|
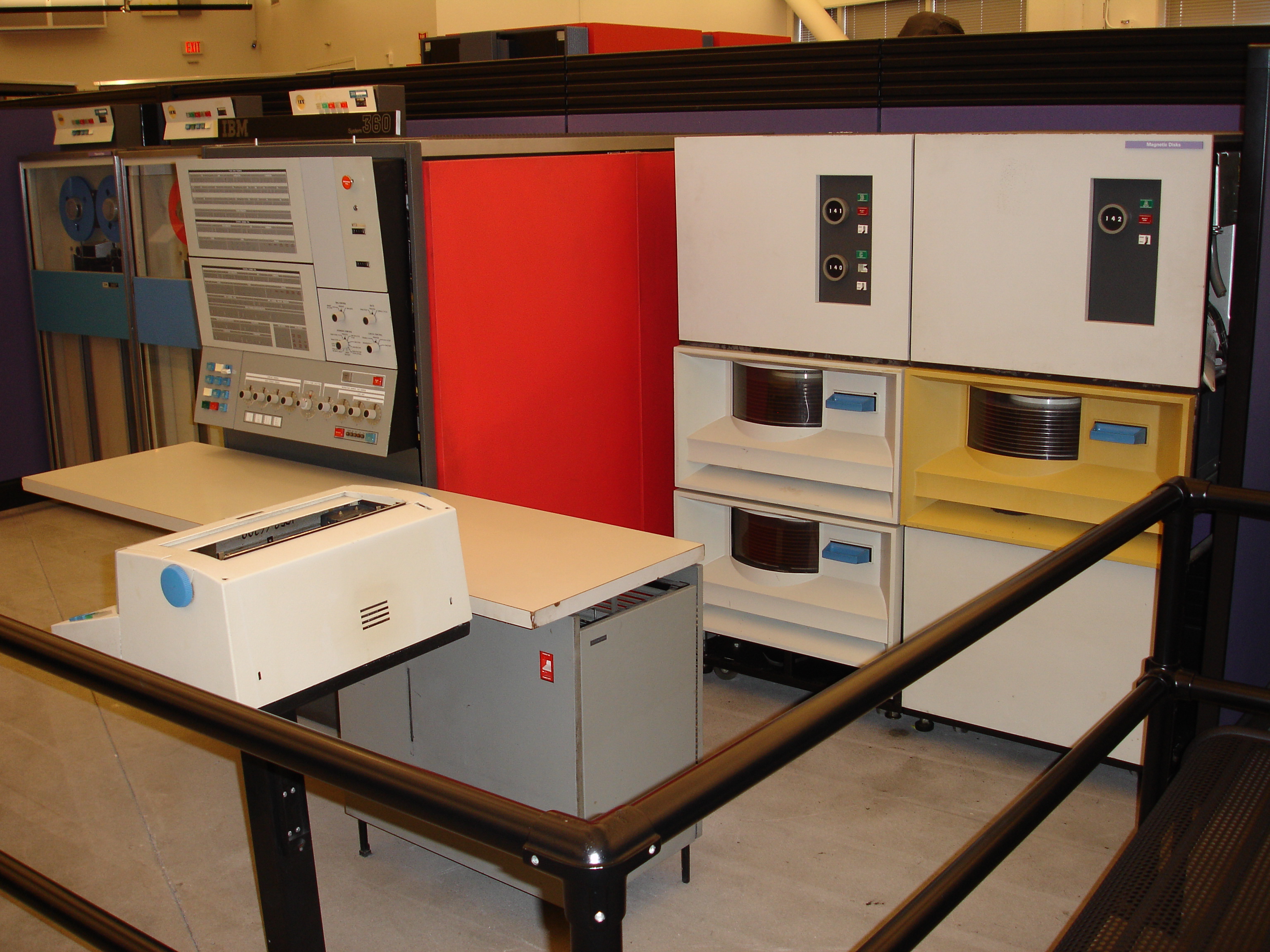
IBM 3081
The IBM 308X is a line of mainframe computers, of which the first model, the Model 3081 Processor Complex, was introduced November 12, 1980.IBM used a capital X when referring to 308X, as did others needing an official reference; see the Congressional Record reference. It consisted of a 3081 Processor Unit with supporting units. Later models in the series were the 3083 and the 3084. The 3083 was announced March 31 and the 3084 on September 3, both in 1982. The IBM 308X line introduced the System/370 Extended Architecture (S/370-XA) required by the new MVS/SP V2 and the Start Interpretive Execution (SIE) instruction used by the new Virtual Machine/eXtended Architecture Migration Aid (VM/XA MA). All three 308X systems, which IBM had marketed as "System/370-Compatibles," were withdrawn August 4, 1987. IBM 3081 The initial 3081 offered, the 3081D, was a 5 MIPS machine. The next offering, the 3081K, was a 7 MIPS machine. Last came the 3081G, again a 5 MIPS machine. The 3081D was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mainframe Computer
A mainframe computer, informally called a mainframe or big iron, is a computer used primarily by large organizations for critical applications like bulk data processing for tasks such as censuses, industry and consumer statistics, enterprise resource planning, and large-scale transaction processing. A mainframe computer is large but not as large as a supercomputer and has more processing power than some other classes of computers, such as minicomputers, server (computing), servers, workstations, and personal computers. Most large-scale computer-system architectures were established in the 1960s, but they continue to evolve. Mainframe computers are often used as servers. The term ''mainframe'' was derived from the large cabinet, called a ''main frame'', that housed the central processing unit and main computer memory, memory of early computers. Later, the term ''mainframe'' was used to distinguish high-end commercial computers from less powerful machines. Design Modern mainfr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
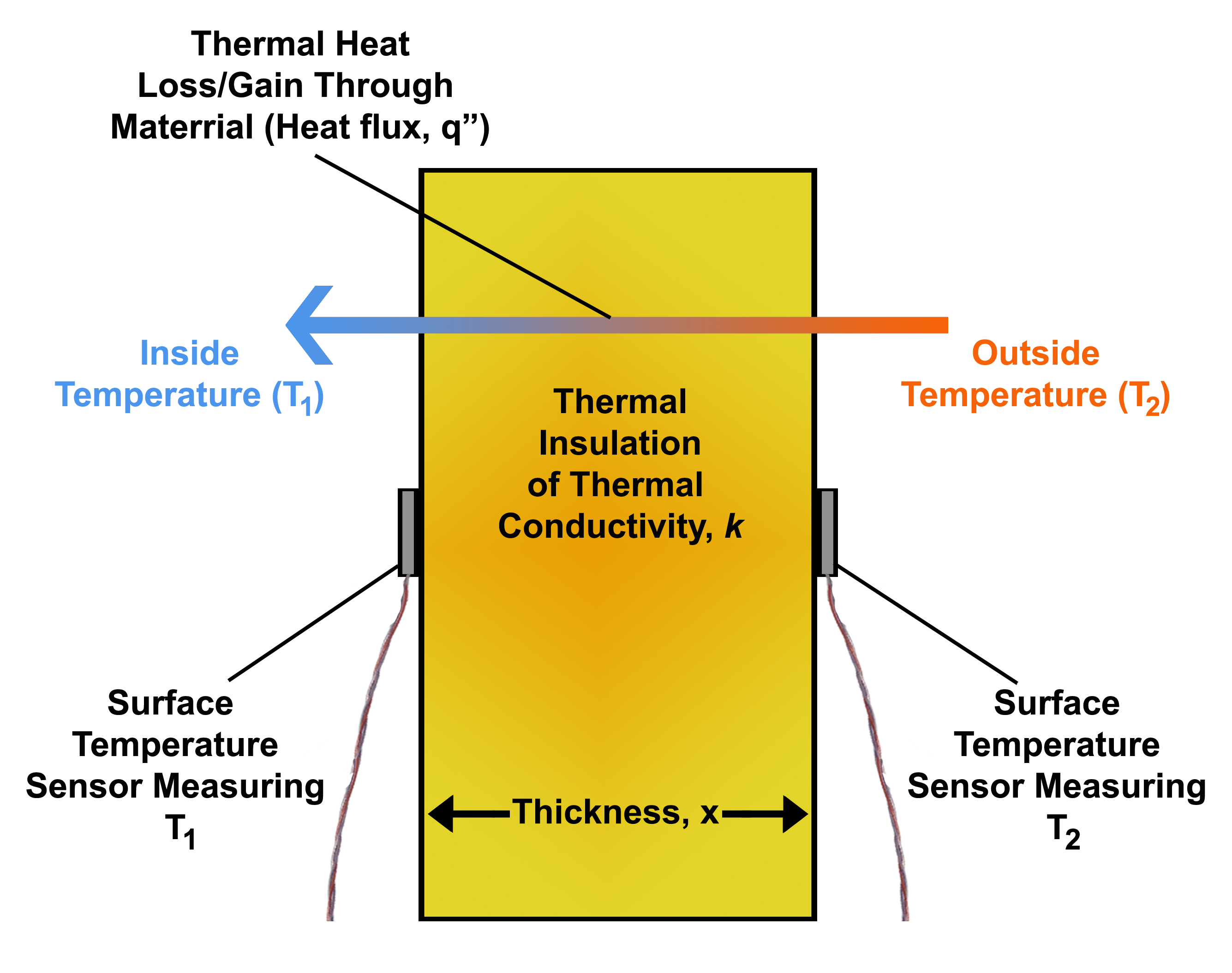
Heat Flux
In physics and engineering, heat flux or thermal flux, sometimes also referred to as heat flux density, heat-flow density or heat-flow rate intensity, is a flow of energy per unit area per unit time (physics), time. Its SI units are watts per square metre (W/m2). It has both a direction and a magnitude, and so it is a Vector (geometric), vector quantity. To define the heat flux at a certain point in space, one takes the Limiting case (mathematics), limiting case where the size of the surface becomes infinitesimally small. Heat flux is often denoted \vec_\mathrm, the subscript specifying ''heat'' flux, as opposed to ''Mass flux, mass'' or Transport phenomena, ''momentum'' flux. Heat conduction#Fourier's law, Fourier's law is an important application of these concepts. Fourier's law For most solids in usual conditions, heat is transported mainly by thermal conduction, conduction and the heat flux is adequately described by Fourier's law. Fourier's law in one dimension \phi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
IBM 3090
The IBM 3090 family is a family of mainframe computers that was a high-end successor to the IBM System/370 series, and thus indirectly the successor to the IBM System/360 launched 25 years earlier. Announced on 12 February 1985, the press releases did not explicitly mention that the two models, Model 200 and Model 400, were backwardly compatible with the 370; instead, they were simply positioned as replacements for the IBM 3033. The IBM 3090/200 version was rated at 18 MIPS and 31,000 UNIX Dhrystones. This was true of the entire line, which expanded with the release of the Model 120E, 150, 150E, 180, 180E, 200, 200E, 300, 300E, 400, 400E, 600E, 600J, and 600S 3090 were described as using "ideas from the ... IBM 3033, extending them ... It also took ... from the ... IBM 308X." The 400 and 600 were respectively two 200s or 300s coupled together as one system and could run in either single-system image mode or partitioned into two systems. Models and feature ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
IBM 303X
The IBM 303XIBM used a capital X when referring to 303X, as did print media; see Computerworld ref below. is a discontinued line of mainframe computers, the first model of which, the IBM 3033 Processor, nicknamed "The Big One", was introduced March 25, 1977. Two additional processors, the 3031 and the 3032, were announced on October 6, 1977. All three 303X systems were withdrawn on February 5, 1985. Features The CPUs feature instruction pipelining, "several instructions can be pre-fetched while one is being executed". "Processor storage ... is four-way interleaved" resulting in "a significantly faster data rate than... non-interleaved". All three systems include a Dual-display console, the newly announced IBM 3036. The 3036 has an L-shaped desk, with two workstations. Each workstation has a service processor, a 3277 display, and two diskette drives (33FD). One diskette is used for logging hardware errors, and the other contains microcode. One of the service processors is the ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
IBM System/370
The IBM System/370 (S/370) is a range of IBM mainframe computers announced as the successors to the IBM System/360, System/360 family on June 30, 1970. The series mostly maintains backward compatibility with the S/360, allowing an easy migration path for customers; this, plus improved performance, were the dominant themes of the product announcement. Early 370 systems differed from the 360 largely in their internal circuitry, moving from the Solid Logic Technology hybrid integrated circuits containing separate transistors to more modern monolithic integrated circuits containing multiple transistors per integrated circuit, which IBM referred to as Monolithic System Technology, or MST. The higher density packaging allowed several formerly optional features from the 360 line to be included as standard features of the machines, floating-point support for instance. The 370 also added a small number of new instructions. At the time of its introduction, the development of virtual mem ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
IBM System/360
The IBM System/360 (S/360) is a family of mainframe computer systems announced by IBM on April 7, 1964, and delivered between 1965 and 1978. System/360 was the first family of computers designed to cover both commercial and scientific applications and a complete range of applications from small to large. The design distinguished between architecture and implementation, allowing IBM to release a suite of compatible designs at different prices. All but the only partially compatible Model 44 and the most expensive systems use microcode to implement the instruction set, featuring 8-bit byte addressing and fixed-point binary, fixed-point decimal and hexadecimal floating-point calculations. The System/360 family introduced IBM's Solid Logic Technology (SLT), which packed more transistors onto a circuit card, allowing more powerful but smaller computers. System/360's chief architect was Gene Amdahl, and the project was managed by Fred Brooks, responsible to Chairman Thomas J. Wat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Uniprocessor System
A uniprocessor system is defined as a computer system that has a single central processing unit that is used to execute computer tasks. As more and more modern software is able to make use of multiprocessing Multiprocessing (MP) is the use of two or more central processing units (CPUs) within a single computer system. The term also refers to the ability of a system to support more than one processor or the ability to allocate tasks between them. The ... architectures, such as SMP and MPP, the term ''uniprocessor'' is therefore used to distinguish the class of computers where all processing tasks share a single CPU. As such, this kind of system uses a type of architecture that is based on a single computing unit. All operations (additions, multiplications, etc.) are thus done sequentially on the unit. Further reading Parallel computing {{Compu-hardware-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transaction Processing Facility
Transaction Processing Facility (TPF) is an IBM real-time operating system for mainframe computers descended from the IBM System/360 family, including zSeries and System z9. TPF delivers fast, high-volume, high-throughput transaction processing, handling large, continuous loads of essentially simple transactions across large, geographically dispersed networks. While there are other industrial-strength transaction processing systems, notably IBM's own CICS and IMS, TPF's specialty is extreme volume, large numbers of concurrent users, and very fast response times. For example, it handles VISA credit card transaction processing during the peak holiday shopping season. The TPF passenger reservation application PARS, or its international version IPARS, is used by many airlines. ''PARS'' is an ''application program''; TPF is an operating system. One of TPF's major optional components is a high performance, specialized database facility called ''TPF Database Facility'' (TPFDF). A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
IBM Airline Control Program
IBM Airline Control Program, or ACP, is a discontinued operating system developed by IBM beginning about 1965. In contrast to previous airline transaction processing systems, the most notable aspect of ACP is that it was designed to run on most models of the IBM System/360 mainframe computer family. This departed from the earlier model in which each airline had a different, machine-specific transaction system. Overview Development began with ''SABRE (Semi-Automatic Business Research Environment)'', ''Deltamatic'', and ''PANAMAC''. From these, the ''Programmed Airline Reservations System (PARS)'' was developed. In 1969 the control program, ''ACP'', was separated from PARS. PARS kept the functions for processing airline reservations and related data. In December 1979, ACP became known as ACP/TPF and then just TPF (Transaction Processing Facility). The transaction operating system became more widely implemented by businesses other than the major airlines, such as online credit car ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Water-cooled
Cooling tower and water discharge of a nuclear power plant Water cooling is a method of heat removal from components and industrial equipment. Evaporative cooling using water is often more efficient than air cooling. Water is inexpensive and non-toxic; however, it can contain impurities and cause corrosion. Water cooling is commonly used for cooling automobile internal combustion engines and power stations. Water coolers utilising convective heat transfer are used inside high-end personal computers to lower the temperature of CPUs and other components. Other uses include the cooling of lubricant oil in pumps; for cooling purposes in heat exchangers; for cooling buildings in HVAC and in chillers. Mechanism Advantages Water is inexpensive, non-toxic, and available over most of the earth's surface. Liquid cooling offers higher thermal conductivity than air cooling. Water has unusually high specific heat capacity among commonly available liquids at room temperature and atmosph ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
IBM System/370-XA
IBM System/370-XA is an instruction set architecture introduced by IBM in 1983 for the IBM 308X processors. It extends the IBM System/370 architecture to support 31-bit virtual and physical addresses, and includes a redesigned I/O architecture. 31-bit virtual addressing In the System/360, other than the 360/67, and System/370 architectures, the general-purpose registers were 32 bits wide, the machine did 32-bit arithmetic operations, and addresses were always stored in 32-bit words, so the architecture was considered 32-bit, but the machines ignored the top 8 bits of the address resulting in 24-bit addressing. Much of System/360's and System/370's large installed code base relied on a 24-bit logical address In computing, a logical address is the address at which an item ( memory cell, storage element, network host) appears to reside from the perspective of an executing application program. A logical address may be different from the physical addr ...; In particula ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Helium
Helium (from ) is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol He and atomic number 2. It is a colorless, odorless, non-toxic, inert gas, inert, monatomic gas and the first in the noble gas group in the periodic table. Its boiling point is the lowest among all the Chemical element, elements, and it does not have a melting point at standard pressures. It is the second-lightest and second-most Abundance of the chemical elements, abundant element in the observable universe, after hydrogen. It is present at about 24% of the total elemental mass, which is more than 12 times the mass of all the heavier elements combined. Its abundance is similar to this in both the Sun and Jupiter, because of the very high nuclear binding energy (per nucleon) of helium-4 with respect to the next three elements after helium. This helium-4 binding energy also accounts for why it is a product of both nuclear fusion and radioactive decay. The most common isotope of helium in the universe is helium-4, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |