|
ITU T.61
T.61 is an ITU-T Recommendation for a Teletex character set. T.61 predated Unicode, and was the primary character set in abstract syntax notation one, ASN.1 used in early versions of X.500 and X.509 for encoding strings containing characters used in Western European languages. It is also used by older versions of LDAP. While T.61 continues to be supported in modern versions of X.500 and X.509, it has been deprecated in favor of Unicode. It is also called Code page 1036, CP1036, or IBM 01036. While ASN.1 does see wide use and the T.61 character set is used on some standards using ASN.1 (for example in RSA Security's PKCS #9), the 1988-11 version of the T.61 standard itself was superseded by a never-published 1993-03 version; the 1993-03 version was withdrawn by the ITU-T. The 1988-11 version is still available. T.61 was one of the encodings supported by Mozilla software in email and HTML until 2014, when the supported encodings were limited to those in the WHATWG Encoding Standa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ITU-T
The International Telecommunication Union Telecommunication Standardization Sector (ITU-T) is one of the three Sectors (branches) of the International Telecommunication Union (ITU). It is responsible for coordinating Standardization, standards for telecommunications and Information Communication Technology, such as X.509 for cybersecurity, Y.3172 and Y.3173 for machine learning, and H.264/MPEG-4 AVC for video compression, between its Member States, Private Sector Members, and Academia Members. The World Telecommunication Standardization Assembly (WTSA), the sector's governing conference, convenes every four years. ITU-T has a permanent Secretariat (administrative office), secretariat called the Telecommunication Standardization Bureau (TSB), which is based at the ITU headquarters in Geneva, Switzerland. The current director of the TSB is Seizo Onoe (of Japan), whose 4-year term commenced on 1 January 2023. Seizo Onoe succeeded Chaesub Lee of South Korea, who was director from 1 J ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Teletext Character Set
This article covers technical details of the character encoding system defined by ETS 300 706 of the ETSI, a standard for World System Teletext, and used for the Viewdata and Teletext variants of Videotex in Europe. Character sets The following tables show various Teletext character sets. Each character is shown with a potential Unicode equivalent if available. Space and control characters are represented by the abbreviations for their names. Control characters Control characters are used to set foreground and background color (black, red, green, yellow, blue, magenta, cyan, white, flash), character height (normal, double width, double height, double), current default character set, and other attributes. In formats where compatibility with ECMA-48 ANSI escape sequences are a standard for in-band signaling to control cursor location, color, font styling, and other options on video text terminals and terminal emulators. Certain sequences of bytes, most starting with an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ISO/IEC 10646
ISO/IEC JTC 1, entitled "Information technology", is a joint technical committee (JTC) of the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) and the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC). Its purpose is to develop, maintain and promote standards in the fields of information and communications technology (ICT). JTC 1 has been responsible for many critical IT standards, ranging from the Joint Photographic Experts Group (JPEG) image formats and Moving Picture Experts Group (MPEG) audio and video formats to the C (programming language), C and C++ programming languages. History ISO/IEC JTC 1 was formed in 1987 as a merger between ISO/TC 97 (Information Technology) and IEC/TC 83, with IEC/SC 47B joining later. The intent was to bring together, in a single committee, the IT standardization activities of the two parent organizations in order to avoid duplicative or possibly incompatible standards. At the time of its formation, the mandate of JTC 1 was to develop base st ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ISO/IEC 2022
ISO/IEC 2022 ''Information technology—Character code structure and extension techniques'', is an ISO/ IEC standard in the field of character encoding. It is equivalent to the ECMA standard ECMA-35, the ANSI standard ANSI X3.41 and the Japanese Industrial Standard JIS X 0202. Originating in 1971, it was most recently revised in 1994. ISO 2022 specifies a general structure which character encodings can conform to, dedicating particular ranges of bytes ( 0x00–1F and 0x7F–9F) to be used for non-printing control codes for formatting and in-band instructions (such as line breaks or formatting instructions for text terminals), rather than graphical characters. It also specifies a syntax for escape sequences, multiple-byte sequences beginning with the control code, which can likewise be used for in-band instructions. Specific sets of control codes and escape sequences designed to be used with ISO 2022 include ISO/IEC 6429, portions of which are implemented by ANSI.SYS and t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
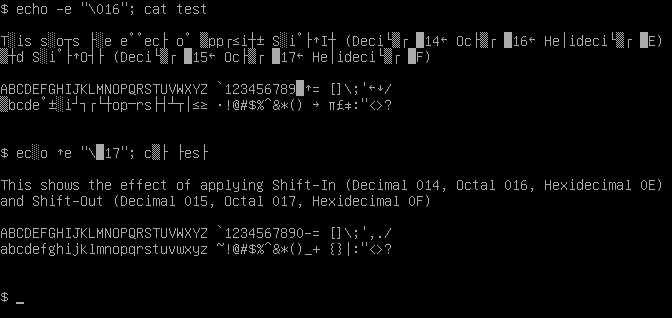
Shift In
Shift Out (SO) and Shift In (SI) are ASCII control characters 14 and 15, respectively (0x0E and 0x0F). These are sometimes also called "Control-N" and "Control-O". The original purpose of these characters was to provide a way to shift a coloured ribbon, split longitudinally usually with red and black, up and down to the other colour in an electro-mechanical typewriter or teleprinter, such as the Teletype Model 38, to automate the same function of manual typewriters. Black was the conventional ambient default colour and so was shifted "in" or "out" with the other colour on the ribbon. Later advancements in technology instigated use of this function for switching to a different font or character set and back. This was used, for instance, in the Russian character set known as KOI7-switched, where SO starts printing Russian letters, and SI starts printing Latin letters again. Similarly, they are used for switching between Katakana and Roman letters in the 7-bit version of the Jap ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carriage Return
A carriage return, sometimes known as a cartridge return and often shortened to CR, or return, is a control character or mechanism used to reset a device's position to the beginning of a line of text. It is closely associated with the line feed and newline concepts, although it can be considered separately in its own right. Typewriters Originally, the term "carriage return" referred to a mechanism or lever on a typewriter. For machines where the type element was fixed and the paper held in a moving ''carriage'', this lever was on the left attached to the moving carriage, and operated after typing a line of text to cause the carriage to return to the far right so the type element would be aligned to the left side of the paper. The lever would also usually ''feed'' the paper to advance to the next line. Many electric typewriters such as IBM Electric or Underwood Electric made carriage return to be another key on the keyboard instead of a lever. The key was usually labeled "car ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Form Feed
A page break is a marker in an electronic document that tells the document interpreter the content which follows is part of a new page. A page break causes a form feed to be sent to the printer during spooling of the document to the printer. It is one of the elements that contributes to pagination. Form feed Form feed is a page-breaking ASCII control character. It directs the printer to eject the current page and to continue printing at the top of another. It will often also cause a carriage return. The form feed character code is defined as 12 (0xC in hexadecimal), and may be represented as or . In a related use, can be pressed to clear the screen in Unix shells such as bash, or redraw the screen in TUI programs like vi/emacs. In the C programming language (and other languages derived from C), the form feed character is represented as '\f'. Unicode also provides the character as a printable symbol for a form feed (not as the form feed itself). The form feed character is con ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Line Feed
A newline (frequently called line ending, end of line (EOL), next line (NEL) or line break) is a control character or sequence of control characters in character encoding specifications such as ASCII, EBCDIC, Unicode, etc. This character, or a sequence of characters, is used to signify the end of a line (text file), line of text and the start of a new one. History In the mid-1800s, long before the advent of teleprinters and teletype machines, Morse code operators or telegraphists invented and used Prosigns for Morse code, Morse code prosigns to encode white space text formatting in formal written text messages. In particular, the International Morse code, Morse prosign (mnemonic break text), represented by the concatenation of literal textual Morse codes "B" and "T" characters, sent without the normal inter-character spacing, is used in Morse code to encode and indicate a ''new line'' or ''new section'' in a formal text message. Later, in the age of modern teleprinters, st ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Backspace
Backspace (, ⌫) is the keyboard key that in typewriters originally pushed the carriage one position backwards, and in modern computer systems typically moves the display cursor one position backwards,The meaning of "backwards" depends on the direction of the text, and could get complicated in text involving several Bidirectional text, bidirectional categories. deletes the character at that position, and shifts back any text after"after" here implies on the same logical line of text that position by one character. Nomenclature Although the term "backspace" is the traditional name of the key which steps the carriage back and/orin some correcting typewriters it did both deletes the previous character, typically to the left of the cursor, the actual key may be labeled in a variety of ways, for example ''delete'', ''erase'', or with a left pointing arrow. A dedicated symbol for "backspace" exists as Miscellaneous Technical#Block, U+232B ⌫ but its use as a keyboard label is not univ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Videotex Character Set
The character sets used by Videotex are based, to greater or lesser extents, on ISO/IEC 2022. Three Data Syntax systems are defined by ITU T.101, corresponding to the Videotex systems of different countries. Data Syntax 1 Data Syntax 1 is defined in Annex B of T.101:1994. It is based on the CAPTAIN system used in Japan. Its graphical sets include JIS X 0201 and JIS X 0208. The following G-sets are available through ISO/IEC 2022-based designation escapes: Mosaic sets for Data Syntax 1 The mosaic sets supply characters for use in semigraphics. � Not in Unicode Data Syntax 2 Data Syntax 2 is defined in Annex C of T.101:1994. It corresponds to some European Videotex systems such as CEPT T/CD 06-01. The graphical character coding of Data Syntax 2 is based on T.51. The default G2 set of Data Syntax 2 is based on an older version of T.51, lacking the non-breaking space, soft hyphen, not sign ( ¬) and broken bar ( ¦) present in the current version, but adding a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
PostScript Standard Encoding
The PostScript Standard Encoding (often spelled StandardEncoding, aliased as PostScript) is one of the character sets (or encoding vectors) used by Adobe Systems' PostScript (PS) since 1984. In 1995, IBM assigned code page 1276 (CCSID 1276) to this character set. NeXT based the character set for its NeXTSTEP and OPENSTEP operating systems on this one. Character set The following table shows the PostScript Standard Encoding. Each character is shown with a potential Unicode equivalent. Codepoints 00hex (0) to 7Fhex (127) are nearly identical to ASCII. (The characters at positions 27hex and 60hex reflect an earlier interpretation of the visual appearance of those ASCII characters than the interpretation that was formalized in Unicode; see .) The upper half of the table contains punctuation and typographic characters, currency symbols, ligatured letters, a selection of modified base letters used in European languages, and a selection of diacritic marks to be used in composing accented ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |