|
Henry Stapp
Henry Pierce Stapp (born March 23, 1928 in Cleveland, Ohio) is an American mathematical physicist, known for his work in quantum mechanics, particularly the development of axiomatic S-matrix theory, the proofs of strong nonlocality properties, and the place of free will in the "orthodox" quantum mechanics of John von Neumann.Kaiser, D. (2011). ''How the Hippies Saved Physics: Science, Counterculture and the Quantum Revival''. W. W. Norton & Company. pp. 15-17, p. 101, p. 254. Biography Stapp received his PhD in particle physics at the University of California, Berkeley, under the supervision of Nobel Laureates Emilio Segrè and Owen Chamberlain. In 1958, Stapp was invited by Wolfgang Pauli to ETH Zurich to work with him personally on basic problems in quantum mechanics. When Pauli died in December 1958, Stapp studied von Neumann's book, and on the basis of that work composed an article entitled "Mind, Matter and Quantum Mechanics", which was not submitted for publication; but ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cleveland
Cleveland ( ), officially the City of Cleveland, is a city in the U.S. state of Ohio and the county seat of Cuyahoga County. Located in the northeastern part of the state, it is situated along the southern shore of Lake Erie, across the U.S. maritime border with Canada, northeast of Cincinnati, northeast of Columbus, and approximately west of Pennsylvania. The largest city on Lake Erie and one of the major cities of the Great Lakes region, Cleveland ranks as the 54th-largest city in the U.S. with a 2020 population of 372,624. The city anchors both the Greater Cleveland metropolitan statistical area (MSA) and the larger Cleveland–Akron–Canton combined statistical area (CSA). The CSA is the most populous in Ohio and the 17th largest in the country, with a population of 3.63 million in 2020, while the MSA ranks as 34th largest at 2.09 million. Cleveland was founded in 1796 near the mouth of the Cuyahoga River by General Moses Cleaveland, after whom the city was named ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ETH Zurich
(colloquially) , former_name = eidgenössische polytechnische Schule , image = ETHZ.JPG , image_size = , established = , type = Public , budget = CHF 1.896 billion (2021) , rector = Günther Dissertori , president = Joël Mesot , academic_staff = 6,612 (including doctoral students, excluding 527 professors of all ranks, 34% female, 65% foreign nationals) (full-time equivalents 2021) , administrative_staff = 3,106 (40% female, 19% foreign nationals, full-time equivalents 2021) , students = 24,534 (headcount 2021, 33.3% female, 37% foreign nationals) , undergrad = 10,642 , postgrad = 8,299 , doctoral = 4,460 , other = 1,133 , address = Rämistrasse 101CH-8092 ZürichSwitzerland , city = Zürich , coor = , campus = Urban , language = German, English (Masters and upwards, sometimes Bachelor) , affiliations = CESAER, EUA, GlobalTech, IARU, IDEA League, UNITECH , website ethz.ch, colors = Black and White , logo = ETH Zürich Logo black.svg ETH Zür ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Synapses
In the nervous system, a synapse is a structure that permits a neuron (or nerve cell) to pass an electrical or chemical signal to another neuron or to the target effector cell. Synapses are essential to the transmission of nervous impulses from one neuron to another. Neurons are specialized to pass signals to individual target cells, and synapses are the means by which they do so. At a synapse, the plasma membrane of the signal-passing neuron (the ''presynaptic'' neuron) comes into close apposition with the membrane of the target (''postsynaptic'') cell. Both the presynaptic and postsynaptic sites contain extensive arrays of molecular machinery that link the two membranes together and carry out the signaling process. In many synapses, the presynaptic part is located on an axon and the postsynaptic part is located on a dendrite or soma. Astrocytes also exchange information with the synaptic neurons, responding to synaptic activity and, in turn, regulating neurotransmission. Sy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quantum Zeno Effect
The quantum Zeno effect (also known as the Turing paradox) is a feature of quantum-mechanical systems allowing a particle's time evolution to be slowed down by measuring it frequently enough with respect to some chosen measurement setting. Sometimes this effect is interpreted as "a system cannot change while you are watching it". One can "freeze" the evolution of the system by measuring it frequently enough in its known initial state. The meaning of the term has since expanded, leading to a more technical definition, in which time evolution can be suppressed not only by measurement: the quantum Zeno effect is the suppression of unitary time evolution in quantum systems provided by a variety of sources: measurement, interactions with the environment, stochastic fields, among other factors. As an outgrowth of study of the quantum Zeno effect, it has become clear that applying a series of sufficiently strong and fast pulses with appropriate symmetry can also ''decouple'' a system ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neurons
A neuron, neurone, or nerve cell is an electrically excitable cell that communicates with other cells via specialized connections called synapses. The neuron is the main component of nervous tissue in all animals except sponges and placozoa. Non-animals like plants and fungi do not have nerve cells. Neurons are typically classified into three types based on their function. Sensory neurons respond to stimuli such as touch, sound, or light that affect the cells of the sensory organs, and they send signals to the spinal cord or brain. Motor neurons receive signals from the brain and spinal cord to control everything from muscle contractions to glandular output. Interneurons connect neurons to other neurons within the same region of the brain or spinal cord. When multiple neurons are connected together, they form what is called a neural circuit. A typical neuron consists of a cell body (soma), dendrites, and a single axon. The soma is a compact structure, and the axon an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quantum Computing
Quantum computing is a type of computation whose operations can harness the phenomena of quantum mechanics, such as superposition, interference, and entanglement. Devices that perform quantum computations are known as quantum computers. Though current quantum computers may be too small to outperform usual (classical) computers for practical applications, larger realizations are believed to be capable of solving certain computational problems, such as integer factorization (which underlies RSA encryption), substantially faster than classical computers. The study of quantum computing is a subfield of quantum information science. There are several models of quantum computation with the most widely used being quantum circuits. Other models include the quantum Turing machine, quantum annealing, and adiabatic quantum computation. Most models are based on the quantum bit, or " qubit", which is somewhat analogous to the bit in classical computation. A qubit can be in a 1 or 0 quan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stuart Hameroff
Stuart Hameroff (born July 16, 1947) is an American anesthesiologist and professor at the University of Arizona known for his studies of consciousness and his controversial contention that consciousness originates from quantum states in neural microtubules. He is the lead organizer of the Science of Consciousness conference. Career Hameroff received his BS degree from the University of Pittsburgh and his MD degree from Hahnemann University Hospital, where he studied before it became part of the Drexel University College of Medicine. He took an internship at the Tucson Medical Center in 1973. From 1975 onwards, he has spent the whole of his career at the University of Arizona, becoming professor in the Department of Anesthesiology and Psychology and director for the Center for Consciousness Studies, both in 1999, and finally Emeritus professor for Anesthesiology and Psychology in 2003. Hypotheses At the very beginning of Hameroff's career, while he was at Hahnemann, cancer-rel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roger Penrose
Sir Roger Penrose (born 8 August 1931) is an English mathematician, mathematical physicist, philosopher of science and Nobel Laureate in Physics. He is Emeritus Rouse Ball Professor of Mathematics in the University of Oxford, an emeritus fellow of Wadham College, Oxford, and an honorary fellow of St John's College, Cambridge and University College London. Penrose has contributed to the mathematical physics of general relativity and cosmology. He has received several prizes and awards, including the 1988 Wolf Prize in Physics, which he shared with Stephen Hawking for the Penrose–Hawking singularity theorems, and one half of the 2020 Nobel Prize in Physics "for the discovery that black hole formation is a robust prediction of the general theory of relativity". He is regarded as one of the greatest living physicists, mathematicians and scientists, and is particularly noted for the breadth and depth of his work in both natural and formal sciences. Early life and education ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quantum
In physics, a quantum (plural quanta) is the minimum amount of any physical entity ( physical property) involved in an interaction. The fundamental notion that a physical property can be "quantized" is referred to as "the hypothesis of quantization". This means that the magnitude of the physical property can take on only discrete values consisting of integer multiples of one quantum. For example, a photon is a single quantum of light (or of any other form of electromagnetic radiation). Similarly, the energy of an electron bound within an atom is quantized and can exist only in certain discrete values. (Atoms and matter in general are stable because electrons can exist only at discrete energy levels within an atom.) Quantization is one of the foundations of the much broader physics of quantum mechanics. Quantization of energy and its influence on how energy and matter interact ( quantum electrodynamics) is part of the fundamental framework for understanding and describing nature. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Free Will
Free will is the capacity of agents to choose between different possible courses of action unimpeded. Free will is closely linked to the concepts of moral responsibility, praise, culpability, sin, and other judgements which apply only to actions that are freely chosen. It is also connected with the concepts of advice, persuasion, deliberation, and prohibition. Traditionally, only actions that are freely willed are seen as deserving credit or blame. Whether free will exists, what it is and the implications of whether it exists or not are some of the longest running debates of philosophy and religion. Some conceive of free will as the right to act outside of external influences or wishes. Some conceive free will to be the capacity to make choices undetermined by past events. Determinism suggests that only one course of events is possible, which is inconsistent with a libertarian model of free will. Ancient Greek philosophy identified this issue, which remains a major foc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Consciousness
Consciousness, at its simplest, is sentience and awareness of internal and external existence. However, the lack of definitions has led to millennia of analyses, explanations and debates by philosophers, theologians, linguisticians, and scientists. Opinions differ about what exactly needs to be studied or even considered consciousness. In some explanations, it is synonymous with the mind, and at other times, an aspect of mind. In the past, it was one's "inner life", the world of introspection, of private thought, imagination and volition. Today, it often includes any kind of cognition, experience, feeling or perception. It may be awareness, awareness of awareness, or self-awareness either continuously changing or not. The disparate range of research, notions and speculations raises a curiosity about whether the right questions are being asked. Examples of the range of descriptions, definitions or explanations are: simple wakefulness, one's sense of selfhood or sou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Esalen Institute
The Esalen Institute, commonly called Esalen, is a non-profit American retreat center and intentional community in Big Sur, California, which focuses on humanistic alternative education. The institute played a key role in the Human Potential Movement beginning in the 1960s. Its innovative use of encounter groups, a focus on the mind-body connection, and their ongoing experimentation in personal awareness introduced many ideas that later became mainstream. Esalen was founded by Michael Murphy and Dick Price in 1962. Their intention was to support alternative methods for exploring human consciousness, what Aldous Huxley described as "human potentialities". Over the next few years, Esalen became the center of practices and beliefs that make up the New Age movement, from Eastern religions/ philosophy, to alternative medicine and mind-body interventions, from transpersonal to Gestalt Practice. Price ran the institute until he died in a hiking accident in 1985. In 2012, th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


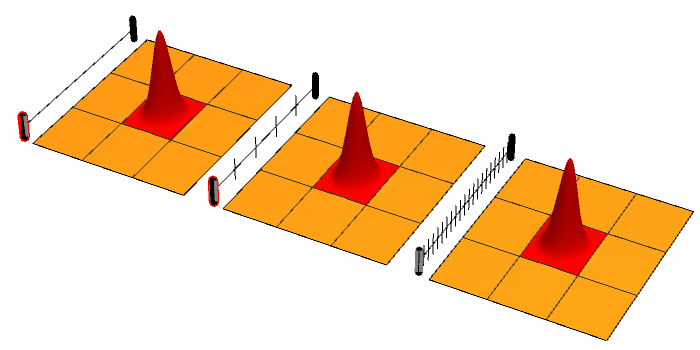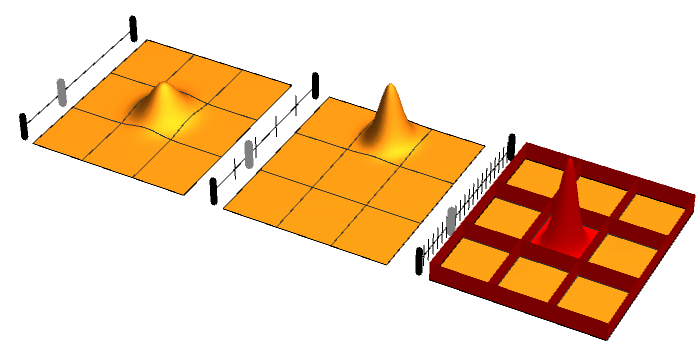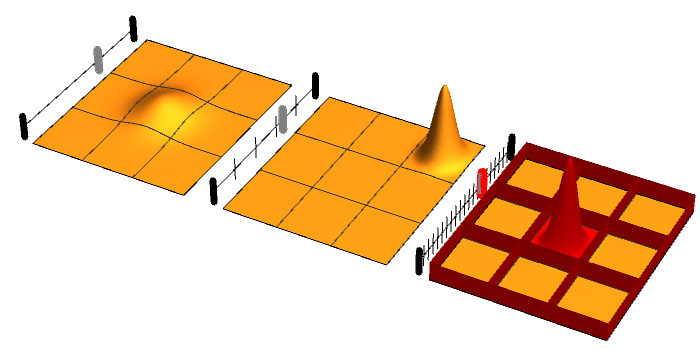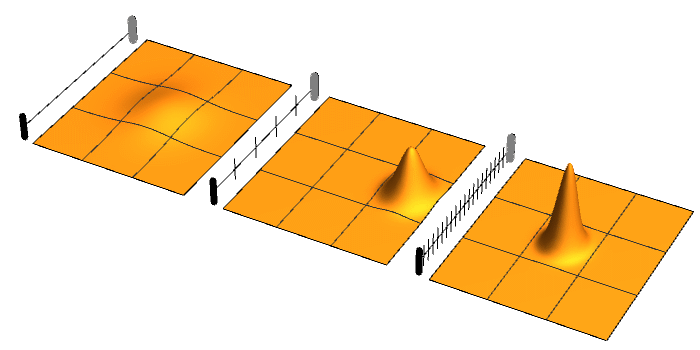

.jpg)


