|
Iconicity
In functional- cognitive linguistics, as well as in semiotics, iconicity is the conceived similarity or analogy between the form of a sign (linguistic or otherwise) and its meaning, as opposed to arbitrariness (which is typically assumed in structuralist, formalist and generative approaches to linguistics). The principle of iconicity is also shared by the approach of linguistic typology. Iconic principles: *Quantity principle: conceptual complexity corresponds to formal complexity *Proximity principle: conceptual distance tends to match with linguistic distance *Sequential order principle: the sequential order of events described is mirrored in the speech chain Quantity principle The use of quantity of phonetic material to iconically mark increased quality or quantity can be noted in the lengthening of words to indicate a greater degree, such as "". It is also common to use reduplication to iconically mark increase, as Edward Sapir is quoted, “The process is genera ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Winfried Nöth
Winfried Nöth (born September 12, 1944 in Gerolzhofen) is a German linguist and semiotician. After graduating from high school in 1963 in Brunswick, from 1965 to 1969 Nöth studied English, French and Portuguese in Münster, Geneva, Lisbon and Bochum, and in 1971 acquired his doctoral degrees at the Ruhr University Bochum. In Bochum he also habilitated in 1976 and became assistant to Walter A. Koch. After teaching in Bochum and Aachen, in 1978 he was appointed full professor in English Linguistics at the University of Kassel. In 1985, Nöth was visiting professor at the University of Wisconsin–Green Bay in Green Bay, Wisconsin, United States, and in 1994 at the Pontifícia Universidade Católica de São Paulo in Brazil. Since 1999 he has been Director of the Scientific Centre for Cultural Research, University of Kassel, and President of the German Society for Semiotics. His ''Handbook of Semiotics'' (first published 1985) gives a comprehensive overview of the history and v ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Formalist Linguistics
In linguistics, the term formalism is used in a variety of meanings which relate to formal linguistics in different ways. In common usage, it is merely synonymous with a grammatical model or a syntactic model: a method for analyzing sentence structures. Such formalisms include different methodologies of generative grammar which are especially designed to produce grammatically correct strings of words; or the likes of Functional Discourse Grammar which builds on predicate logic. Additionally, ''formalism'' can be thought of as a theory of language. This is most commonly a reference to mathematical formalism which argues that syntax is purely axiomatic being based on sequences generated by mathematical operations. This idea stands in contradistinction to psychologism and logicism which, respectively, argue that syntax is based on human psychology; or on semantic a priori structures which exist independently of humans. Definitions Rudolph Carnap defined the meaning of the adje ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indexicality
In semiotics, linguistics, anthropology, and philosophy of language, indexicality is the phenomenon of a ''Sign (semiotics), sign'' pointing to (or ''indexing'') some element in the context (language use), context in which it occurs. A sign that signifies indexically is called an index or, in philosophy, an indexical. The modern concept originates in the semiotic theory of Charles Sanders Peirce, in which indexicality is one of the three fundamental sign modalities by which a sign relates to its referent (the others being iconicity and Symbolic anthropology, symbolism).Charles Sanders Peirce, Peirce, C.S., "Division of Signs" in ''Collected Papers'', 1932 [1897]. Peirce's concept has been adopted and extended by several twentieth-century academic traditions, including those of linguistic pragmatics, linguistic anthropology, and Anglo-American philosophy of language. Words and expressions in language often derive some part of their referential meaning from indexicality. For example ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Semiotics
Semiotics ( ) is the systematic study of sign processes and the communication of meaning. In semiotics, a sign is defined as anything that communicates intentional and unintentional meaning or feelings to the sign's interpreter. Semiosis is any activity, conduct, or process that involves signs. Signs often are communicated by verbal language, but also by gestures, or by other forms of language, e.g. artistic ones (music, painting, sculpture, etc.). Contemporary semiotics is a branch of science that generally studies meaning-making (whether communicated or not) and various types of knowledge. Unlike linguistics, semiotics also studies non-linguistic sign systems. Semiotics includes the study of indication, designation, likeness, analogy, allegory, metonymy, metaphor, symbolism, signification, and communication. Semiotics is frequently seen as having important anthropological and sociological dimensions. Some semioticians regard every cultural phenomenon as being able to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Analogy
Analogy is a comparison or correspondence between two things (or two groups of things) because of a third element that they are considered to share. In logic, it is an inference or an argument from one particular to another particular, as opposed to deduction, induction, and abduction. It is also used where at least one of the premises, or the conclusion, is general rather than particular in nature. It has the general form ''A is to B as C is to D''. In a broader sense, analogical reasoning is a cognitive process of transferring some information or meaning of a particular subject (the analog, or source) onto another (the target); and also the linguistic expression corresponding to such a process. The term analogy can also refer to the relation between the source and the target themselves, which is often (though not always) a similarity, as in the biological notion of analogy. Analogy plays a significant role in human thought processes. It has been argued that analogy li ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Terrence Deacon
Terrence William Deacon (born 1950) is an American neuroanthropologist (Ph.D. in Biological Anthropology, Harvard University 1984). He taught at Harvard for eight years, relocated to Boston University in 1992, and is currently Professor of Anthropology and member of the Cognitive Science Faculty at the University of California, Berkeley. Theoretical interests Deacon's theoretical interests include the study of evolution-like processes at multiple levels, including their role in embryonic development, neural signal processing, language change, social processes, and focusing especially on how these different processes interact and depend on each other. He has long stated an interest in developing a scientific semiotics (particularly biosemiotics) that would contribute to both linguistic theory and cognitive neuroscience.http://anthropology.berkeley.edu/users/terrence-w-deacon UC Berkeley faculty profile Fields of research Deacon's research combines human evolutionary biology an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Symbolic Species
''The Symbolic Species'' is a 1997 book by biological anthropologist Terrence Deacon on the evolution of language. Combining perspectives from neurobiology, evolutionary theory, linguistics, and semiotics Semiotics ( ) is the systematic study of sign processes and the communication of meaning. In semiotics, a sign is defined as anything that communicates intentional and unintentional meaning or feelings to the sign's interpreter. Semiosis is a ..., Deacon proposes that language, along with the unique human capacity for symbolic thought, co-evolved with the brain. ''The Symbolic Species'' is a multi-disclipinary book that at the time of publishing was seen as groundbreaking. It is considered to have bound together a wide array of ideas in a way that advanced the understanding of professionals in several fields. Symbolic thought and language The reasons for the unique cognitive capacity of humans are explored, along with those for the large number of human activities impo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Megafauna
In zoology, megafauna (from Ancient Greek, Greek μέγας ''megas'' "large" and Neo-Latin ''fauna'' "animal life") are large animals. The precise definition of the term varies widely, though a common threshold is approximately , this lower end being centered on humans, with other thresholds being more relative to the sizes of animals in an ecosystem, the spectrum of lower-end thresholds ranging from to . Large body size is generally associated with other traits, such as having a slow rate of reproduction and, in large herbivores, reduced or negligible adult mortality from being killed by predators. Megafauna species have considerable effects on their local environment, including the suppression of the growth of woody vegetation and a consequent reduction in wildfire frequency. Megafauna also play a role in regulating and stabilizing the abundance of smaller animals. During the Pleistocene, megafauna were diverse across the globe, with most continental ecosystems exhibiting s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Haspelmath
Martin Haspelmath (; born 2 February 1963 in Hoya, Germany, Hoya, Lower Saxony) is a German linguistics, linguist working in the field of linguistic typology. He is a researcher at the Max Planck Institute for Evolutionary Anthropology in Leipzig, where he worked from 1998 to 2015 and again since 2020. Between 2015 and 2020, he worked at the Max Planck Institute for the Science of Human History. He is also an honorary professor of linguistics at the University of Leipzig. Career Haspelmath is one of the editors of the World Atlas of Language Structures and the Glottolog online database, one of the founders of the open access publisher Language Science Press, and has worked on the Standard Average European sprachbund. Besides typology, his research interests include syntax, syntactic and morphology (linguistics), morphological theory, language change and language contact. He is a member of the Academia Europaea. According to Google Scholar, his work has been cited over 42,000 tim ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Niche Construction
Niche construction is the ecological process by which an organism alters its own (or another species') local environment. These alterations can be a physical change to the organism’s environment, or it can encompass the active movement of an organism from one habitat to another where it then experiences different environmental pressures. Examples of Ecological niche, niche construction include the building of nests and burrows by animals, the creation of shade, the influencing of wind speed, and alternations to nutrient cycling by plants. Although these modifications are often directly beneficial to the ''constructor'', they are not necessarily always. For example, when organisms dump detritus, they can degrade their own local environments. Within some biological evolutionary frameworks, niche construction can actively beget processes pertaining to ecological inheritance whereby the organism in question “constructs” new or unique ecologic, and perhaps even sociologic environm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Displacement (linguistics)
In linguistics, displacement is the capability of language to communicate about things that are not immediately present (spatially or temporally); i.e., things that are either not here or are not here now. In 1960, Charles F. Hockett proposed displacement as one of 13 design features of language that distinguish human language from animal communication systems (ACSs): In animal communication systems Honeybees use the waggle dance to communicate the location of a patch of flowers suitable for foraging. The degree of displacement in this example remains limited when compared to human language. A bee can only communicate the location of the most recent food source it has visited. It cannot communicate an idea about a food source at a specific point in the past, nor can it speculate about food sources in the future. In addition, displacement in the waggle dance is restricted by the language's lack of creativity and productivity. The bees can express direction and distance, but it ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
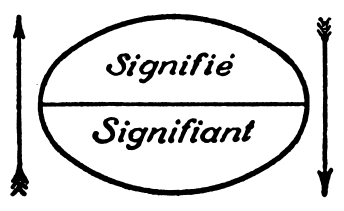
Signifier
In semiotics, signified and signifier (French language, French: ''signifié'' and ''signifiant'') are the two main components of a Sign (semiotics), sign, where ''signified'' is what the sign represents or refers to, known as the "plane of content", and ''signifier'' which is the "plane of expression" or the observable aspects of the sign itself. The idea was first proposed in the work of Swiss linguist Ferdinand de Saussure, one of the two founders of semiotics. Concept of signs The concept of signs has been around for a long time, having been studied by many classic philosophers such as Plato, Aristotle, Augustine, William of Ockham, and Francis Bacon, among others. The term ''semiotics'' derives from the Greek root ''seme'', as in ''semeiotikos'' (an 'interpreter of signs').Arthur Asa Berger, Berger, Arthur Asa. 2012. ''Media Analysis Techniques''. Beverly Hills: Sage Publications. It was not until the early part of the 20th century, however, that Saussure and American phi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |