|
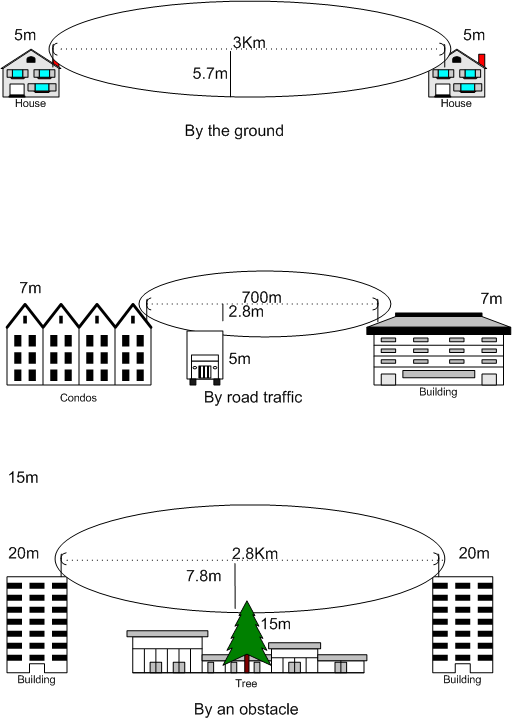
ITU Terrain Model
The ITU terrain loss model is a radio propagation model that provides a method to predict the median path loss for a telecommunication link. Developed on the basis of diffraction theory, this model predicts the path loss as a function of the height of path blockage and the First Fresnel zone for the transmission link. Applicable to / under conditions This model is applicable on any terrain. This model accounts for obstructions in the middle of the telecommunication link, and therefore, is suitable to be used inside cities as well as in open fields. Coverage Frequency: Any Distance: Any Mathematical formulation The model is mathematically formulated as: : A \; = \; 10 \; - \; 20 \; C_N : C_N \; = \; \frac : h \; = \; h_L \; - \; h_O : F_1 \; = \; 17.3 \; \sqrt Where, : A \; = Additional loss (in excess of free-space loss) due to diffraction (dB) : C_N \; = Normalized terrain clearance : h \; = The height difference (negative in the case that the LOS path is completely ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radio Propagation Model
Radio propagation is the behavior of radio waves as they travel, or are propagated, from one point to another in vacuum, or into various parts of the atmosphere. As a form of electromagnetic radiation, like light waves, radio waves are affected by the phenomena of reflection, refraction, diffraction, absorption, polarization, and scattering. Understanding the effects of varying conditions on radio propagation has many practical applications, from choosing frequencies for amateur radio communications, international shortwave broadcasters, to designing reliable mobile telephone systems, to radio navigation, to operation of radar systems. Several different types of propagation are used in practical radio transmission systems. '' Line-of-sight propagation'' means radio waves which travel in a straight line from the transmitting antenna to the receiving antenna. Line of sight transmission is used for medium-distance radio transmission, such as cell phones, cordless phones, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Median
The median of a set of numbers is the value separating the higher half from the lower half of a Sample (statistics), data sample, a statistical population, population, or a probability distribution. For a data set, it may be thought of as the “middle" value. The basic feature of the median in describing data compared to the Arithmetic mean, mean (often simply described as the "average") is that it is not Skewness, skewed by a small proportion of extremely large or small values, and therefore provides a better representation of the center. Median income, for example, may be a better way to describe the center of the income distribution because increases in the largest incomes alone have no effect on the median. For this reason, the median is of central importance in robust statistics. Median is a 2-quantile; it is the value that partitions a set into two equal parts. Finite set of numbers The median of a finite list of numbers is the "middle" number, when those numbers are liste ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Path Loss
Path loss, or path attenuation, is the reduction in power density (attenuation) of an electromagnetic wave as it propagates through space. Path loss is a major component in the analysis and design of the link budget of a telecommunication system. This term is commonly used in wireless communications and signal propagation. Path loss may be due to many effects, such as free-space loss, refraction, diffraction, reflection, aperture- medium coupling loss, and absorption. Path loss is also influenced by terrain contours, environment (urban or rural, vegetation and foliage), propagation medium (dry or moist air), the distance between the transmitter and the receiver, and the height and location of antennas. Overview In wireless communications, path loss is the reduction in signal strength as the signal travels from a transmitter to a receiver, and is an application for verifying the loss. There are several factors that affect this: *Free-space path loss: This is the fundame ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Telecommunication
Telecommunication, often used in its plural form or abbreviated as telecom, is the transmission of information over a distance using electronic means, typically through cables, radio waves, or other communication technologies. These means of transmission may be divided into communication channels for multiplexing, allowing for a single medium to transmit several concurrent Session (computer science), communication sessions. Long-distance technologies invented during the 20th and 21st centuries generally use electric power, and include the electrical telegraph, telegraph, telephone, television, and radio. Early telecommunication networks used metal wires as the medium for transmitting signals. These networks were used for telegraphy and telephony for many decades. In the first decade of the 20th century, a revolution in wireless communication began with breakthroughs including those made in radio communications by Guglielmo Marconi, who won the 1909 Nobel Prize in Physics. Othe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diffraction
Diffraction is the deviation of waves from straight-line propagation without any change in their energy due to an obstacle or through an aperture. The diffracting object or aperture effectively becomes a secondary source of the Wave propagation, propagating wave. Diffraction is the same physical effect as Wave interference, interference, but interference is typically applied to superposition of a few waves and the term diffraction is used when many waves are superposed. Italian scientist Francesco Maria Grimaldi coined the word ''diffraction'' and was the first to record accurate observations of the phenomenon in 1660 in science, 1660. In classical physics, the diffraction phenomenon is described by the Huygens–Fresnel principle that treats each point in a propagating wavefront as a collection of individual spherical wavelets. The characteristic pattern is most pronounced when a wave from a Coherence (physics), coherent source (such as a laser) encounters a slit/aperture tha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fresnel Zone
A Fresnel zone ( ), named after physicist Augustin-Jean Fresnel, is one of a series of confocal prolate ellipsoidal regions of space between and around a transmitter and a receiver. The size of the calculated Fresnel zone at any particular distance from the transmitter and receiver can help to predict whether obstructions or discontinuities along the path will cause significant interference. The primary wave will travel in a relative straight line from the transmitter to the receiver. Aberrant transmitted radio, sound, or light waves which are transmitted at the same time can follow slightly different paths before reaching a receiver, especially if there are obstructions or deflecting objects between the two. The two waves can arrive at the receiver at slightly different times and the aberrant wave may arrive out of phase with the primary wave due to the different path lengths. Depending on the magnitude of the phase difference between the two waves, the waves can interf ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Normalization (statistics)
In statistics and applications of statistics, normalization can have a range of meanings. In the simplest cases, normalization of ratings means adjusting values measured on different scales to a notionally common scale, often prior to averaging. In more complicated cases, normalization may refer to more sophisticated adjustments where the intention is to bring the entire probability distributions of adjusted values into alignment. In the case of normalization of scores in educational assessment, there may be an intention to align distributions to a normal distribution. A different approach to normalization of probability distributions is quantile normalization, where the quantiles of the different measures are brought into alignment. In another usage in statistics, normalization refers to the creation of shifted and scaled versions of statistics, where the intention is that these normalized values allow the comparison of corresponding normalized values for different datasets in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Line-of-sight Propagation
Line-of-sight propagation is a characteristic of electromagnetic radiation or acoustic wave propagation which means waves can only travel in a direct visual path from the source to the receiver without obstacles. Electromagnetic transmission includes light emissions traveling in a straight line. The rays or waves may be diffracted, refracted, reflected, or absorbed by the atmosphere and obstructions with material and generally cannot travel over the horizon or behind obstacles. In contrast to line-of-sight propagation, at low frequency (below approximately 3 MHz) due to diffraction, radio waves can travel as ground waves, which follow the contour of the Earth. This enables AM radio stations to transmit beyond the horizon. Additionally, frequencies in the shortwave bands between approximately 1 and 30 MHz, can be refracted back to Earth by the ionosphere, called skywave or "skip" propagation, thus giving radio transmissions in this range a potentially global reach ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Friis Transmission Equation
The Friis transmission formula is used in telecommunications engineering, equating the power at the terminals of a receive antenna as the product of power density of the incident wave and the effective aperture of the receiving antenna under idealized conditions given another antenna some distance away transmitting a known amount of power. The formula was presented first by Danish-American radio engineer Harald T. Friis in 1946. The formula is sometimes referenced as the Friis transmission equation. Friis' original formula Friis' original idea behind his transmission formula was to dispense with the usage of directivity or gain when describing antenna performance. In their place is the descriptor of antenna aperture area as one of two important parts of the transmission formula that characterizes the behavior of a free-space radio circuit. This leads to his published form of his transmission formula: :\frac = \left( \frac \right) where: *P_t is the power fed into the tra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Egli Model
The Egli model is a terrain model for radio frequency propagation. This model, which was first introduced by John Egli in his 1957 paper, was derived from real-world data on UHF and VHF television transmissions in several large cities. It predicts the total path loss for a point-to-point link. Typically used for outdoor line-of-sight transmission, this model provides the path loss as a single quantity. Applicable to/under conditions The Egli model is typically suitable for cellular communication scenarios where one antenna is fixed and another is mobile. The model is applicable to scenarios where the transmission has to go over an irregular terrain. However, the model does not take into account travel through some vegetative obstruction, such as trees or shrubbery. Coverage Frequency: The model is typically applied to VHF and UHF spectrum transmissions. Mathematical formulation The Egli model is formally expressed as: P_ R= G_B G_M \left frac\right^2 \leftright2 P_T Whe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radio Propagation Model
Radio propagation is the behavior of radio waves as they travel, or are propagated, from one point to another in vacuum, or into various parts of the atmosphere. As a form of electromagnetic radiation, like light waves, radio waves are affected by the phenomena of reflection, refraction, diffraction, absorption, polarization, and scattering. Understanding the effects of varying conditions on radio propagation has many practical applications, from choosing frequencies for amateur radio communications, international shortwave broadcasters, to designing reliable mobile telephone systems, to radio navigation, to operation of radar systems. Several different types of propagation are used in practical radio transmission systems. '' Line-of-sight propagation'' means radio waves which travel in a straight line from the transmitting antenna to the receiving antenna. Line of sight transmission is used for medium-distance radio transmission, such as cell phones, cordless phones, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |