|
Hypotonic-hyporesponsive Episode
A hypotonic-hyporesponsive episode (HHE) is defined as sudden onset of poor muscle tone, reduced consciousness, and pale or bluish skin occurring within 48 hours after vaccination Vaccination is the administration of a vaccine to help the immune system develop immunity from a disease. Vaccines contain a microorganism or virus in a weakened, live or killed state, or proteins or toxins from the organism. In stimulating ..., most commonly pertussis vaccination. An HHE is estimated to occur after 1 in 4,762 to 1 in 1,408 doses of whole cell pertussis vaccine, and after 1 in 14,286 to 1 in 2,778 doses of acellular pertussis vaccine. References {{reflist Vaccination Symptoms and signs: Nervous system ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hypotonia
Hypotonia is a state of low muscle tone (the amount of tension or resistance to stretch in a muscle), often involving reduced muscle strength. Hypotonia is not a specific medical disorder, but a potential manifestation of many different diseases and disorders that affect motor nerve control by the brain or muscle strength. Hypotonia is a lack of resistance to passive movement, whereas muscle weakness results in impaired active movement. Central hypotonia originates from the central nervous system, while peripheral hypotonia is related to problems within the spinal cord, peripheral nerves and/or skeletal muscles. Severe hypotonia in infancy is commonly known as floppy baby syndrome. Recognizing hypotonia, even in early infancy, is usually relatively straightforward, but diagnosing the underlying cause can be difficult and often unsuccessful. The long-term effects of hypotonia on a child's development and later life depend primarily on the severity of the muscle weakness and the n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pallor
Pallor is a pale color of the skin that can be caused by illness, emotional shock or stress, stimulant use, or anemia, and is the result of a reduced amount of oxyhaemoglobin and may also be visible as pallor of the conjunctivae of the eyes on physical examination. Pallor is more evident on the face and palms. It can develop suddenly or gradually, depending on the cause. It is not usually clinically significant unless it is accompanied by a general pallor (pale lips, tongue, palms, mouth and other regions with mucous membranes). It is distinguished from similar presentations such as hypopigmentation (lack or loss of skin pigment) or simply a fair complexion. Causes * migraine attack or headache * excess estradiol and/or estrone * osteoporosis * emotional response, due to fear, embarrassment, grief, rage * anorexia * anemia, due to blood loss, poor nutrition, or underlying disease such as sickle cell anemia * iron deficiency * vitamin B12 deficiency * shock, a me ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cyanosis
Cyanosis is the change of body tissue color to a bluish-purple hue as a result of having decreased amounts of oxygen bound to the hemoglobin in the red blood cells of the capillary bed. Body tissues that show cyanosis are usually in locations where the skin is thinner, including the mucous membranes, lips, nail beds, and ear lobes. Some medications containing amiodarone or silver, Mongolian spots, large birth marks, and the consumption of food products with blue or purple dyes can also result in the bluish skin tissue discoloration and may be mistaken for cyanosis. Cyanosis is further classified into central cyanosis vs. peripheral cyanosis. Pathophysiology The mechanism behind cyanosis is different depending on whether it is central or peripheral. Central cyanosis Central cyanosis is caused by a decrease in arterial oxygen saturation (SaO2) and begins to show once the concentration of deoxyhemoglobin in the blood reaches a concentration of ≥ 5.0 g/dL (≥ 3.1 mmol/ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vaccination
Vaccination is the administration of a vaccine to help the immune system develop immunity from a disease. Vaccines contain a microorganism or virus in a weakened, live or killed state, or proteins or toxins from the organism. In stimulating the body's adaptive immunity, they help prevent sickness from an infectious disease. When a sufficiently large percentage of a population has been vaccinated, herd immunity results. Herd immunity protects those who may be immunocompromised and cannot get a vaccine because even a weakened version would harm them. The effectiveness of vaccination has been widely studied and verified. Vaccination is the most effective method of preventing infectious diseases; widespread immunity due to vaccination is largely responsible for the worldwide eradication of smallpox and the elimination of diseases such as polio and tetanus from much of the world. However, some diseases, such as measles outbreaks in America, have seen rising cases due to relati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
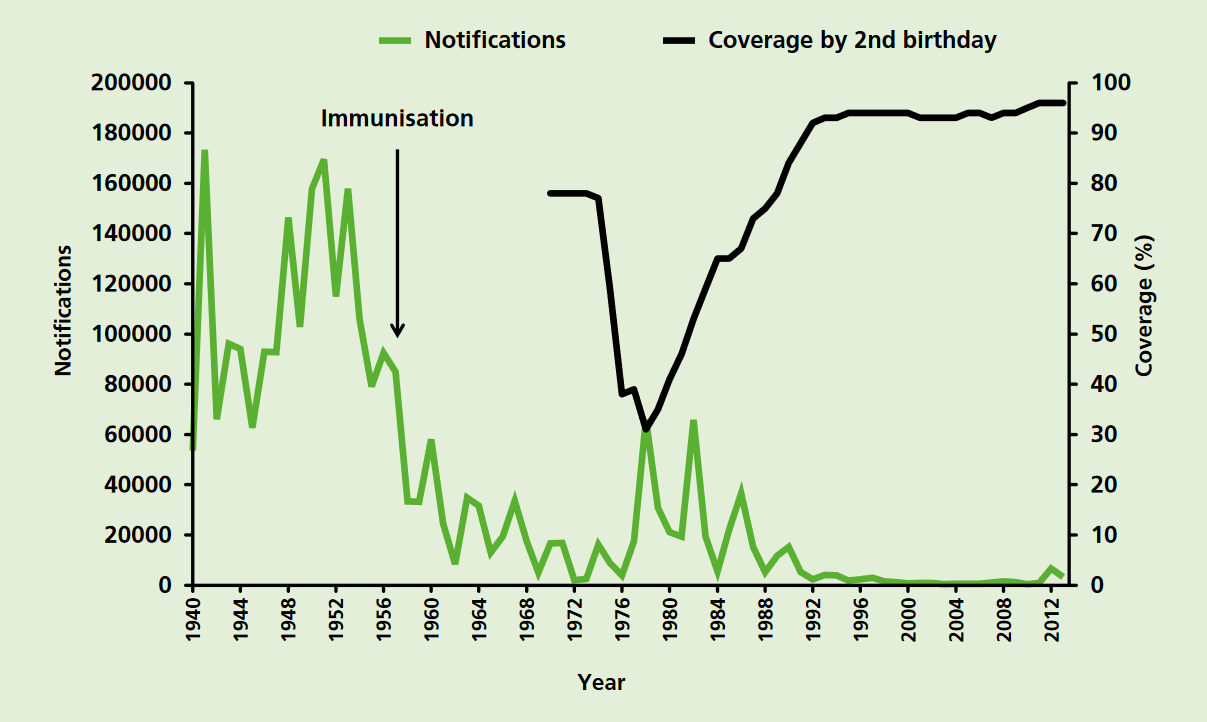
Pertussis Vaccine
Pertussis vaccine is a vaccine that protects against whooping cough (pertussis). There are two main types: whole-cell vaccines and acellular vaccines. The whole-cell vaccine is about 78% effective while the acellular vaccine is 71–85% effective. The effectiveness of the vaccines appears to decrease by between 2 and 10% per year after vaccination with a more rapid decrease with the acellular vaccines. The vaccine is only available in combination with tetanus and diphtheria vaccines. Pertussis vaccine is estimated to have saved over 500,000 lives in 2002. Vaccinating the mother during pregnancy may protect the baby. The World Health Organization and Center for Disease Control and Prevention recommend all children be vaccinated for pertussis and that it be included in routine vaccinations. Three doses starting at six weeks of age are typically recommended in young children. Additional doses may be given to older children and adults. This recommendation includes people who have H ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vasovagal Syncope
Reflex syncope is a brief loss of consciousness due to a neurologically induced drop in blood pressure and/or a decrease in heart rate. Before an affected person passes out, there may be sweating, a decreased ability to see, or ringing in the ears. Occasionally, the person may twitch while unconscious. Complications of reflex syncope include injury due to a fall. Reflex syncope is divided into three types: vasovagal, situational, and carotid sinus. Vasovagal syncope is typically triggered by seeing blood, pain, emotional stress, or prolonged standing. Situational syncope is often triggered by urination, swallowing, or coughing. Carotid sinus syncope is due to pressure on the carotid sinus in the neck. The underlying mechanism involves the nervous system slowing the heart rate and dilating blood vessels, resulting in low blood pressure and thus not enough blood flow to the brain. Diagnosis is based on the symptoms after ruling out other possible causes. Recovery from a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hypotonia
Hypotonia is a state of low muscle tone (the amount of tension or resistance to stretch in a muscle), often involving reduced muscle strength. Hypotonia is not a specific medical disorder, but a potential manifestation of many different diseases and disorders that affect motor nerve control by the brain or muscle strength. Hypotonia is a lack of resistance to passive movement, whereas muscle weakness results in impaired active movement. Central hypotonia originates from the central nervous system, while peripheral hypotonia is related to problems within the spinal cord, peripheral nerves and/or skeletal muscles. Severe hypotonia in infancy is commonly known as floppy baby syndrome. Recognizing hypotonia, even in early infancy, is usually relatively straightforward, but diagnosing the underlying cause can be difficult and often unsuccessful. The long-term effects of hypotonia on a child's development and later life depend primarily on the severity of the muscle weakness and the n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vaccination
Vaccination is the administration of a vaccine to help the immune system develop immunity from a disease. Vaccines contain a microorganism or virus in a weakened, live or killed state, or proteins or toxins from the organism. In stimulating the body's adaptive immunity, they help prevent sickness from an infectious disease. When a sufficiently large percentage of a population has been vaccinated, herd immunity results. Herd immunity protects those who may be immunocompromised and cannot get a vaccine because even a weakened version would harm them. The effectiveness of vaccination has been widely studied and verified. Vaccination is the most effective method of preventing infectious diseases; widespread immunity due to vaccination is largely responsible for the worldwide eradication of smallpox and the elimination of diseases such as polio and tetanus from much of the world. However, some diseases, such as measles outbreaks in America, have seen rising cases due to relati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pertussis Vaccination
Pertussis vaccine is a vaccine that protects against whooping cough (pertussis). There are two main types: whole-cell vaccines and acellular vaccines. The whole-cell vaccine is about 78% effective while the acellular vaccine is 71–85% effective. The effectiveness of the vaccines appears to decrease by between 2 and 10% per year after vaccination with a more rapid decrease with the acellular vaccines. The vaccine is only available in combination with tetanus and diphtheria vaccines. Pertussis vaccine is estimated to have saved over 500,000 lives in 2002. Vaccinating the mother during pregnancy may protect the baby. The World Health Organization and Center for Disease Control and Prevention recommend all children be vaccinated for pertussis and that it be included in routine vaccinations. Three doses starting at six weeks of age are typically recommended in young children. Additional doses may be given to older children and adults. This recommendation includes people who have H ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |