|
Hysteria
Hysteria is a term used colloquially to mean ungovernable emotional excess and can refer to a temporary state of mind or emotion. In the nineteenth century, hysteria was considered a diagnosable physical illness in women. It is assumed that the basis for diagnosis operated under the belief that women are predisposed to mental and behavioral conditions; an interpretation of sex-related differences in stress responses. In the twentieth century, it shifted to being considered a mental illness. Many influential people such as Sigmund Freud and Jean-Martin Charcot dedicated research to hysteria patients. Currently, most doctors practicing medicine do not accept hysteria as a medical diagnosis. The blanket diagnosis of hysteria has been fragmented into myriad medical categories such as epilepsy, histrionic personality disorder, conversion disorders, dissociative disorders, or other medical conditions. Furthermore, lifestyle choices, such as choosing not to wed, are no longer cons ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
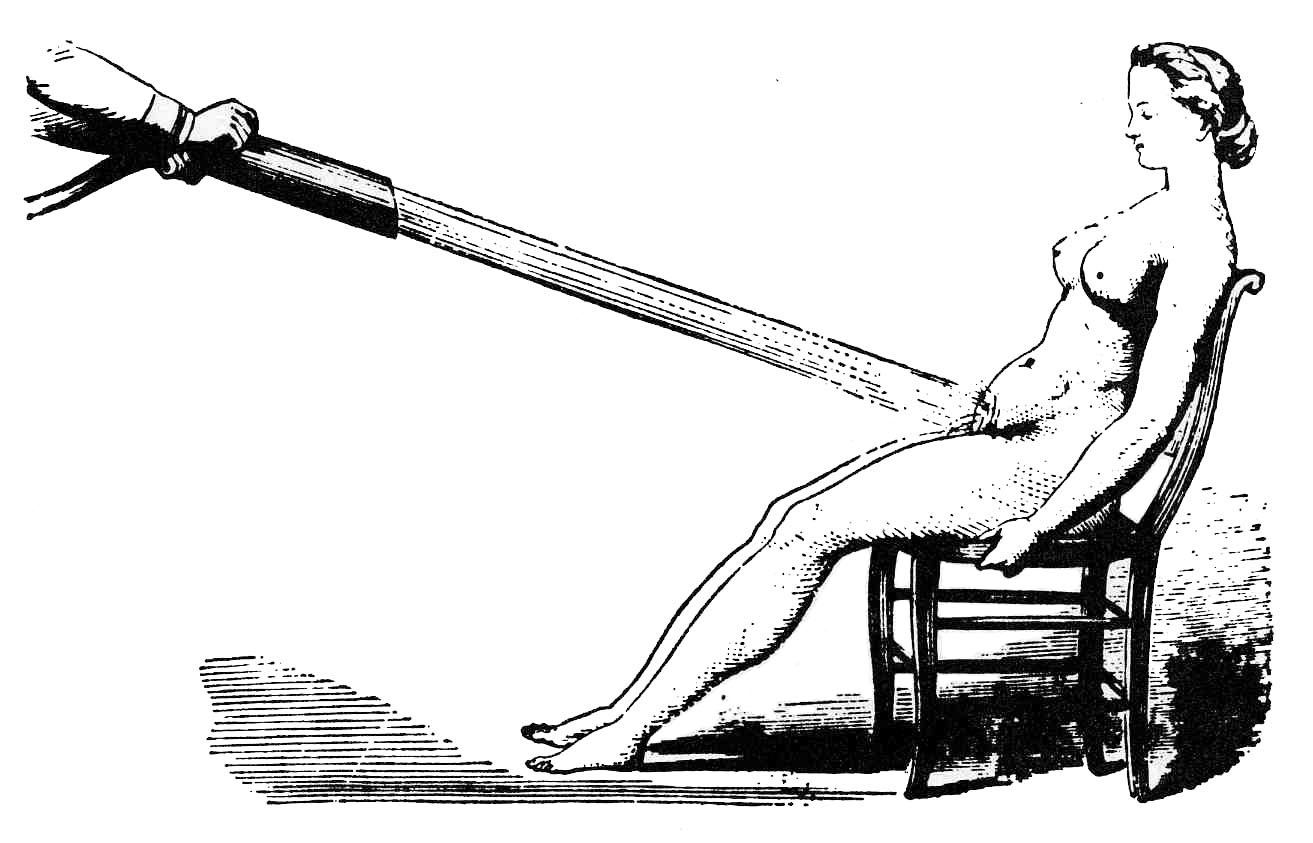
Female Hysteria
Female hysteria was once a common medical diagnosis for women, which was described as exhibiting a wide array of symptoms, including anxiety, shortness of breath, fainting, nervousness, sexual desire, insomnia, fluid retention, heaviness in the abdomen, irritability, loss of appetite for food or sex, (paradoxically) sexually forward behaviour, and a "tendency to cause trouble for others". It is no longer recognized by medical authorities as a medical disorder. Its diagnosis and treatment were routine for hundreds of years in Western Europe. In Western medicine, hysteria was considered both common and chronic among women. Even though it was categorized as a disease, hysteria's symptoms were synonymous with normal functioning female sexuality. In extreme cases, the woman may have been forced to enter an insane asylum or to have undergone surgical hysterectomy. Early history The history of hysteria can be traced to ancient times. Dating back to 1900 BC in ancient Egypt, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sigmund Freud
Sigmund Freud ( , ; born Sigismund Schlomo Freud; 6 May 1856 – 23 September 1939) was an Austrian neurologist and the founder of psychoanalysis, a clinical method for evaluating and treating pathologies explained as originating in conflicts in the psyche, through dialogue between a patient and a psychoanalyst. Freud was born to Galician Jewish parents in the Moravian town of Freiberg, in the Austrian Empire. He qualified as a doctor of medicine in 1881 at the University of Vienna. Upon completing his habilitation in 1885, he was appointed a docent in neuropathology and became an affiliated professor in 1902. Freud lived and worked in Vienna, having set up his clinical practice there in 1886. In 1938, Freud left Austria to escape Nazi persecution. He died in exile in the United Kingdom in 1939. In founding psychoanalysis, Freud developed therapeutic techniques such as the use of free association and discovered transference, establishing its central role in the analytic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Conversion Disorder
Conversion disorder (CD), or functional neurologic symptom disorder, is a diagnostic category used in some psychiatric classification systems. It is sometimes applied to patients who present with neurological symptoms, such as numbness, blindness, paralysis, or fits, which are not consistent with a well-established organic cause, which cause significant distress, and can be traced back to a psychological trigger. It is thought that these symptoms arise in response to stressful situations affecting a patient's mental health or an ongoing mental health condition such as depression. Conversion disorder was retained in DSM-5, but given the subtitle functional neurological symptom disorder. The new criteria cover the same range of symptoms, but remove the requirements for a psychological stressor to be present and for feigning to be disproved. ICD-10 classifies conversion disorder as a dissociative disorder while DSM-IV classifies it as a somatoform disorder A somatic sympto ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jean-Martin Charcot
Jean-Martin Charcot (; 29 November 1825 – 16 August 1893) was a French neurologist and professor of anatomical pathology. He worked on hypnosis and hysteria, in particular with his hysteria patient Louise Augustine Gleizes. Charcot is known as "the founder of modern neurology",Lamberty (2007), p. 5 and his name has been associated with at least 15 medical eponyms, including various conditions sometimes referred to as Charcot diseases. Charcot has been referred to as "the father of French neurology and one of the world's pioneers of neurology". His work greatly influenced the developing fields of neurology and psychology; modern psychiatry owes much to the work of Charcot and his direct followers.Bogousslavsky (2010), p. 7 He was the "foremost neurologist of late nineteenth-century France" and has been called "the Napoleon of the neuroses". Personal life Born in Paris, Charcot worked and taught at the famous Pitié-Salpêtrière Hospital for 33 years. His reputation as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paul Briquet
Paul Briquet or Pierre Briquet (12 January 1796 – 25 January 1881) was a French physician and psychologist who advanced the reasoned treatment of disturbed people said to be hysterics. Briquet became a medical doctor in 1824, a professor in 1827. In 1836 he operated at the Cochin hospital and in 1846 at La Charité hospital. In 1853 he described the preparation and use of quinine. He published ''Traité clinique et thérapeutique de l’Hystérie'' in 1859, and the following year he was admitted to the Academie de Medecine. A type of personality disorder called ''Briquet’s syndrome'' is classified as somatic symptom disorder. He first described this in 1859. "Although many of his theoretical concepts, basic scientific knowledge and data processing techniques were primitive by our standards, his approach, his emphasis on demonstrable facts, and his many well-substantiated conclusions mark his ''Treatise on Hysteria'' as an avant-garde work relevant even today" Briquet w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pierre Janet
Pierre Marie Félix Janet (; 30 May 1859 – 24 February 1947) was a pioneering French psychologist, physician, philosopher, and psychotherapist in the field of dissociation and traumatic memory. He is ranked alongside William James and Wilhelm Wundt as one of the founding fathers of psychology. Biography Janet studied under Jean-Martin Charcot at the Psychological Laboratory in the Pitié-Salpêtrière Hospital in Paris. He first published the results of his research in his philosophy thesis in 1889 and in his medical thesis, ''L'état mental des hystériques'', in 1892. He earned a degree in medicine the following year in 1893. In 1898, Janet was appointed lecturer in psychology at the Sorbonne, and in 1902 he attained the chair of experimental and comparative psychology at the Collège de France, a position he held until 1936. He was a member of the Institut de France from 1913, and was a central figure in French psychology in the first half of the 20th century. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Uterus
The uterus (from Latin ''uterus'', plural ''uteri'') or womb () is the organ in the reproductive system of most female mammals, including humans that accommodates the embryonic and fetal development of one or more embryos until birth. The uterus is a hormone-responsive sex organ that contains glands in its lining that secrete uterine milk for embryonic nourishment. In the human, the lower end of the uterus, is a narrow part known as the isthmus that connects to the cervix, leading to the vagina. The upper end, the body of the uterus, is connected to the fallopian tubes, at the uterine horns, and the rounded part above the openings to the fallopian tubes is the fundus. The connection of the uterine cavity with a fallopian tube is called the uterotubal junction. The fertilized egg is carried to the uterus along the fallopian tube. It will have divided on its journey to form a blastocyst that will implant itself into the lining of the uterus – the endometrium ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arthur Frederick Hurst
Sir Arthur Frederick Hurst, aka Arthur Frederick Hertz FRCP (23 July 1879 – 17 August 1944) was a British physician, and a cofounder of the British Society of Gastroenterology. The society's annual lecture is named for him. Biography Aurthur Frederick Hertz was born in Bradford to Fanny Mary and William Martin Hertz, a merchant of German Jewish descent. Hertz changed the spelling of his surname to Hurst in 1916. He attended Bradford Grammar School and Manchester Grammar School before graduating from Magdalen College, Oxford in 1904. He joined the staff of Guy's Hospital in 1906 and ran his own private practice before serving in World War I as a consulting physician stationed in Salonika. From 1916 to 1918, Hurst led the neurology department at Netley Hospital. Seale-Hayne College was repurposed as a military hospital that same year. Hurst moved there to help with treatment of shell shock, working at Netley until 1919. After the war, Hurst relocated his private practice to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Somatization Disorder
Somatization disorder is a mental and behavioral disorder characterized by recurring, multiple, and current, clinically significant complaints about somatic symptoms. It was recognized in the DSM-IV-TR classification system, but in the latest version DSM-5, it was combined with undifferentiated somatoform disorder to become '' somatic symptom disorder'', a diagnosis which no longer requires a specific number of somatic symptoms. ICD-10, the latest version of the International Statistical Classification of Diseases and Related Health Problems, still includes somatization syndrome. Criteria DSM-5 In the DSM-5 the disorder has been renamed somatic symptom disorder (SSD), and includes SSD with predominantly somatic complaints (previously referred to as somatization disorder), and SSD with pain features (previously known as pain disorder). DSM-IV-TR The DSM-IV-TR diagnostic criteria are: * A history of somatic complaints over several years, starting prior to the age of 30. * Such ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shell Shock
Shell shock is a term coined in World War I by the British psychologist Charles Samuel Myers to describe the type of post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) many soldiers were afflicted with during the war (before PTSD was termed). It is a reaction to the intensity of the bombardment and fighting that produced a helplessness appearing variously as panic and being scared, flight, or an inability to reason, sleep, walk or talk. During the war, the concept of shell shock was ill-defined. Cases of "shell shock" could be interpreted as either a physical or psychological injury, or as a lack of moral fibre. The term ''shell shock'' is still used by the United States’ Department of Veterans Affairs to describe certain parts of PTSD, but mostly it has entered into memory, and it is often identified as the signature injury of the war. In World War II and thereafter, diagnosis of "shell shock" was replaced by that of combat stress reaction, a similar but not identical response to the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Drawings Of A Woman In Catalepsy By Albert Londe
Drawing is a form of visual art in which an artist uses instruments to mark paper or other two-dimensional surface. Drawing instruments include graphite pencils, pen and ink, various kinds of paints, inked brushes, colored pencils, crayons, charcoal, chalk, pastels, erasers, markers, styluses, and metals (such as silverpoint). Digital drawing is the act of drawing on graphics software in a computer. Common methods of digital drawing include a stylus or finger on a touchscreen device, stylus- or finger-to-touchpad, or in some cases, a mouse. There are many digital art programs and devices. A drawing instrument releases a small amount of material onto a surface, leaving a visible mark. The most common support for drawing is paper, although other materials, such as cardboard, wood, plastic, leather, canvas, and board, have been used. Temporary drawings may be made on a blackboard or whiteboard. Drawing has been a popular and fundamental means of public expression throughout hum ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Colin McEvedy
Colin Peter McEvedy (6 June 1930 – 1 August 2005) was a British polymath scholar, psychiatrist, historian, demographer and non-fiction author. Early life Colin Peter McEvedy was born in Salford, Lancashire on 6 June 1930. He was the third son of Peter George McEvedy, a renowned surgeon, who was born in New Zealand. Colin was educated at Harrow School, where he was a scholar, and Magdalen College, Oxford. Career McEvedy's profession was psychiatry, in which he had a distinguished career. He became perhaps better known, though, as a historian and demographer, and certainly so by the public at large. Between 1961 and 2002 he produced a number of historical atlases which, unlike most such atlases, feature fixed base-maps; in most cases, each atlas uses a single principal base-map, which is shown repeatedly, at many dates, as the atlas goes along, thus illustrating changes over the ages, from ancient down to modern, within the chosen area. The accompanying text, typically, is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




.jpg)