|
ICMP
The Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP) is a supporting protocol in the Internet protocol suite. It is used by network devices, including routers, to send error messages and operational information indicating success or failure when communicating with another IP address. For example, an error is indicated when a requested service is not available or that a host or router could not be reached. ICMP differs from transport protocols such as TCP and UDP in that it is not typically used to exchange data between systems, nor is it regularly employed by end-user network applications (with the exception of some diagnostic tools like ping and traceroute). A separate Internet Control Message Protocol (called ICMPv6) is used with IPv6. Technical details ICMP is part of the Internet protocol suite as defined in RFC 792. ICMP messages are typically used for diagnostic or control purposes or generated in response to errors in IP operations (as specified in RFC 1122). ICMP err ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ICMPv6
Internet Control Message Protocol version 6 (ICMPv6) is the implementation of the Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP) for Internet Protocol version 6 (IPv6). ICMPv6 is an integral part of IPv6 and performs error reporting and diagnostic functions. ICMPv6 has a framework for extensions to implement new features. Several extensions have been published, defining new ICMPv6 message types as well as new options for existing ICMPv6 message types. For example, Neighbor Discovery Protocol (NDP) is a node discovery protocol based on ICMPv6 which replaces and enhances functions of ARP. Secure Neighbor Discovery (SEND) is an extension of NDP with extra security. Multicast Listener Discovery (MLD) is used by IPv6 routers for discovering multicast listeners on a directly attached link, much like Internet Group Management Protocol (IGMP) is used in IPv4. Multicast Router Discovery (MRD) allows the discovery of multicast routers. Message types and formats ICMPv6 messages may be cla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
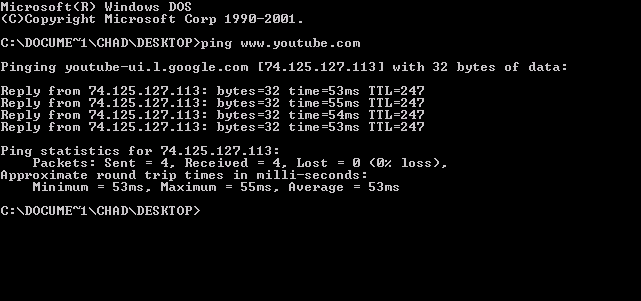
Ping (networking Utility)
ping is a computer network administration software utility used to test the reachability of a host (network), host on an Internet Protocol (IP) network. It is available in a wide range of operating systems including most embedded network administration software. Ping measures the round-trip time for messages sent from the originating host to a destination computer that are echoed back to the source. The name comes from active sonar terminology that sends a Pulse (signal processing), pulse of sound and listens for the echo to detect objects under water. Ping operates by means of Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP) Network packet, packets. ''Pinging'' involves sending an ICMP echo request to the target host and waiting for an ICMP echo reply. The program reports errors, packet loss, and a statistical summary of the results, typically including the minimum, maximum, the mean (average), mean round-trip times, and standard deviation of the mean. Command-line options and Comp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ICMP Tunnel
An ICMP tunnel establishes a covert connection between two remote computers (a client and proxy), using ICMP echo requests and reply packets. An example of this technique is tunneling complete TCP traffic over ping requests and replies. Technical details ICMP tunneling works by injecting arbitrary data into an echo packet sent to a remote computer. The remote computer replies in the same manner, injecting an answer into another ICMP packet and sending it back. The client performs all communication using ICMP echo request packets, while the proxy uses echo reply packets. In theory, it is possible to have the proxy use echo request packets (which makes implementation much easier), but these packets are not necessarily forwarded to the client, as the client could be behind a translated address ( NAT). This bidirectional data flow can be abstracted with an ordinary serial line. ICMP tunneling is possible becausRFC 792 which defines the structure of ICMP packets, allows for an ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Traceroute
In computing, traceroute and tracert are diagnostic command-line interface commands for displaying possible routes (paths) and transit delays of packets across an Internet Protocol (IP) network. The command reports the round-trip times of the packets received from each successive host (remote node) along the route to a destination. The sum of the mean times in each hop is a measure of the total time spent to establish the connection. The command aborts if all (usually three) sent packets are lost more than twice. Ping, however, only computes the final round-trip times from the destination point. For Internet Protocol Version 6 (IPv6), the tool sometimes has the name traceroute6 and tracert6. Implementations A command is available in many modern operating systems, generally named traceroute in Unix-like systems such as FreeBSD, macOS, and Linux and named tracert in Windows and ReactOS. The functionality was available graphically in macOS, but has been deprecated sinc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Denial-of-service Attacks
In computing, a denial-of-service attack (DoS attack) is a cyberattack in which the perpetrator seeks to make a machine or network resource unavailable to its intended users by temporarily or indefinitely disrupting services of a host connected to a network. Denial of service is typically accomplished by flooding the targeted machine or resource with superfluous requests in an attempt to overload systems and prevent some or all legitimate requests from being fulfilled. The range of attacks varies widely, spanning from inundating a server with millions of requests to slow its performance, overwhelming a server with a substantial amount of invalid data, to submitting requests with an illegitimate IP address. In a distributed denial-of-service attack (DDoS attack), the incoming traffic flooding the victim originates from many different sources. More sophisticated strategies are required to mitigate this type of attack; simply attempting to block a single source is insuffic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ping Of Death
A ping of death is a type of attack on a computer system that involves sending a malformed or otherwise malicious ping to a computer. In this attack, a host sends hundreds of ping requests with a packet size that is large or illegal to another host to try to take it offline or to keep it preoccupied responding with ICMP Echo replies. A correctly formed ping packet is typically 56 bytes in size, or 64 bytes when the Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP) header is considered, and 84 bytes including Internet Protocol (IP) version 4 header. However, any IPv4 packet (including pings) may be as large as 65,535 bytes. Some computer systems were never designed to properly handle a ping packet larger than the maximum packet size because it violates the Internet Protocol. Like other large but well-formed packets, a ping of death is fragmented into groups of 8 octets before transmission. However, when the target computer reassembles the malformed packet, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Internet Protocol Suite
The Internet protocol suite, commonly known as TCP/IP, is a framework for organizing the communication protocols used in the Internet and similar computer networks according to functional criteria. The foundational protocols in the suite are the Transmission Control Protocol (TCP), the User Datagram Protocol (UDP), and the Internet Protocol (IP). Early versions of this networking model were known as the Department of Defense (DoD) model because the research and development were funded by the United States Department of Defense through DARPA. The Internet protocol suite provides end-to-end data communication specifying how data should be packetized, addressed, transmitted, routed, and received. This functionality is organized into four abstraction layers, which classify all related protocols according to each protocol's scope of networking. An implementation of the layers for a particular application forms a protocol stack. From lowest to highest, the layers are the l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of IP Protocol Numbers
This is a list of the IP protocol numbers found in the 8-bit ''Protocol'' field of the IPv4 header and the 8-bit ''Next Header'' field of the IPv6 header. It is an identifier for the encapsulated protocol and determines the layout of the data that immediately follows the header. Because both fields are eight bits wide, the possible values are limited to the 256 values from 0 (0x00) to 255 (0xFF), of which just over half had been allocated Protocol numbers are maintained and published by the Internet Assigned Numbers Authority (IANA). {, class="wikitable" , - ! class="nomobile" , Hex ! Protocol Number !! Keyword !! Protocol !! References/ RFC , - , style="text-align:right" class="nomobile" , 0x00 , style="text-align:right" , 0 , HOPOPT , IPv6 Hop-by-Hop Option , , - , style="text-align:right" class="nomobile" , 0x01 , style="text-align:right" , 1 , ICMP , Internet Control Message Protocol , , - , style="text-align:right" class="nomobile" , 0x02 , style="te ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
IPv4 Header
Internet Protocol version 4 (IPv4) is the first version of the Internet Protocol (IP) as a standalone specification. It is one of the core protocols of standards-based internetworking methods in the Internet and other packet-switched networks. IPv4 was the first version deployed for production on SATNET in 1982 and on the ARPANET in January 1983. It is still used to route most Internet traffic today, even with the ongoing deployment of Internet Protocol version 6 (IPv6), its successor. IPv4 uses a 32-bit address space which provides 4,294,967,296 (232) unique addresses, but large blocks are reserved for special networking purposes. Purpose The Internet Protocol ("IP") is the protocol that defines and enables internetworking at the internet layer of the Internet Protocol Suite. It gives the Internet a global-scale logical addressing system which allows the routing of IP data packets from a source host to the next router that is one hop closer to the intended destination h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
IPv6
Internet Protocol version 6 (IPv6) is the most recent version of the Internet Protocol (IP), the communication protocol, communications protocol that provides an identification and location system for computers on networks and routes traffic across the Internet. IPv6 was developed by the Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF) to deal with the long-anticipated problem of IPv4 address exhaustion, and was intended to replace IPv4. In December 1998, IPv6 became a Draft Standard for the IETF, which subsequently ratified it as an Internet Standard on 14 July 2017. Devices on the Internet are assigned a unique IP address for identification and location definition. With the rapid growth of the Internet after commercialization in the 1990s, it became evident that far more addresses would be needed to connect devices than the 4,294,967,296 (232) IPv4 address space had available. By 1998, the IETF had formalized the successor protocol, IPv6 which uses 128-bit addresses, theoretically all ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Time To Live
Time to live (TTL) or hop limit is a mechanism which limits the lifespan or lifetime of data in a computer or network. TTL may be implemented as a counter (digital), counter or timestamp attached to or embedded in the data. Once the prescribed event count or timespan has elapsed, data is discarded or revalidated. In computer networking, TTL prevents a data packet from circulating indefinitely. In computing applications, TTL is commonly used to improve the performance and manage the cache (computing), caching of data. Description The original DARPA Internet Protocol's Request for Comment, RFC describes TTL as: IP packets Under the Internet Protocol, TTL is an 8-bit field. In the IPv4 header, TTL is the 9th octet (computing), octet of 20. In the IPv6 header, it is the 8th octet of 40. The maximum TTL value is 255, the maximum value of a single octet. A recommended initial value is 64. The time-to-live value can be thought of as an upper bound on the time that an IP datagram c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Internet Protocol
The Internet Protocol (IP) is the network layer communications protocol in the Internet protocol suite for relaying datagrams across network boundaries. Its routing function enables internetworking, and essentially establishes the Internet. IP has the task of delivering Packet (information technology), packets from the source Host (network), host to the destination host solely based on the IP addresses in the packet Header (computing), headers. For this purpose, IP defines packet structures that encapsulation (networking), encapsulate the data to be delivered. It also defines addressing methods that are used to label the datagram with source and destination information. IP was the connectionless datagram service in the original ''Transmission Control Program'' introduced by Vint Cerf and Bob Kahn in 1974, which was complemented by a connection-oriented service that became the basis for the Transmission Control Protocol (TCP). The Internet protocol suite is therefore often referre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |