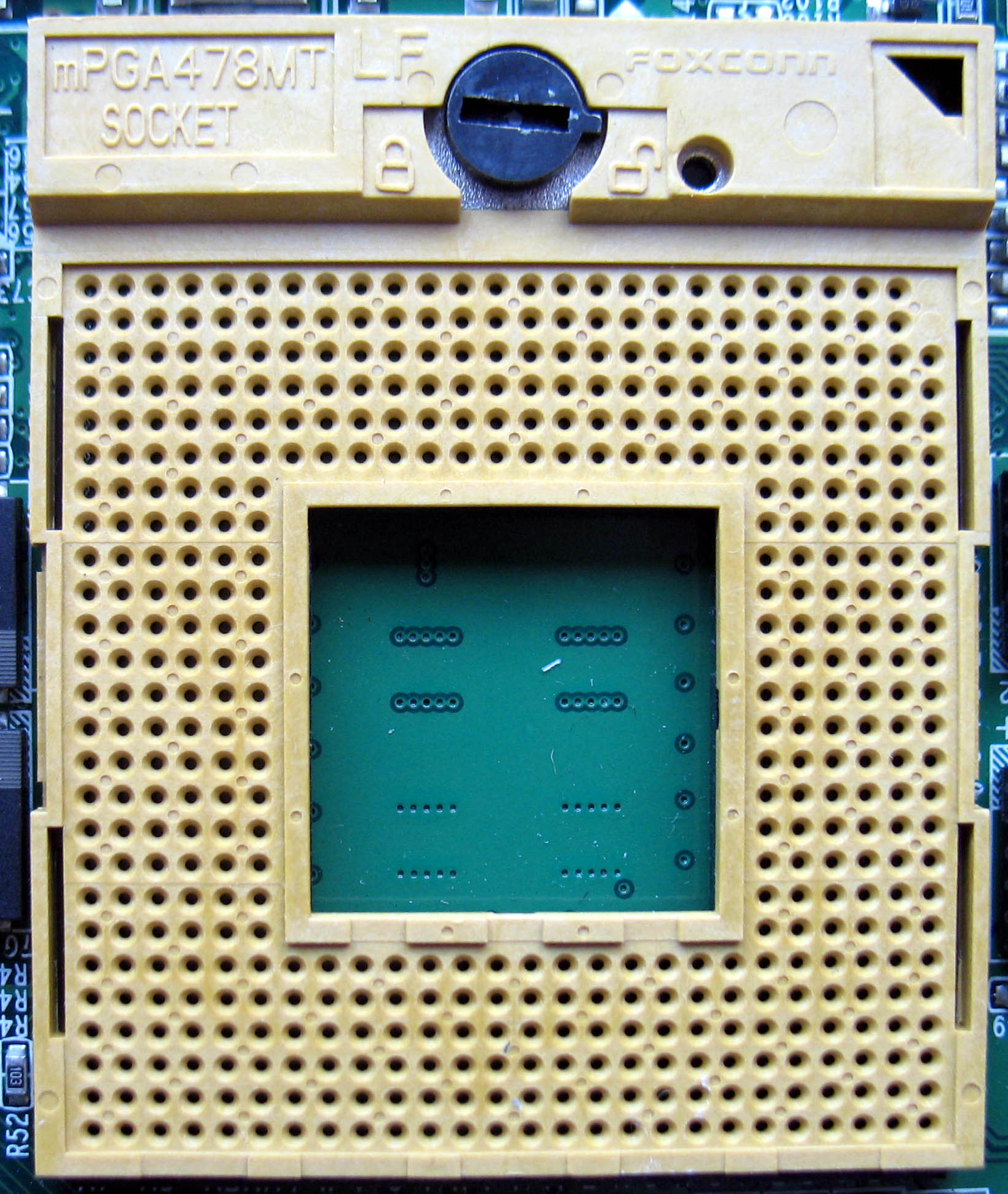
Micro-FCPGA
Socket M (mPGA478MT) is a CPU interface introduced by Intel in 2006 for the Intel Core line of mobile processors. Technical specifications Socket M is used in all Intel Core products, as well as the Core-derived Dual-Core Xeon codenamed Sossaman. It was also used in the first generation of the mobile version of Intel's Core 2 Duo, specifically, the T5x00 and T7x00 Merom lines (referred to as Napa Refresh), though that line switched to Socket P (Santa Rosa) in 2007. It typically uses the Intel 945PM/945GM chipsets which support up to 667 MHz FSB and the Intel PM965/GM965 which allows 800 MHz FSB support, though the Socket M, PM965/GM965 combination is less common. The "Sossaman" Xeons use the E7520 chipset. Relation to other sockets Socket M is pin-compatible with desktop socket mPGA478A but it is not electrically compatible. Socket M is not pin-compatible with the older desktop Socket 478 (mPGA478B) or the newer mobile Socket P (mPGA478MN) by location of one pin; i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
List Of Intel Microprocessors
This generational list of Intel processors attempts to present all of Intel's processors from the 4-bit 4004 (1971) to the present high-end offerings. Concise technical data is given for each product. Latest 15th generation Core Desktop - Core Ultra Series 2 (codenamed " Arrow Lake") Released on October 24, 2024. It follows on from Meteor Lake which saw Intel move from monolithic silicon to a disaggregated MCM design. Meteor Lake was limited to a mobile release while Arrow Lake includes desktop processors and mobile processors. Desktop - Arrow Lake-S Mobile - Arrow Lake-U Arrow Lake-U uses refreshed Meteor Lake silicon fabricated on the Intel 3 node. Mobile - Arrow Lake-H Mobile - Arrow Lake-HX 13th and 14th generation Core Desktop - Raptor Lake-S Refresh (codenamed "Raptor Lake") (14th Gen) An iterative refresh of Raptor Lake-S desktop processors, called the 14th generation of Intel Core, was launched on October 17, 2023. CPUs in bold below ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Steamroller (microarchitecture)
AMD Steamroller Family 15h is a microarchitecture developed by AMD for AMD APUs, which succeeded Piledriver in the beginning of 2014 as the third-generation Bulldozer-based microarchitecture. Steamroller APUs continue to use two-core modules as their predecessors, while aiming at achieving greater levels of parallelism. Microarchitecture ''Steamroller'' still features two-core modules found in ''Bulldozer'' and ''Piledriver'' designs called clustered multi-thread (CMT), meaning that one module is marketed as a dual-core processor. The focus of ''Steamroller'' is for greater parallelism. Improvements center on independent instruction decoders for each core within a module, 25% more of the maximum width dispatches per thread, better instruction schedulers, improved perceptron branch predictor, larger and smarter caches, up to 30% fewer instruction cache misses, branch misprediction rate reduced by 20%, dynamically resizable L2 cache, micro-operations queue, more internal regi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Ball Grid Array
A ball grid array (BGA) is a type of surface-mount packaging (a chip carrier) used for integrated circuits. BGA packages are used to permanently mount devices such as microprocessors. A BGA can provide more interconnection pins than can be put on a dual in-line or flat package. The whole bottom surface of the device can be used, instead of just the perimeter. The traces connecting the package's leads to the wires or balls which connect the die to package are also on average shorter than with a perimeter-only type, leading to better performance at high speeds. Soldering of BGA devices requires precise control and is usually done by automated processes such as in computer-controlled automatic reflow ovens. Description The BGA is descended from the pin grid array (PGA), which is a package with one face covered (or partly covered) with pins in a grid pattern which, in operation, conduct electrical signals between the integrated circuit and the printed circuit board (PCB) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Platform Controller Hub
The Platform Controller Hub (PCH) is a family of Intel's single-chip chipsets, first introduced in 2009. It is the successor to the Intel Hub Architecture, which used two chipsa northbridge and southbridge, and first appeared in the Intel 5 Series. The PCH controls certain data paths and support functions used in conjunction with Intel CPUs. These include clocking (the system clock), Flexible Display Interface (FDI) and Direct Media Interface (DMI), although FDI is used only when the chipset is required to support a processor with integrated graphics. As such, I/O functions are reassigned between this new central hub and the CPU compared to the previous architecture: some northbridge functions, the memory controller and PCIe lanes, were integrated into the CPU while the PCH took over the remaining functions in addition to the traditional roles of the southbridge. AMD has its equivalent for the PCH, known simply as a chipset since the release of the Zen architecture in 2017. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Lynx Point
Acromelanism is a genetic condition that results in pigmentation being affected by temperature. It results in point coloration where the extremities of an animal are a different colour to the rest of the body. It is commonly known for the coloration of Siamese and related breeds of cat, but can be found in many other species including dogs, rabbits, rats, mice, guinea pigs, minks, and gerbils. It is a specific type of point coloration. Description Colorpoint patterns are where the extremities (paws, face, ears and tail) of the animal are colored differently compared to the rest of the body. The areas with different color may be referred as 'points' or being 'pointed'. Color can spread to the rest of the body, but is concentrated on the extremities. Colorpoint patterns occur due to acromelanism, which is a type of partial albinism where pigmentation is affected by temperature. Cold temperatures trigger pigment development while warm temperatures decrease pigment development. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
CPU Socket
In computer hardware, a CPU socket or CPU slot contains one or more mechanical components providing mechanical and electrical connections between a microprocessor and a printed circuit board (PCB). This allows for placing and replacing the central processing unit (CPU) without soldering. Common sockets have retention clips that apply a constant force, which must be overcome when a device is inserted. For chips with many pins, zero insertion force (ZIF) sockets are preferred. Common sockets include pin grid array (PGA) or land grid array (LGA). These designs apply a compression force once either a handle (PGA type) or a surface plate (LGA type) is put into place. This provides superior mechanical retention while avoiding the risk of bending pins when inserting the chip into the socket. Certain devices use Ball Grid Array (BGA) sockets, although these require soldering and are generally not considered user replaceable. CPU sockets are used on the motherboard in desktop and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Direct Media Interface
In computing, Direct Media Interface (DMI) is Intel's proprietary link between the northbridge (or CPU) and southbridge (e.g. Platform Controller Hub family) chipset on a computer motherboard. It was first used between the 9xx chipsets and the ICH6, released in 2004. Previous Intel chipsets had used the Intel Hub Architecture to perform the same function, and server chipsets use a similar interface called ''Enterprise Southbridge Interface'' (ESI). While the "DMI" name dates back to ICH6, Intel mandates specific combinations of compatible devices, so the presence of a DMI does not guarantee by itself that a particular northbridge–southbridge combination is allowed. DMI is essentially PCI Express, using multiple lanes and differential signaling to form a point-to-point link. Most implementations use a ×8 or ×4 link, while some mobile systems (e.g. 915GMS, 945GMS/GSE/GU and the Atom N450) use a ×2 link, halving the bandwidth. The original implementation provides 10& ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |