|
IBM Rational Unified Process
The rational unified process (RUP) is an Iterative and incremental development, iterative software development process framework created by the Rational Software Corporation, a division of IBM since 2003. RUP is not a single concrete prescriptive process, but rather an adaptable process Software framework, framework, intended to be tailored by the development organizations and software project teams that will select the elements of the process that are appropriate for their needs. RUP is a specific implementation of the Unified Process. History Rational Software originally developed the rational unified process as a software process product. The product includes a hyperlinked knowledge-base with sample Artifact (software development), artifacts and detailed descriptions for many different types of activities. RUP is included in the IBM Rational Method Composer (RMC) product which allows customization of the process. Philippe Kruchten, an experienced Rational technical representa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iterative And Incremental Development
Iterative and incremental development is any combination of both iterative design (or iterative method) and incremental build model for New product development, development. Usage of the term began in software development, with a long-standing combination of the two terms ''iterative'' and ''incremental'' having been widely suggested for large development efforts. For example, the 1985 DOD-STD-2167 mentions (in section 4.1.2): "During software development, more than one iteration of the software development cycle may be in progress at the same time." and "This process may be described as an 'evolutionary acquisition' or 'incremental build' approach." In software, the relationship between iterations and increments is determined by the overall software development process. Overview The basic idea behind this method is to develop a system through repeated cycles (iterative) and in smaller portions at a time (incremental), allowing software developers to take advantage of what was l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Agile Software Development
Agile software development is an umbrella term for approaches to software development, developing software that reflect the values and principles agreed upon by ''The Agile Alliance'', a group of 17 software practitioners, in 2001. As documented in their ''Manifesto for Agile Software Development'' the practitioners value: * Individuals and interactions over processes and tools * Working software over comprehensive documentation * Customer collaboration over contract negotiation * Responding to change over following a plan The practitioners cite inspiration from new practices at the time including extreme programming, Scrum (software development), scrum, dynamic systems development method, adaptive software development and being sympathetic to the need for an alternative to documentation driven, heavyweight software development processes. Many software development practices emerged from the agile mindset. These agile-based practices, sometimes called ''Agile'' (with a capital ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Macroscope (methodology Suite)
Macroscope is an integrated set of methods aimed at enterprise IT activities. Macroscope was developed and is maintained by Fujitsu in Canada. It is primarily used as their core body of knowledge to support the consulting services that they provide to their clients and is also licensed as a commercial product to a number of their clients History 1984-1985: "DMR" Information System Development Guides The first publication of methods that are at the source of Macroscope were two "Information System Development Guides": Part 1 Managing the Project and Part 2 Developing the System. The same books were published in French in 1984. These two methods were known as the "DMR" methods and were later attributed version number 1.0. The two methods were based on fundamentals or principles that established the general approach. The methods were described in terms of processes, techniques and deliverables. The main approach for system design was by integrating the French Merise data an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
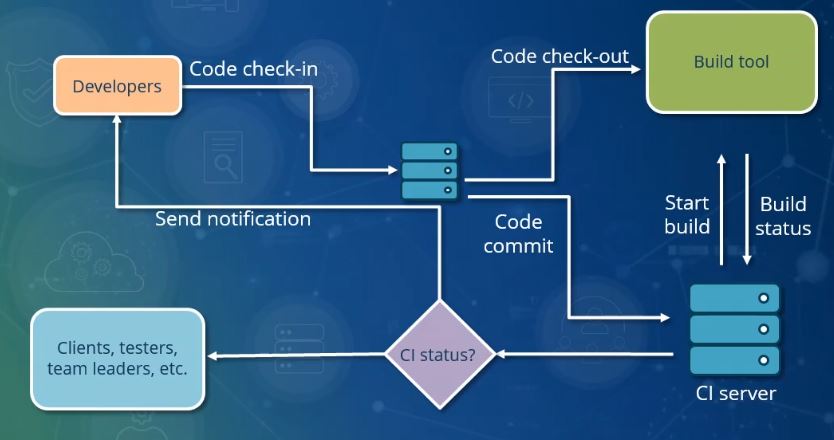
Continuous Integration
Continuous integration (CI) is the practice of integrating source code changes frequently and ensuring that the integrated codebase is in a workable state. Typically, developers Merge (version control), merge changes to an Branching (revision control), integration branch, and an automated system Software build, builds and software testing, tests the software system. Often, the automated process runs on each Commit (version control), commit or runs on a schedule such as once a day. Grady Booch first proposed the term CI in Booch method, 1991, although he did not advocate integrating multiple times a day, but later, CI came to include that aspect. History The earliest known work (1989) on continuous integration was the Infuse environment developed by G. E. Kaiser, D. E. Perry, and W. M. Schell. In 1994, Grady Booch used the phrase continuous integration in ''Object-Oriented Analysis and Design with Applications'' (2nd edition) to explain how, when developing using micro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Object-oriented Programming
Object-oriented programming (OOP) is a programming paradigm based on the concept of '' objects''. Objects can contain data (called fields, attributes or properties) and have actions they can perform (called procedures or methods and implemented in code). In OOP, computer programs are designed by making them out of objects that interact with one another. Many of the most widely used programming languages (such as C++, Java, and Python) support object-oriented programming to a greater or lesser degree, typically as part of multiple paradigms in combination with others such as imperative programming and declarative programming. Significant object-oriented languages include Ada, ActionScript, C++, Common Lisp, C#, Dart, Eiffel, Fortran 2003, Haxe, Java, JavaScript, Kotlin, Logo, MATLAB, Objective-C, Object Pascal, Perl, PHP, Python, R, Raku, Ruby, Scala, SIMSCRIPT, Simula, Smalltalk, Swift, Vala and Visual Basic.NET. History The idea of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Software Engineering
Software engineering is a branch of both computer science and engineering focused on designing, developing, testing, and maintaining Application software, software applications. It involves applying engineering design process, engineering principles and computer programming expertise to develop software systems that meet user needs. The terms ''programmer'' and ''coder'' overlap ''software engineer'', but they imply only the construction aspect of a typical software engineer workload. A software engineer applies a software development process, which involves defining, Implementation, implementing, Software testing, testing, Project management, managing, and Software maintenance, maintaining software systems, as well as developing the software development process itself. History Beginning in the 1960s, software engineering was recognized as a separate field of engineering. The development of software engineering was seen as a struggle. Problems included software that was over ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eclipse Process Framework
The Eclipse process framework (EPF) is an Open-source software, open source project that is managed by the Eclipse Foundation. It lies under the top-level Eclipse Technology Project, and has two goals: *To provide an extensible framework and exemplary tools for software process engineering - method and process authoring, library management, configuring and publishing a process. *To provide exemplary and extensible process content for a range of software development and management processes supporting iterative, agile, and Iterative and incremental development, incremental development, and applicable to a broad set of development platforms and applications. For instance, EPF provides the OpenUP, an agile software development process optimized for small projects. By using EPF Composer, engineers can create their own software development process by structuring it using a predefined schema. This schema is an evolution of the SPEM [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stakeholder (corporate)
In a corporation, a stakeholder is a member of "groups without whose support the organization would cease to exist", as defined in the first usage of the word in a 1963 internal memorandum at the Stanford Research Institute. The theory was later developed and championed by R. Edward Freeman in the 1980s. Since then it has gained wide acceptance in business practice and in theorizing relating to strategic management, corporate governance, business purpose and corporate social responsibility (CSR). The definition of corporate responsibilities through a classification of stakeholders to consider has been criticized as creating a false dichotomy between the "shareholder model" and the "stakeholder model", or a false analogy of the obligations towards shareholders and other interested parties. Types Any action taken by any organization or any group might affect those people who are linked with them in the private sector. For examples these are parents, children, customers, owners ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
RUP Hump
A RUP ‘hump’ is a plot of effort spent over time during a particular Rational Unified Process (RUP) discipline. The RUP hump chart consists of a collection of humps for all RUP disciplines. This diagram was created in 1993 during a workshop on architecture and process P. Kruchten. A brief history of the RUP’s “hump chart”. Technical report, University of British Columbia, 2003. and was inspired by work by Grady Booch and Boehm. It has been part of the Rational Objectory Process Rationality is the quality of being guided by or based on reason. In this regard, a person acts rationally if they have a good reason for what they do, or a belief is rational if it is based on strong evidence. This quality can apply to an abi ... after reviews by Dyrhage and Bylund and moved on to play a more important role in the RUP in 1998 when it served as the initial page for using the digital version of the process. Its final form was published by Philippe Kruchten in 1998. An older ve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Environment Discipline
In the Unified Process, " e Environment discipline refers to the tools and customization of the process for the project A project is a type of assignment, typically involving research or design, that is carefully planned to achieve a specific objective. An alternative view sees a project managerially as a sequence of events: a "set of interrelated tasks to be ... - that is, setting up the tool and process environment". References :* :* Object-oriented programming {{Software-eng-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |