|
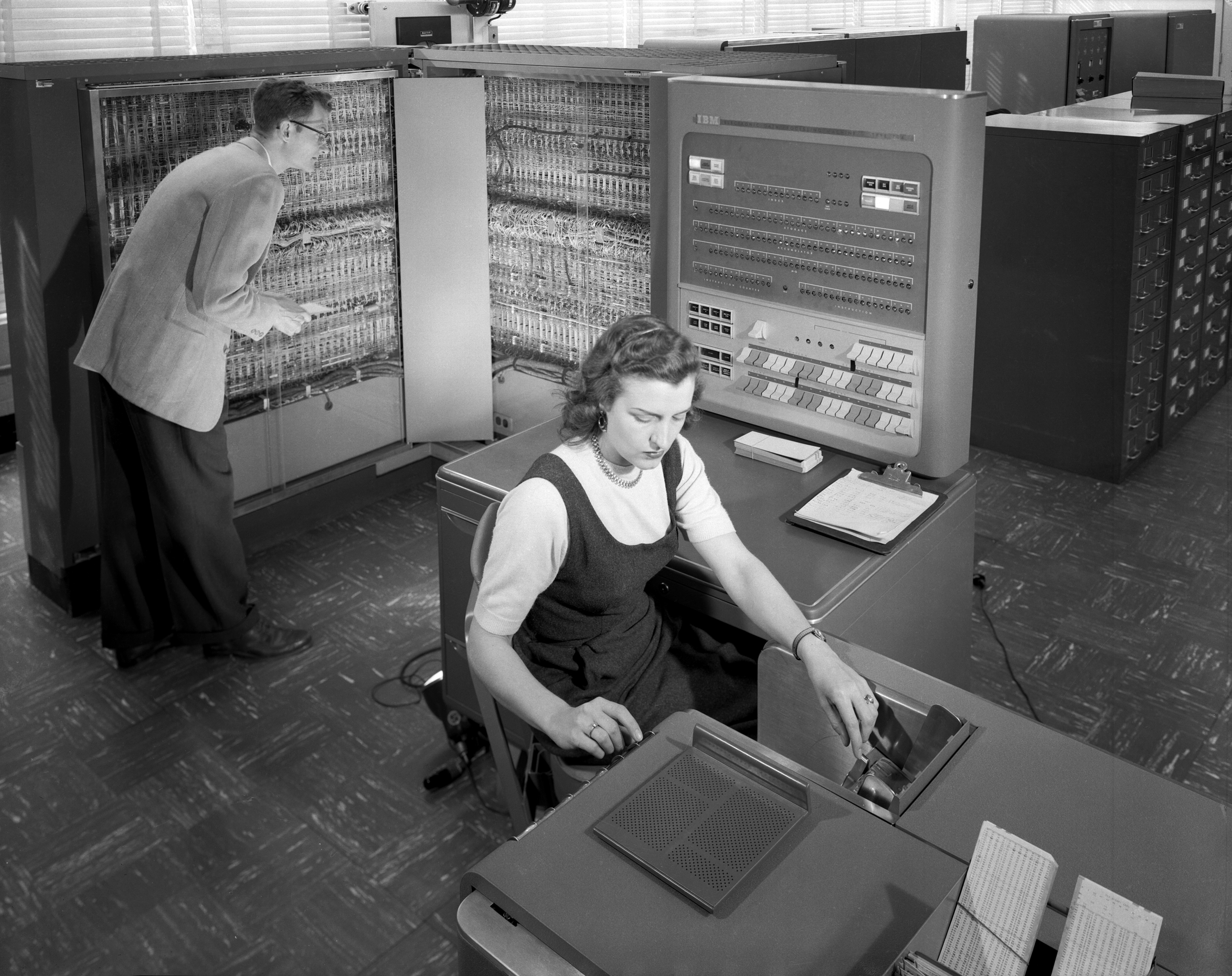
IBM 7060
IBM S/390 Multiprise was a short-lived series of small, compact, entry-level mainframes. Multiprise 2000 The first model of the Multiprise series, the Multiprise 2000, was released in 1996 as a compact and affordable version of S/390 G3 mainframe. Multiprise 3000 The IBM's Multiprise 3000 (product number 7060) was a compact mainframe measuring just 82 x 52 x 111 cm introduced in 1999. There were three models available (7060-H30, -H50, -H70), that differed in the capacity and throughput and, thus, in software license costs. Both H30/H50 had one main processor with 1GB/2GB of memory while the H70 model had two main processors with 4GB of memory. All models also had one System Assistance Processor (SAP). The main processors were the same CMOS chips used in the G5 series of IBM 9672, the flagship S/390 systems. The Multiprise 3000 had ESCON channels and a limited number of network adapters for external I/O. It had a similar use case to that of the S/390 Integrated Server, w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
IBM Mainframe
IBM mainframes are large computer systems produced by IBM since 1952. During the 1960s and 1970s, IBM dominated the computer market with the 7000 series and the later System/360, followed by the System/370. Current mainframe computers in IBM's line of business computers are developments of the basic design of the System/360. First and second generation From 1952 into the late 1960s, IBM manufactured and marketed several large computer models, known as the IBM 700/7000 series. The first-generation 700s were based on vacuum tubes, while the later, second-generation 7000s used transistors. These machines established IBM's dominance in electronic data processing ("EDP"). IBM had two model categories: one (701, 704, 709, 7030, 7090, 7094, 7040, 7044) for engineering and scientific use, and one (702, 705, 705-II, 705-III, 7080, 7070, 7072, 7074, 7010) for commercial or data processing use. The two categories, scientific and commercial, generally used common peripherals but had co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
VM/CMS
VM (often: VM/CMS) is a family of IBM virtual machine operating systems used on IBM mainframes System/370, System/390, zSeries, System z and compatible systems, including the Hercules emulator for personal computers. Design The heart of the VM architecture is the ''Control Program'' or hypervisor abbreviated CP, VM-CP and sometimes, ambiguously, VM. It runs on the physical hardware, and creates the virtual machine environment. VM-CP provides full virtualization of the physical machine – including all I/O and other privileged operations. It performs the system's resource-sharing, including device management, dispatching, virtual storage management, and other traditional operating system tasks. Each VM user is provided with a separate virtual machine having its own address space, virtual devices, etc., and which is capable of running any software that could be run on a stand-alone machine. A given VM mainframe typically runs hundreds or thousands of virtual machine inst ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of IBM Products
The list of IBM products is a partial list of products, services, and subsidiaries of IBM, International Business Machines (IBM) Corporation and its predecessor corporations, beginning in the 1890s. Context Products, services, and subsidiaries have been offered from IBM, International Business Machines (IBM) Corporation and its predecessor corporations since the 1890s. This list comprises those offerings and is wikt:eclectic, eclectic; it includes, for example, the ''AN/FSQ-7 Combat Direction Central, AN/FSQ-7'', which was not a product in the sense of ''offered for sale'', but was a product in the sense of ''manufactured—produced by the labor of IBM''. Several machines manufactured for the Astronomical Computing Bureau at Columbia University are included, as are some machines built only as demonstrations of IBM technology. Missing are many Request price quotation, RPQs, Original equipment manufacturer, OEM products (semiconductors, for example), and supplies (punched cards, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Information Management System
The IBM Information Management System (IMS) is a joint hierarchical database and information management system that supports transaction processing. Development began in 1966 to keep track of the bill of materials for the Saturn V rocket of the Apollo program, and the first version on the IBM System/360 Model 65 was completed in 1967 as ICS/DL/I and officially installed in August 1968. IBM rebranded it IMS/360 in 1969, and ported it to new platforms as they emerged. In 1988, the company claimed that there were 7,000 IMS sites active worldwide. and went on to see extensive use and continual improvement to this day. IMS's most successful year in terms of sales was in 2003, 35 years after it was released. It was in use by over 95% of the Fortune 1000. History DATE and DL/1 IMS ultimately traces its history to a 1963 contract from NASA to help control the continual list of changes being made to the Apollo command and service module at the North American Rockwell (NAR) plants i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Z/VM
z/VM is the current version in IBM's VM family of virtual machine operating systems. First released in October 2000, z/VM remains in active use and development . It is directly based on technology and concepts dating back to the 1960s, particularly IBM's CP/CMS on the IBM System/360-67 (see article History of CP/CMS for historical details). z/VM runs on IBM's IBM Z family of computers and can support large numbers (thousands) of Linux virtual machines. (See Linux on IBM Z.) On 16 September 2022, IBM released z/VM Version 7.3 which requires z/Architecture, implemented in IBM's EC12, BC12 and later models. See also * OpenSolaris for System z * PR/SM * Time-sharing system evolution * z/OS * z/TPF * z/VSE References Citations ; Primary CP/CMS sources: * R. J. Creasy,The origin of the VM/370 time-sharing system, ''IBM Journal of Research & Development'', Vol. 25, No. 5 (September 1981), ''pp.'' 483–90, PDF― perspective on CP/CMS and VM history by the CP-40 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Z/TPF
Transaction Processing Facility (TPF) is an IBM real-time operating system for mainframe computers descended from the IBM System/360 family, including zSeries and System z9. TPF delivers fast, high-volume, high-throughput transaction processing, handling large, continuous loads of essentially simple transactions across large, geographically dispersed networks. While there are other industrial-strength transaction processing systems, notably IBM's own CICS and IMS, TPF's specialty is extreme volume, large numbers of concurrent users, and very fast response times. For example, it handles VISA credit card transaction processing during the peak holiday shopping season. The TPF passenger reservation application PARS, or its international version IPARS, is used by many airlines. ''PARS'' is an ''application program''; TPF is an operating system. One of TPF's major optional components is a high performance, specialized database facility called ''TPF Database Facility'' (TPFDF). A clo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
IBM Z
IBM Z is a family name used by IBM for all of its z/Architecture mainframe computers. In July 2017, with another generation of products, the official family was changed to IBM Z from IBM z Systems; the IBM Z family will soon include the newest model, the IBM z17, as well as the z16, z15, z14, and z13 (released under the IBM z Systems/IBM System z names), the IBM zEnterprise models (in common use the zEC12 and z196), the IBM System z10 models (in common use the z10 EC), the IBM System z9 models (in common use the z9EC) and ''IBM eServer zSeries'' models (in common use refers only to the z900 and z990 generations of mainframe). Architecture The ''zSeries,'' ''zEnterprise,'' ''System z'' and ''IBM Z'' families were named for their availability – ''z'' stands for zero downtime. The systems are built with spare components capable of hot failovers to ensure continuous operations. The IBM Z family maintains full backward compatibility. In effect, current systems are the direc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
System Z9
IBM System z9 is a line of IBM mainframe computers. The first models were available on September 16, 2005. The System z9 also marks the end of the previously used eServer zSeries naming convention. It was also the last mainframe computer that NASA ever used. Background System z9 is a mainframe using the z/Architecture, previously known as ESAME. z/Architecture is a 64-bit architecture which replaces the previous 31-bit-addressing/32-bit-data ESA/390 architecture while remaining completely compatible with it as well as the older 24-bit-addressing/32-bit-data System/360 architecture. The primary advantage of this arrangement is that memory intensive applications like DB2 are no longer bounded by 31-bit memory restrictions while older applications can run without modifications. Name change With the announcement of the System z9 Business Class server, IBM has renamed the System z9 109 as the System z9 Enterprise Class server. IBM documentation abbreviates them as the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
64-bit Computing
In computer architecture, 64-bit integers, memory addresses, or other data units are those that are 64 bits wide. Also, 64-bit central processing units (CPU) and arithmetic logic units (ALU) are those that are based on processor registers, address buses, or data buses of that size. A computer that uses such a processor is a 64-bit computer. From the software perspective, 64-bit computing means the use of machine code with 64-bit virtual memory addresses. However, not all 64-bit instruction sets support full 64-bit virtual memory addresses; x86-64 and AArch64, for example, support only 48 bits of virtual address, with the remaining 16 bits of the virtual address required to be all zeros (000...) or all ones (111...), and several 64-bit instruction sets support fewer than 64 bits of physical memory address. The term ''64-bit'' also describes a generation of computers in which 64-bit processors are the norm. 64 bits is a Word (computer architecture), word size that defines ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Z/Architecture
z/Architecture, initially and briefly called ESA Modal Extensions (ESAME), is IBM's 64-bit complex instruction set computer (CISC) instruction set architecture, implemented by its mainframe computers. IBM introduced its first z/Architecture-based system, the z900, in late 2000. Subsequent z/Architecture systems include the IBM z800, z990, z890, System z9, System z10, zEnterprise 196, zEnterprise 114, zEC12, zBC12, z13, z14, z15, z16, and z17. z/Architecture retains backward compatibility with previous 32-bit-data/31-bit-addressing architecture ESA/390 and its predecessors back to the 32-bit-data/24-bit-addressing System/360. The IBM z13 is the last z Systems server to support running an operating system in ESA/390 architecture mode. However, all 24-bit and 31-bit problem-state application programs originally written to run on the ESA/390 architecture will be unaffected by this change. Features z/Architecture includes almost all of the features of ESA/390, and a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Linux On IBM Z
Linux ( ) is a family of open source Unix-like operating systems based on the Linux kernel, an kernel (operating system), operating system kernel first released on September 17, 1991, by Linus Torvalds. Linux is typically package manager, packaged as a Linux distribution (distro), which includes the kernel and supporting system software and library (computing), libraries—most of which are provided by third parties—to create a complete operating system, designed as a clone of Unix and released under the copyleft GPL license. List of Linux distributions, Thousands of Linux distributions exist, many based directly or indirectly on other distributions; popular Linux distributions include Debian, Fedora Linux, Linux Mint, Arch Linux, and Ubuntu, while commercial distributions include Red Hat Enterprise Linux, SUSE Linux Enterprise, and ChromeOS. Linux distributions are frequently used in server platforms. Many Linux distributions use the word "Linux" in their name, but the Free ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |