|
Hyperbolic Angle
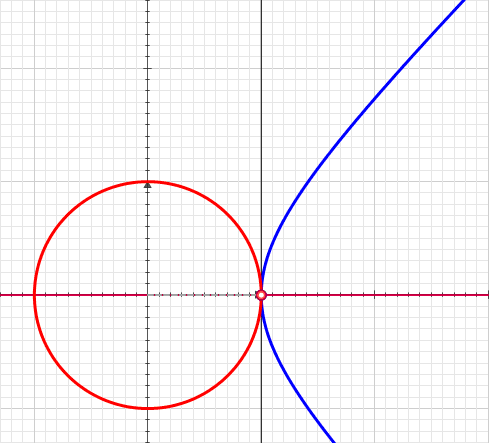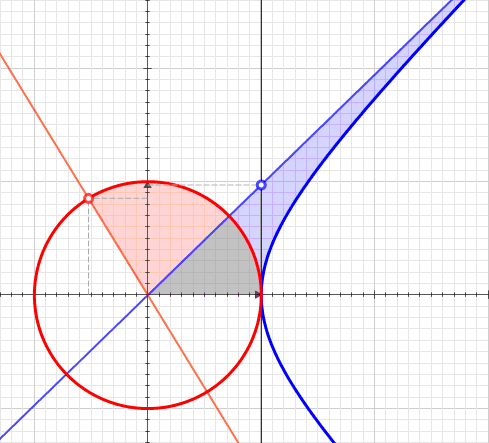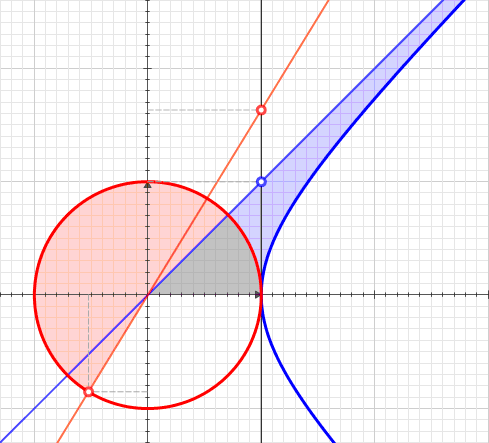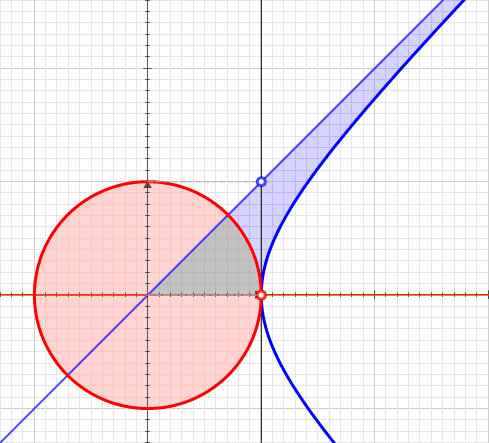
In geometry, hyperbolic angle is a real number determined by the area of the corresponding hyperbolic sector of ''xy'' = 1 in Quadrant I of the Cartesian plane. The hyperbolic angle parametrises the unit hyperbola, which has hyperbolic functions as coordinates. In mathematics, hyperbolic angle is an invariant measure as it is preserved under hyperbolic rotation. The hyperbola ''xy'' = 1 is rectangular with a semi-major axis of \sqrt 2, analogous to the magnitude of a circular angle corresponding to the area of a circular sector in a circle with radius \sqrt 2. Hyperbolic angle is used as the independent variable for the hyperbolic functions sinh, cosh, and tanh, because these functions may be premised on hyperbolic analogies to the corresponding circular trigonometric functions by regarding a hyperbolic angle as defining a hyperbolic triangle. The parameter thus becomes one of the most useful in the calculus of real variables. Definition Consider the rectangular hyperbola ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hyperbolic Sector
A hyperbolic sector is a region of the Cartesian plane bounded by a hyperbola and two rays from the origin to it. For example, the two points and on the rectangular hyperbola , or the corresponding region when this hyperbola is re-scaled and its orientation is altered by a rotation leaving the center at the origin, as with the unit hyperbola. A hyperbolic sector in standard position has and . Hyperbolic sectors are the basis for the hyperbolic functions. Area The area of a hyperbolic sector in standard position is natural logarithm of ''b'' . Proof: Integrate under 1/''x'' from 1 to ''b'', add triangle , and subtract triangle . When in standard position, a hyperbolic sector corresponds to a positive hyperbolic angle at the origin, with the measure of the latter being defined as the area of the former. Hyperbolic triangle When in standard position, a hyperbolic sector determines a hyperbolic triangle, the right triangle with one vertex at the origin, base on the dia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Positive Real Numbers
In mathematics, the set of positive real numbers, \R_ = \left\, is the subset of those real numbers that are greater than zero. The non-negative real numbers, \R_ = \left\, also include zero. Although the symbols \R_ and \R^ are ambiguously used for either of these, the notation \R_ or \R^ for \left\ and \R_^ or \R^_ for \left\ has also been widely employed, is aligned with the practice in algebra of denoting the exclusion of the zero element with a star, and should be understandable to most practicing mathematicians. In a complex plane, \R_ is identified with the positive real axis, and is usually drawn as a horizontal ray. This ray is used as reference in the polar form of a complex number. The real positive axis corresponds to complex numbers z = , z, \mathrm^, with argument \varphi = 0. Properties The set \R_ is closed under addition, multiplication, and division. It inherits a topology from the real line and, thus, has the structure of a multiplicative topological group or o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Measurable Set
In mathematics, the concept of a measure is a generalization and formalization of geometrical measures (length, area, volume) and other common notions, such as mass and probability of events. These seemingly distinct concepts have many similarities and can often be treated together in a single mathematical context. Measures are foundational in probability theory, integration theory, and can be generalized to assume negative values, as with electrical charge. Far-reaching generalizations (such as spectral measures and projection-valued measures) of measure are widely used in quantum physics and physics in general. The intuition behind this concept dates back to ancient Greece, when Archimedes tried to calculate the area of a circle. But it was not until the late 19th and early 20th centuries that measure theory became a branch of mathematics. The foundations of modern measure theory were laid in the works of Émile Borel, Henri Lebesgue, Nikolai Luzin, Johann Radon, Consta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Measure (mathematics)
In mathematics, the concept of a measure is a generalization and formalization of geometrical measures (length, area, volume) and other common notions, such as mass and probability of events. These seemingly distinct concepts have many similarities and can often be treated together in a single mathematical context. Measures are foundational in probability theory, integration theory, and can be generalized to assume negative values, as with electrical charge. Far-reaching generalizations (such as spectral measures and projection-valued measures) of measure are widely used in quantum physics and physics in general. The intuition behind this concept dates back to ancient Greece, when Archimedes tried to calculate the area of a circle. But it was not until the late 19th and early 20th centuries that measure theory became a branch of mathematics. The foundations of modern measure theory were laid in the works of Émile Borel, Henri Lebesgue, Nikolai Luzin, Johann Radon, C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pseudo-Euclidean Space
In mathematics and theoretical physics, a pseudo-Euclidean space is a finite-dimensional real -space together with a non- degenerate quadratic form . Such a quadratic form can, given a suitable choice of basis , be applied to a vector , giving q(x) = \left(x_1^2 + \dots + x_k^2\right) - \left( x_^2 + \dots + x_n^2\right) which is called the ''scalar square'' of the vector . For Euclidean spaces, , implying that the quadratic form is positive-definite. When , is an isotropic quadratic form, otherwise it is ''anisotropic''. Note that if , then , so that is a null vector. In a pseudo-Euclidean space with , unlike in a Euclidean space, there exist vectors with negative scalar square. As with the term ''Euclidean space'', the term ''pseudo-Euclidean space'' may be used to refer to an affine space or a vector space depending on the author, with the latter alternatively being referred to as a pseudo-Euclidean vector space (see point–vector distinction). Geometry The geometry of a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
American Mathematical Society
The American Mathematical Society (AMS) is an association of professional mathematicians dedicated to the interests of mathematical research and scholarship, and serves the national and international community through its publications, meetings, advocacy and other programs. The society is one of the four parts of the Joint Policy Board for Mathematics and a member of the Conference Board of the Mathematical Sciences. History The AMS was founded in 1888 as the New York Mathematical Society, the brainchild of Thomas Fiske, who was impressed by the London Mathematical Society on a visit to England. John Howard Van Amringe was the first president and Fiske became secretary. The society soon decided to publish a journal, but ran into some resistance, due to concerns about competing with the American Journal of Mathematics. The result was the '' Bulletin of the American Mathematical Society'', with Fiske as editor-in-chief. The de facto journal, as intended, was influential i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chord (geometry)
A chord of a circle is a straight line segment whose endpoints both lie on a circular arc. The infinite line extension of a chord is a secant line, or just ''secant''. More generally, a chord is a line segment joining two points on any curve, for instance, an ellipse. A chord that passes through a circle's center point is the circle's diameter. The word ''chord'' is from the Latin ''chorda'' meaning ''bowstring''. In circles Among properties of chords of a circle are the following: # Chords are equidistant from the center if and only if their lengths are equal. # Equal chords are subtended by equal angles from the center of the circle. # A chord that passes through the center of a circle is called a diameter and is the longest chord of that specific circle. # If the line extensions (secant lines) of chords AB and CD intersect at a point P, then their lengths satisfy AP·PB = CP·PD ( power of a point theorem). In conics The midpoints of a set of parallel chords of a c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Projective Geometry
In mathematics, projective geometry is the study of geometric properties that are invariant with respect to projective transformations. This means that, compared to elementary Euclidean geometry, projective geometry has a different setting, projective space, and a selective set of basic geometric concepts. The basic intuitions are that projective space has more points than Euclidean space, for a given dimension, and that geometric transformations are permitted that transform the extra points (called " points at infinity") to Euclidean points, and vice-versa. Properties meaningful for projective geometry are respected by this new idea of transformation, which is more radical in its effects than can be expressed by a transformation matrix and translations (the affine transformations). The first issue for geometers is what kind of geometry is adequate for a novel situation. It is not possible to refer to angles in projective geometry as it is in Euclidean geometry, because a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Projective Range
In mathematics, a projective range is a set of points in projective geometry considered in a unified fashion. A projective range may be a projective line or a conic. A projective range is the dual of a pencil of lines on a given point. For instance, a correlation interchanges the points of a projective range with the lines of a pencil. A projectivity is said to act from one range to another, though the two ranges may coincide as sets. A projective range expresses projective invariance of the relation of projective harmonic conjugates. Indeed, three points on a projective line determine a fourth by this relation. Application of a projectivity to this quadruple results in four points likewise in the harmonic relation. Such a quadruple of points is termed a harmonic range. In 1940 Julian Coolidge described this structure and identified its originator: :Two fundamental one-dimensional forms such as point ranges, pencils of lines, or of planes are defined as projective, when their mem ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
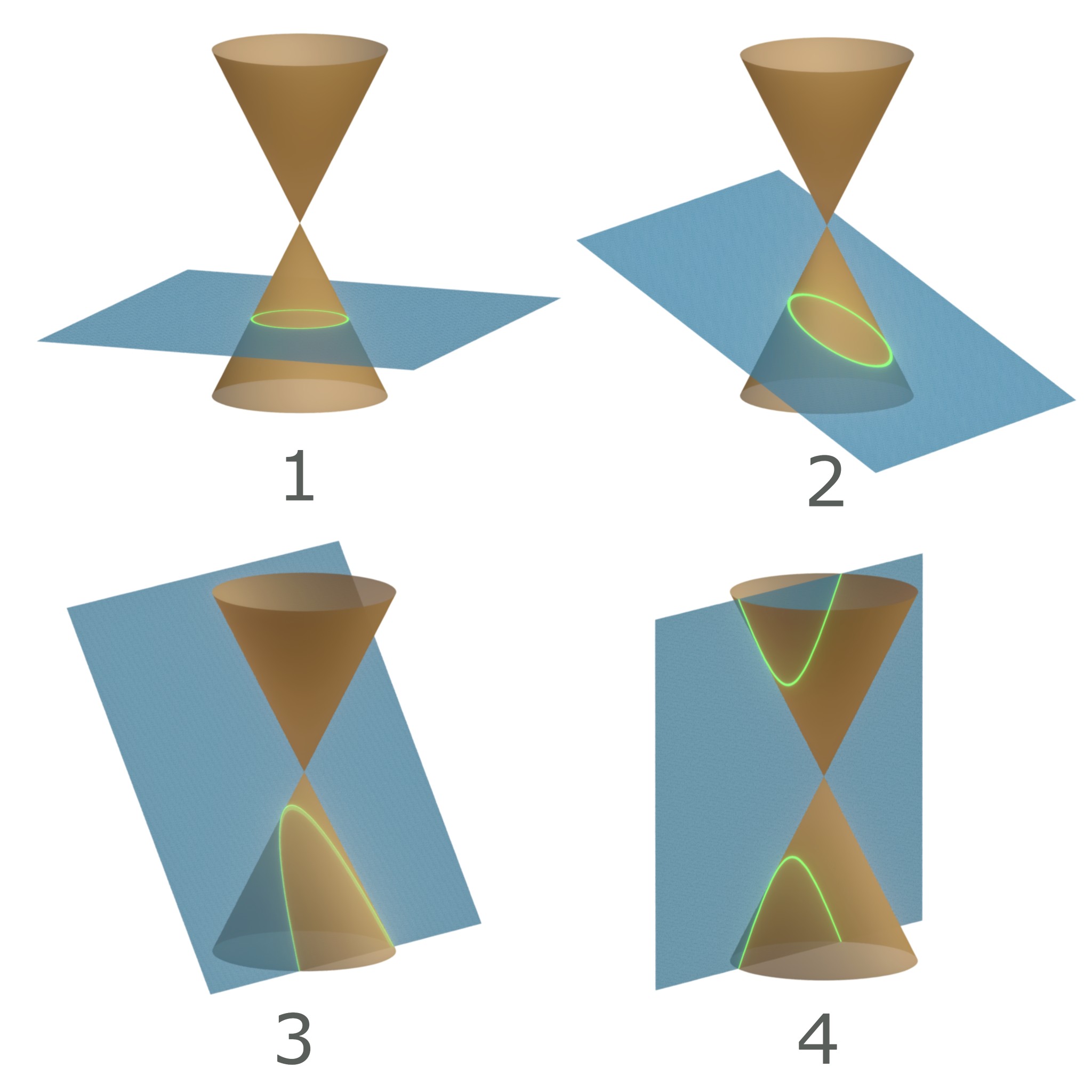
Conic Section
In mathematics, a conic section, quadratic curve or conic is a curve obtained as the intersection of the surface of a cone with a plane. The three types of conic section are the hyperbola, the parabola, and the ellipse; the circle is a special case of the ellipse, though historically it was sometimes called a fourth type. The ancient Greek mathematicians studied conic sections, culminating around 200 BC with Apollonius of Perga's systematic work on their properties. The conic sections in the Euclidean plane have various distinguishing properties, many of which can be used as alternative definitions. One such property defines a non-circular conic to be the set of those points whose distances to some particular point, called a ''focus'', and some particular line, called a ''directrix'', are in a fixed ratio, called the ''eccentricity''. The type of conic is determined by the value of the eccentricity. In analytic geometry, a conic may be defined as a plane algebraic curv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Unit Circle
In mathematics, a unit circle is a circle of unit radius—that is, a radius of 1. Frequently, especially in trigonometry, the unit circle is the circle of radius 1 centered at the origin (0, 0) in the Cartesian coordinate system in the Euclidean plane. In topology, it is often denoted as because it is a one-dimensional unit -sphere. If is a point on the unit circle's circumference, then and are the lengths of the legs of a right triangle whose hypotenuse has length 1. Thus, by the Pythagorean theorem, and satisfy the equation x^2 + y^2 = 1. Since for all , and since the reflection of any point on the unit circle about the - or -axis is also on the unit circle, the above equation holds for all points on the unit circle, not only those in the first quadrant. The interior of the unit circle is called the open unit disk, while the interior of the unit circle combined with the unit circle itself is called the closed unit disk. One may also use other notions of "dist ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |