|
IBM 2301
In addition to the drums used as main memory by IBM in, e.g., IBM 305, IBM 650, IBM offered drum devices as secondary storage for the 700/7000 series and System/360 series of computers. IBM 731 The IBM 731 is a discontinued storage unit used on the IBM 701. It has a storage capacity of 2,048 36-bit words (9,216 8-bit bytes). IBM 732 The IBM 732 is a discontinued storage unit used on the IBM 702. It has a storage capacity of 60,000 6-bit characters (45,000 8-bit bytes). IBM 733 The IBM 733 is a discontinued storage unit used on the IBM 704 and IBM 709. It has a storage capacity of 8192 36-bit words (36,864 8-bit bytes). IBM 734 The IBM 734 is a discontinued storage unit used on the IBM 705 It has a storage capacity of 60,000 6-bit characters (45,000 8-bit bytes). IBM 7320 The IBM 7320 is a discontinued storage unit manufactured by IBM announced on December 10, 1962 for the IBM 7090 and 7094 computer systems, was retained for the earliest System/360 systems as a count key d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Main Memory
Computer data storage or digital data storage is a technology consisting of computer components and recording media that are used to retain digital data. It is a core function and fundamental component of computers. The central processing unit (CPU) of a computer is what manipulates data by performing computations. In practice, almost all computers use a storage hierarchy, which puts fast but expensive and small storage options close to the CPU and slower but less expensive and larger options further away. Generally, the fast technologies are referred to as "memory", while slower persistent technologies are referred to as "storage". Even the first computer designs, Charles Babbage's Analytical Engine and Percy Ludgate's Analytical Machine, clearly distinguished between processing and memory (Babbage stored numbers as rotations of gears, while Ludgate stored numbers as displacements of rods in shuttles). This distinction was extended in the Von Neumann architecture, wh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
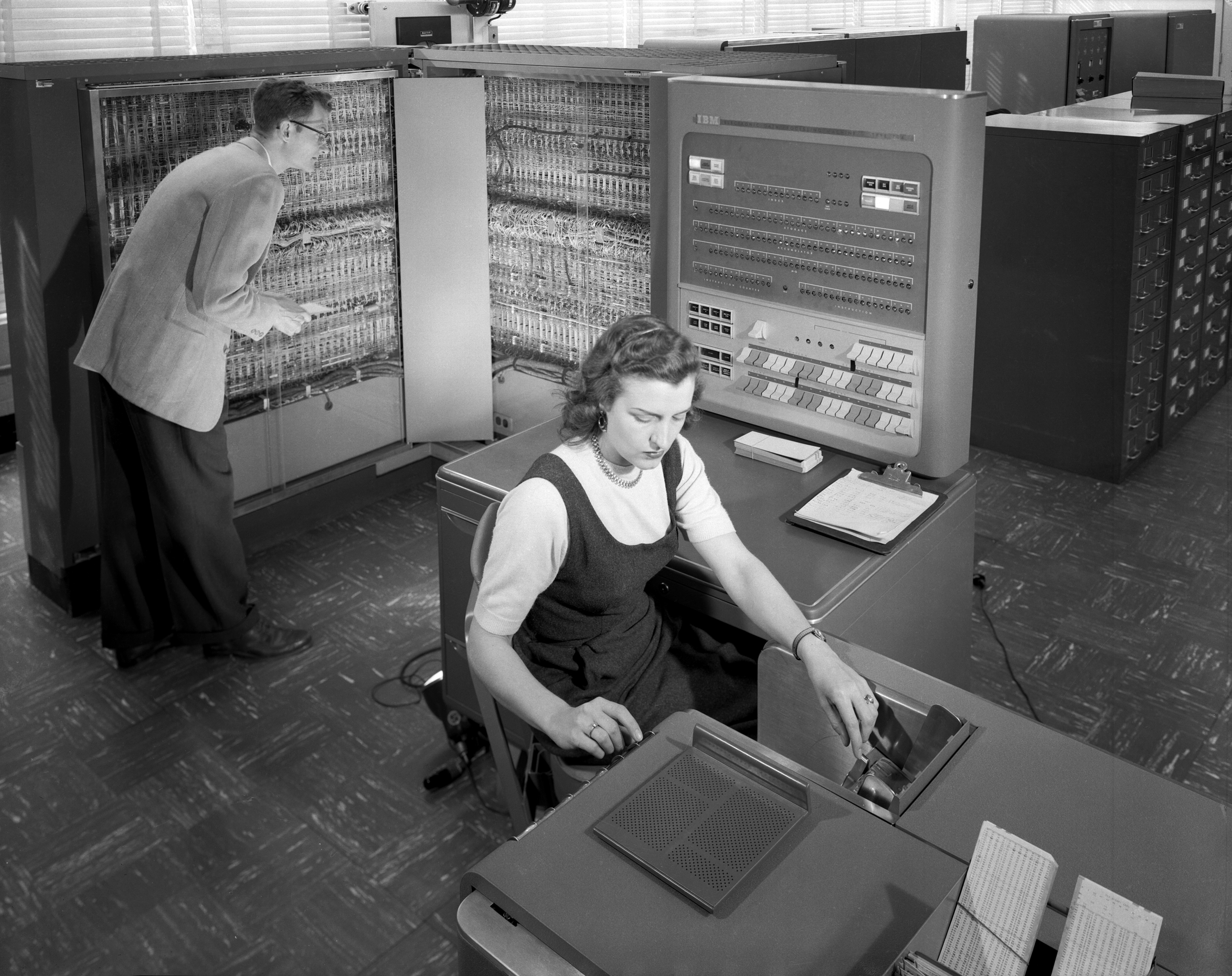
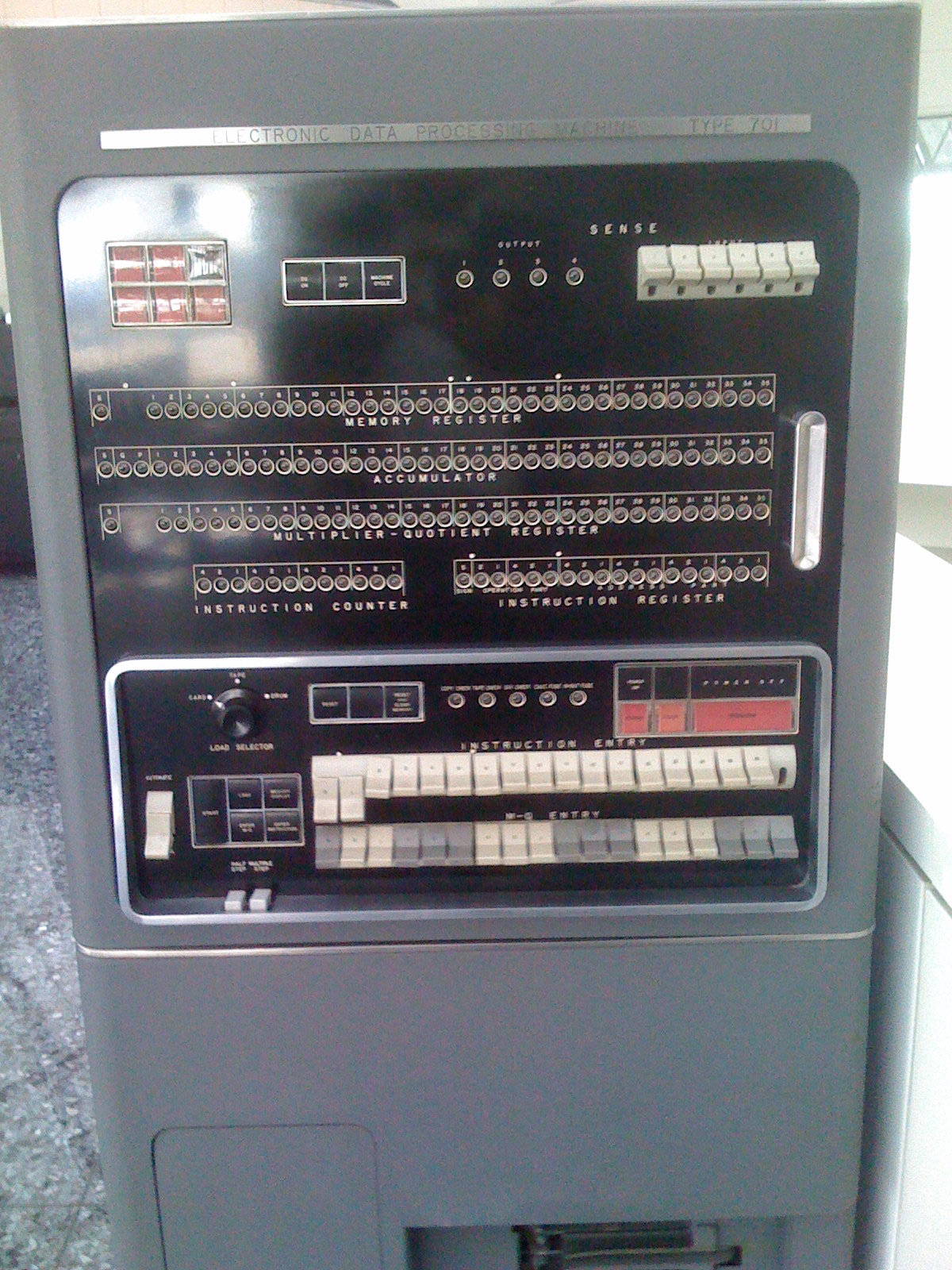
IBM 7090
The IBM 7090 is a second-generation Transistor computer, transistorized version of the earlier IBM 709 vacuum tube mainframe computer that was designed for "large-scale scientific and technological applications". The 7090 is the fourth member of the IBM 700/7000 series#Scientific Architecture, IBM 700/7000 series scientific computers. The first 7090 installation was in December 1959. In 1960, a typical system sold for $2.9 million (equivalent to $ million in ) or could be rented for $63,500 a month (). The 7090 uses a 36-bit word length, with an address space of 32,768 words (15-bit addresses). It operates with a basic memory cycle of 2.18 μs, using the IBM 7302 Core Storage Magnetic-core memory, core memory technology from the IBM 7030 (Stretch) project. With a processing speed of around 100 FLOPS, Kflop/s, the 7090 is six times faster than the 709, and could be rented for half the price. An upgraded version, the 7094, was up to twice as fast. Both the 7090 and the 7094 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
History Of Computing Hardware
The history of computing hardware spans the developments from early devices used for simple calculations to today's complex computers, encompassing advancements in both analog and digital technology. The first aids to computation were purely mechanical devices which required the operator to set up the initial values of an elementary arithmetic operation, then manipulate the device to obtain the result. In later stages, computing devices began representing numbers in continuous forms, such as by distance along a scale, rotation of a shaft, or a specific voltage level. Numbers could also be represented in the form of digits, automatically manipulated by a mechanism. Although this approach generally required more complex mechanisms, it greatly increased the precision of results. The development of transistor technology, followed by the invention of integrated circuit chips, led to revolutionary breakthroughs. Transistor-based computers and, later, integrated circuit-based computers ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
IBM 2820
In addition to the drums used as main memory by IBM in, e.g., IBM 305, IBM 650, IBM offered drum devices as secondary storage for the 700/7000 series and System/360 series of computers. IBM 731 The IBM 731 is a discontinued storage unit used on the IBM 701. It has a storage capacity of 2,048 36-bit words (9,216 8-bit bytes). IBM 732 The IBM 732 is a discontinued storage unit used on the IBM 702. It has a storage capacity of 60,000 6-bit characters (45,000 8-bit bytes). IBM 733 The IBM 733 is a discontinued storage unit used on the IBM 704 and IBM 709. It has a storage capacity of 8192 36-bit words (36,864 8-bit bytes). IBM 734 The IBM 734 is a discontinued storage unit used on the IBM 705 It has a storage capacity of 60,000 6-bit characters (45,000 8-bit bytes). IBM 7320 The IBM 7320 is a discontinued storage unit manufactured by IBM announced on December 10, 1962 for the IBM 7090 and 7094 computer systems, was retained for the earliest System/360 systems as a count key d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
History Of IBM Magnetic Disk Drives
IBM manufactured magnetic disk storage devices from 1956 to 2003, when it sold its hard disk drive business to Hitachi. Both the hard disk drive (HDD) and floppy disk drive (FDD) were invented by IBM and as such IBM's employees were responsible for many of the innovations in these products and their technologies. The basic mechanical arrangement of hard disk drives has not changed since the IBM 1301. Disk drive performance and characteristics are measured by the same standards now as they were in the 1950s. Few products in history have enjoyed such spectacular declines in cost and physical size along with equally dramatic improvements in capacity and performance. IBM manufactured 8-inch floppy disk drives from 1969 until the mid-1980s, but did not become a significant manufacturer of smaller-sized, 5.25- or 3.5-inch floppy disk drives (the dimension refers to the diameter of the floppy disk, not the size of the drive). IBM always offered its magnetic disk drives for sale but did no ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
IBM 2841
Beginning with its 1964 System/360 announcement, IBM's mainframes initially accessed count key data (CKD) subsystems via a channel connected to separate Storage Control Units (SCUs) with attached Direct Access Storage Devices (DASD), typically a hard disk drive. This practice continued in IBM's larger mainframes thru IBM Z; however low end systems generally used lower cost integrated attachments where the function of the SCU was combined with that of the channel, typically called an Integrated File Adapter. The System/360 selector channel was followed by the System/370 block multiplexor channel which could operate as a selector channel to allow attachment of legacy subsystems. The SCU evolved into a Director and Controller, the latter typically labelled an "A-unit" (or A-Box") with the controller and at least one DASD physically in an A-unit. An Integrated Storage Control (ISC) is a Director within the cabinet of an IBM System. A Director could attach from one to four A-uni ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
IBM 1302
IBM manufactured magnetic disk storage devices from 1956 to 2003, when it sold its hard disk drive business to Hitachi. Both the hard disk drive (HDD) and floppy disk drive (FDD) were invented by IBM and as such IBM's employees were responsible for many of the innovations in these products and their technologies. The basic mechanical arrangement of hard disk drives has not changed since the IBM 1301. Disk drive performance and characteristics are measured by the same standards now as they were in the 1950s. Few products in history have enjoyed such spectacular declines in cost and physical size along with equally dramatic improvements in capacity and performance. IBM manufactured 8-inch floppy disk drives from 1969 until the mid-1980s, but did not become a significant manufacturer of smaller-sized, 5.25- or 3.5-inch floppy disk drives (the dimension refers to the diameter of the floppy disk, not the size of the drive). IBM always offered its magnetic disk drives for sale but did not ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
IBM 7631
International Business Machines Corporation (using the trademark IBM), nicknamed Big Blue, is an American multinational technology company headquartered in Armonk, New York, and present in over 175 countries. It is a publicly traded company and one of the 30 companies in the Dow Jones Industrial Average. IBM is the largest industrial research organization in the world, with 19 research facilities across a dozen countries; for 29 consecutive years, from 1993 to 2021, it held the record for most annual U.S. patents generated by a business. IBM was founded in 1911 as the Computing-Tabulating-Recording Company (CTR), a holding company of manufacturers of record-keeping and measuring systems. It was renamed "International Business Machines" in 1924 and soon became the leading manufacturer of punch-card tabulating systems. During the 1960s and 1970s, the IBM mainframe, exemplified by the System/360 and its successors, was the world's dominant computing platform, with the company p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Count Key Data
Count key data (CKD) is a direct-access storage device (DASD) data recording format introduced in 1964, by IBM with its IBM System/360 and still being emulated on IBM mainframes. It is a self-defining format with each data record represented by a Count Area that identifies the record and provides the number of bytes in an optional Key Area and an optional Data Area. This is in contrast to devices using fixed sector size or a separate format track. Count key data (CKD) also refers to the set of channel commands (collectively Channel Command Words, CCWs) that are generated by an IBM mainframe for execution by a DASD subsystem employing the CKD recording format. The initial set of CKD CCWs, introduced in 1964, was substantially enhanced and improved into the 1990s. CKD track format The reason for CKD track format is to allow data field lengths to vary, each recorded block of data on a DASD track, called a record has an associated count field which identifies the record and indicat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
IBM 705
The IBM 700/7000 series is a series of large-scale (mainframe) computer systems that were made by IBM through the 1950s and early 1960s. The series includes several different, incompatible processor architectures. The 700s use vacuum-tube logic and were made obsolete by the introduction of the transistorized 7000s. The 7000s, in turn, were eventually replaced with System/360, which was announced in 1964. However the 360/65, the first 360 powerful enough to replace 7000s, did not become available until November 1965. Early problems with OS/360 and the high cost of converting software kept many 7000s in service for years afterward. Architectures The IBM 700/7000 series has six completely different ways of storing data and instructions: *First scientific (36/18- bit words): 701 (Defense Calculator) *Later scientific (36-bit words, hardware floating-point): 704, 709, 7040, 7044, 7090, 7094 *Commercial (variable-length character strings): 702, 705, 7080 * 1400 series (varia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
IBM 305
The IBM 305 RAMAC was the first commercial computer that used a moving-head hard disk drive (magnetic disk storage) for secondary storage. The system was publicly announced on September 14, 1956,650 RAMAC announcement The 305 RAMAC and the 650 RAMAC were internally announced on September 4, 1956. with test units already installed at the U.S. Navy and at private corporations. RAMAC stood for "Random Access Method of Accounting and Control", as its design was motivated by the need for real-time accounting in business.IBM RAMAC promotional film /ref> History RAMAC wa ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |